您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“Python實現人工語音對話的方法”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
gtts是將文字轉化為語音,但是需要在虛擬網絡下使用。這個因為要接谷歌服務器。
具體gtts的官方文檔:
下面,讓我們看一段簡單的的代碼
from gtts import gTTS def speak(audioString): print(audioString) tts = gTTS(text=audioString, lang='en') tts.save("audio.mp3") os.system("audio.mp3") speak("Hi Runsen, what can I do for you?")執行上面的代碼,就可以生成一個mp3文件,播放就可以聽到了Hi Runsen, what can I do for you?。這個MP3會自動彈出來的。
speech_recognition用于執行語音識別的庫,支持在線和離線的多個引擎和API。
speech_recognition具體官方文檔
安裝speech_recognition可以會出現錯誤,對此解決的方法是通過該網址安裝對應的whl包
在官方文檔中提供了具體的識別來自麥克風的語音輸入的代碼
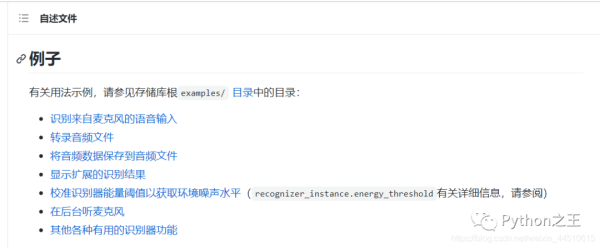
下面就是 speech_recognition 用麥克風記錄下你的話,這里我使用的是 recognize_google,speech_recognition 提供了很多的類似的接口。
import time import speech_recognition as sr # 錄下來你講的話 def recordAudio(): # 用麥克風記錄下你的話 print("開始麥克風記錄下你的話") r = sr.Recognizer() with sr.Microphone() as source: audio = r.listen(source) data = "" try: data = r.recognize_google(audio) print("You said: " + data) except sr.UnknownValueError: print("Google Speech Recognition could not understand audio") except sr.RequestError as e: print("Could not request results from Google Speech Recognition service; {0}".format(e)) return data if __name__ == '__main__': time.sleep(2) while True: data = recordAudio() print(data)下面是我亂說的英語
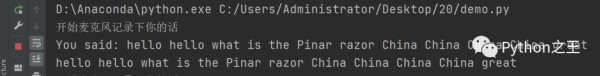
上面,我們實現了用麥克風記錄下你的話,并且得到了對應的文本,那么下一步就是字符串的文本操作了,比如說how are you,那回答"I am fine”,然后將"I am fine”通過gtts是將文字轉化為語音
# @Author:Runsen # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import speech_recognition as sr from time import ctime import time import os from gtts import gTTS # 講出來AI的話 def speak(audioString): print(audioString) tts = gTTS(text=audioString, lang='en') tts.save("audio.mp3") os.system("audio.mp3") # 錄下來你講的話 def recordAudio(): # 用麥克風記錄下你的話 r = sr.Recognizer() with sr.Microphone() as source: audio = r.listen(source) data = "" try: data = r.recognize_google(audio) print("You said: " + data) except sr.UnknownValueError: print("Google Speech Recognition could not understand audio") except sr.RequestError as e: print("Could not request results from Google Speech Recognition service; {0}".format(e)) return data # 自帶的對話技能(邏輯代碼:rules) def jarvis(): while True: data = recordAudio() print(data) if "how are you" in data: speak("I am fine") if "time" in data: speak(ctime()) if "where is" in data: data = data.split(" ") location = data[2] speak("Hold on Runsen, I will show you where " + location + " is.") # 打開谷歌地址 os.system("open -a Safari https://www.google.com/maps/place/" + location + "/&") if "bye" in data: speak("bye bye") break if __name__ == '__main__': # 初始化 time.sleep(2) speak("Hi Runsen, what can I do for you?") # 跑起 jarvis() 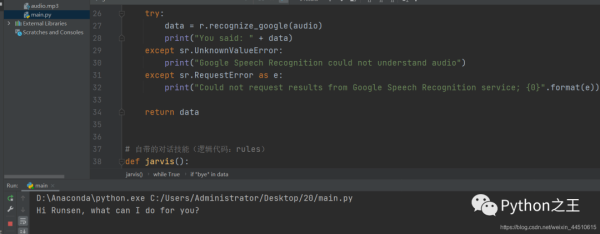
當我說how are you?會彈出I am fine的mp3
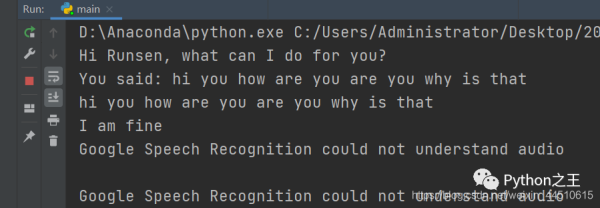
當我說where is Chiana?會彈出Hold on Runsen, I will show you where China is.的MP3
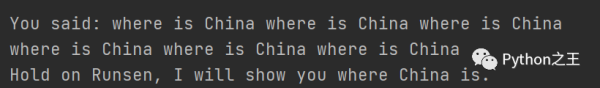
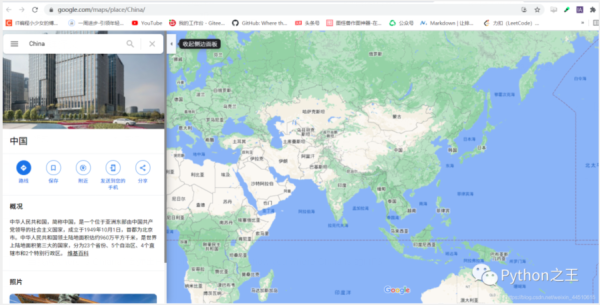
同樣也會彈出China的谷歌地圖
本項目對應的Github
https://github.com/MaoliRUNsen/Simple-intelligent-voice-dialogue
“Python實現人工語音對話的方法”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。