您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“c++如何實現yolov5轉onnx”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
訓練部分根據呼聲再決定要不要寫一份博客吧!!
注意事項:
1.訓練代碼一定要選擇yolov5 5.0版本
2. 進入models/exprort.py;
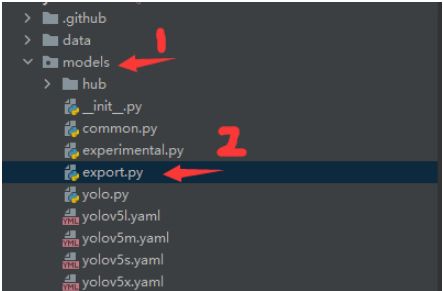
3.將紅框區域換成你自己的訓練完的模型
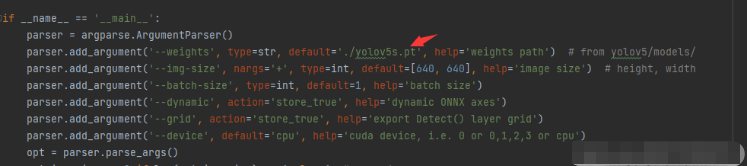
4.將版本換成12;
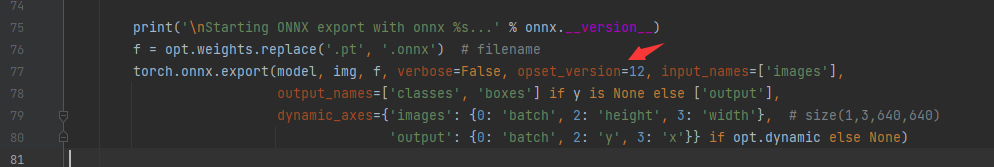
5.直接運行即可,會生成出onnx的模型出來。
博主使用的是opencv4.5.3版本,已經編譯好的,需要直接掃碼加我發你
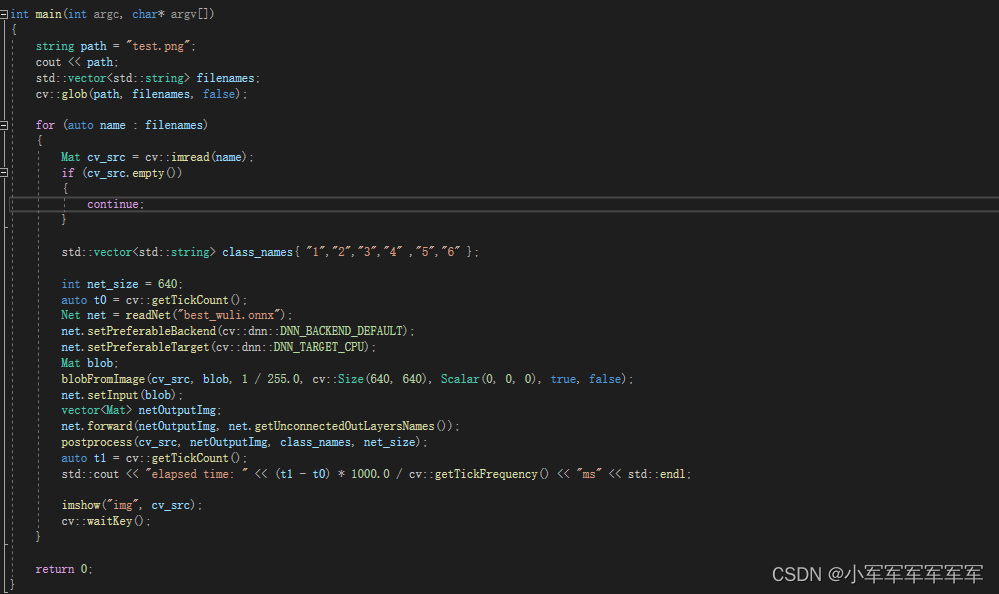
讀取模型利用的是dnn::readNet,opencv其實挺強大的博主已經讀過tf模型,torch模型后續都會出對應博客,這里總共有三點改,輸入圖片path,輸入類別名class_names,net部分改成自己的模型
net.set這些參數都固定就好,有興趣的同學可以研究研究DNN_TARGET_CPU這個地方,是可以使用gpu和cuda的,但是博主還沒復現過
void postprocess(cv::Mat& cv_src, std::vector<cv::Mat>& outs, const std::vector<std::string>& classes, int net_size)
{
float confThreshold = 0.1f;
float nmsThreshold = 0.1f;
std::vector<int> classIds;
std::vector<float> confidences;
std::vector<cv::Rect> boxes;
int strides[] = { 8, 16, 32 };
std::vector<std::vector<int> > anchors =
{
{ 10,13, 16,30, 33,23 },
{ 30,61, 62,45, 59,119 },
{ 116,90, 156,198, 373,326 }
};
for (size_t k = 0; k < outs.size(); k++)
{
float* data = outs[k].ptr<float>();
int stride = strides[k];
int num_classes = outs[k].size[4] - 5;
for (int i = 0; i < outs[k].size[2]; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < outs[k].size[3]; j++)
{
for (int a = 0; a < outs[k].size[1]; ++a)
{
float* record = data + a * outs[k].size[2] * outs[k].size[3] * outs[k].size[4] +
i * outs[k].size[3] * outs[k].size[4] + j * outs[k].size[4];
float* cls_ptr = record + 5;
for (int cls = 0; cls < num_classes; cls++)
{
float score = sigmoid(cls_ptr[cls]) * sigmoid(record[4]);
if (score > confThreshold)
{
float cx = (sigmoid(record[0]) * 2.f - 0.5f + (float)j) * (float)stride;
float cy = (sigmoid(record[1]) * 2.f - 0.5f + (float)i) * (float)stride;
float w = pow(sigmoid(record[2]) * 2.f, 2) * anchors[k][2 * a];
float h = pow(sigmoid(record[3]) * 2.f, 2) * anchors[k][2 * a + 1];
float x1 = std::max(0, std::min(cv_src.cols, int((cx - w / 2.f) * (float)cv_src.cols / (float)net_size)));
