您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章將為大家詳細講解有關Android 中的目錄結構有哪些,文章內容質量較高,因此小編分享給大家做個參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后對相關知識有一定的了解。
1、Android項目目錄結構
android項目和java項目一樣,,src文件夾是項目的所有包及源文件(.java),res文件夾中包含了項目中的所有資源,比如:程序圖標(drawable)、布局文件(layout)、常量(values)。android項目中多了gen文件夾,里面是R.java文件,定義該項目所有資源的索引文件。還有一個android項目必須的AndroidManfest.xml文件。項目結構圖如下:
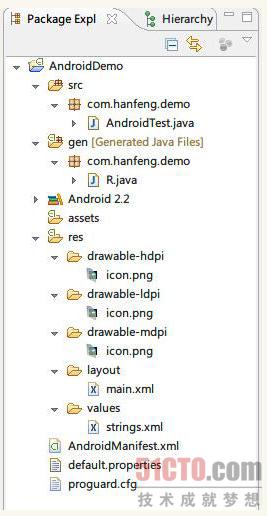
1 R.java文件是項目創建的時候自動生成,是只讀文件,不能夠更改。其代碼如下:
/* AUTO-GENERATED FILE. DO NOT MODIFY. * * This class was automatically generated by the * aapt tool from the resource data it found. It * should not be modified by hand. */ package com.hanfeng.demo; public final class R { public static final class attr { } public static final class drawable { public static final int icon=0x7f020000; } public static final class layout { public static final int main=0x7f030000; } public static final class string { public static final int app_name=0x7f040001; public static final int hello=0x7f040000; } }通過上面代碼,我們可以看到這些常量與res文件夾中的文件名字一樣,說明了R.java文件存儲了該項目中的所有資源索引。R.java文件的存在,方便資源的使用,當我們在項目中加入新資源,只需刷新項目,R.java文件就會自動生成所有資源的索引。分析上面的xml文件:
2 AndroidManfest.xml文件包含了項目中所有使用的Activity、Service、Receiver,代碼如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.hanfeng.demo" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0"> <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" /> <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name"> <activity android:name=".AndroidTest" android:label="@string/app_name"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
分析上面的xml文件:
【xmlns:android】:包含命名空間的聲明。xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android",使得Android中各種標準屬性能夠在文件中使用,提供大部分元素的數據。
【package】:聲明應用程序包。
【application】:包含package中application級別組件聲明的根節點。此元素耶可包含application的一些全局和默認的屬性,如標簽、icon、主題、必要權限等。一個manifest能夠包含零個或一個此元素,不能大于一個。
【android:icon】:應用程序圖標。
【android:lebel】:應用程序名字。
【Activity】:用戶交互工具。
【android:name】:應用程序默認啟動的Activity。
【intent-filter】:聲明了指定一組組件支持的Intent值,從而形成IntentFilter。
【action】:組件支持的Intent action 。
【category】:組件支持的Intent Category。指定應用程序默認啟動的Activity。
【uses-sdk】: 應用程序所使用的sdk版本。
3 String.xml 資源文件中的常量定義。代碼如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">Hello World, AndroidTest!</string> <string name="app_name">AndroidDemo</string> </resources>
從上面的代碼可以看出,文件中定義的字符串資源常量"hello"、"app_name"指向了R.java文件中的字符串資源。
下面看如何使用定義的這些資源。我們可以通過Context的getResource實例化一個Resource對象,然后通過Resource的getSting方法獲取指定索引的字符串。代碼如下:
Resource r = this.getContext().getResource(); String appname = ((String) r.getString(R.string.app_name)); String hello = ((String) r.getString(R.string.hello));
4 main.xml布局文件,代碼如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello" /> </LinearLayout>
布局參數解析:
【<linearLayout>】:線性版面配置,在這個標簽中,所有元件都是按由上到下的排列排成。
【android:orientation】:表示這個介質的版面配置方式是從上到下的垂直地排列其內部視圖。
【android:layout_width】:定義當前視圖在屏幕上所占的寬度,fill_parent即填充整個屏幕。
【android:layout_height】:定義當前視圖在屏幕上所占的高度。
【wrap_weight】:隨著文字欄位的不同而改變這個視圖的高度或寬度。
5 AndroidTest.java 項目的豬程序文件。代碼如下:
package com.hanfeng.demo; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; public class AndroidTest extends Activity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); } }主程序AndroidTest繼承自Activity類,重寫了void onCreate(Bundle saveInstanceState)方法。在onCreate方法中通過setContentView(R.layout.main)設置Activity要顯示的布局文件。
關于Android 中的目錄結構有哪些就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。