float y1 = std::max(0, std::min(cv_src.rows, int((cy - h / 2.f) * (float)cv_src.rows / (float)net_size)));
float x2 = std::max(0, std::min(cv_src.cols, int((cx + w / 2.f) * (float)cv_src.cols / (float)net_size)));
float y2 = std::max(0, std::min(cv_src.rows, int((cy + h / 2.f) * (float)cv_src.rows / (float)net_size)));
classIds.push_back(cls);
confidences.push_back(score);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(x1, y1), cv::Point(x2, y2)));
}
}
}
}
}
}
std::vector<int> indices;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); i++)
{
int idx = indices[i];
cv::Rect box = boxes[idx];
drawPred(classIds[idx], confidences[idx], box.x, box.y,
box.x + box.width, box.y + box.height, cv_src, classes);
}
}抬頭部分是兩大目標檢測的閾值設置,然后anchors這些都不建議動,除非你在訓練的時候用了你自己生成的anchors的話,就改成你自己的,然后根據訓練推理后,會生成我們所對應的坐標框以及分數,將分數和狂送到容器中,dnn中有nms等底層函數哦
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold, indices);
對應輸入就可以了,然后得到我們的Box,index,和置信度,接下來就到了我們的畫圖環節。
void drawPred(int classId, float conf, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, cv::Mat& frame,
const std::vector<std::string>& classes)
{
cv::rectangle(frame, cv::Point(left, top), cv::Point(right, bottom), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3);
std::string label = cv::format("%.2f", conf);
if (!classes.empty()) {
CV_Assert(classId < (int)classes.size());
label = classes[classId] + ": " + label;
}
int baseLine;
cv::Size labelSize = cv::getTextSize(label, cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
top = std::max(top, labelSize.height);
cv::rectangle(frame, cv::Point(left, top - round(1.5 * labelSize.height)), cv::Point(left + round(1.5 * labelSize.width), top + baseLine), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), cv::FILLED);
cv::putText(frame, label, cv::Point(left, top), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, cv::Scalar(), 2);
}inline float sigmoid(float x)
{
return 1.f / (1.f + exp(-x));
}“c++如何實現yolov5轉onnx”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。