您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章給大家分享的是有關如何用Python輕松開發數據庫取數下載工具,小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家學習,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲,話不多說,跟著小編一起來看看吧。
這是我的系列教程「Python+Dash快速web應用開發」的第十四期,在前兩期中,我們針對dash_table的自定義樣式、前后端分頁、單元格內容編輯等特點展開了介紹。
而在dash_table中還有很多高級特性,可以極大程度上豐富DataTable()所渲染網頁表格的交互能力,我們就來一起學習其中比較實用的一些特性。
圖1
上一期文章最后我們學習了通過設置參數editable=True,使得渲染出的表格可以通過鼠標雙擊進行編輯,而dash_table除此之外,還有更多實用的交互能力:
普通單列排序
在DataTable()中,我們只需要設置參數sort_action='native',即可開啟列排序功能,此時每一列列名單元格內都會出現部件供我們點擊切換排序方式:
app1.py
import dash import dash_table import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc import seaborn as sns df = sns.load_dataset('iris') app = dash.Dash(__name__) app.layout = dbc.Container( [ dash_table.DataTable( data=df.to_dict('records'), columns=[ {'name': column, 'id': column} for column in df.columns ], style_table={ 'height': '500px', 'overflow-y': 'auto' }, sort_action='native' ) ], style={ 'margin-top': '50px' } ) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run_server(debug=True)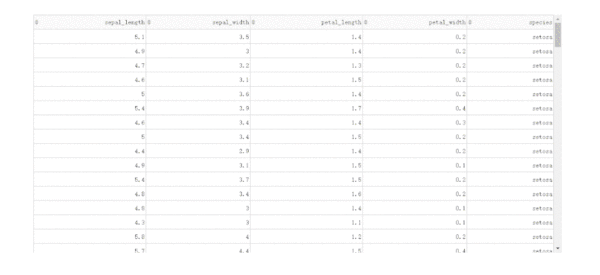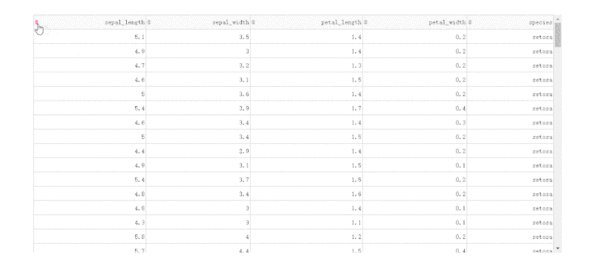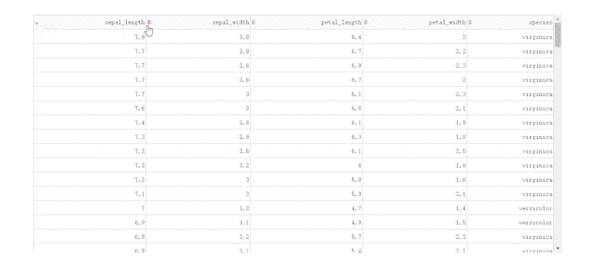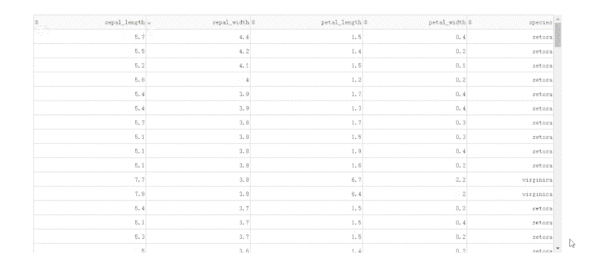
圖2
基于后端排序的多列排序
在DataTable()中設置sort_action='native'時,對應的是「按列排序」的前端模式,也即是數據一次性灌注到瀏覽器的前提下進行排序,這種方式不僅不適合大型數據集,而且只支持「單列排序」。
而當數據渲染方式為后端模式時,我們通過設置參數sort_action='custom'以及sort_mode='multi',配合在回調中獲取屬性sort_by中記錄的參與排序的列名及升序降序方式,就可以實現多列排序。
我們在上一期的app2.py的基礎上修改得到下面的例子:
app2.py
import dash import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc import dash_table from dash.dependencies import Input, Output import seaborn as sns df = sns.load_dataset('iris') df.insert(0, '#', df.index) app = dash.Dash(__name__) app.layout = dbc.Container( [ dbc.Spinner( dash_table.DataTable( id='dash-table', columns=[ {'name': column, 'id': column} for column in df.columns ], page_size=15, # 設置單頁顯示15行記錄行數 page_action='custom', page_current=0, style_header={ 'font-family': 'Times New Romer', 'font-weight': 'bold', 'text-align': 'center' }, style_data={ 'font-family': 'Times New Romer', 'text-align': 'center' }, sort_action='custom', sort_mode='multi' ) ) ], style={ 'margin-top': '50px' } ) @app.callback( [Output('dash-table', 'data'), Output('dash-table', 'page_count')], [Input('dash-table', 'page_current'), Input('dash-table', 'page_size'), Input('dash-table', 'sort_by')] ) def refresh_page_data(page_current, page_size, sort_by): if sort_by: return ( df .sort_values( [col['column_id'] for col in sort_by], ascending=[ col['direction'] == 'asc' for col in sort_by ] ) .iloc[page_current * page_size:(page_current + 1) * page_size] .to_dict('records'), 1 + df.shape[0] // page_size ) return ( df.iloc[page_current * page_size:(page_current + 1) * page_size].to_dict('records'), 1 + df.shape[0] // page_size ) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run_server(debug=True)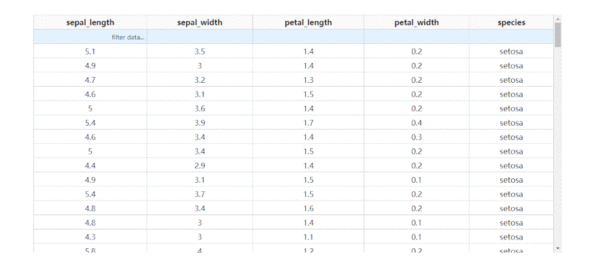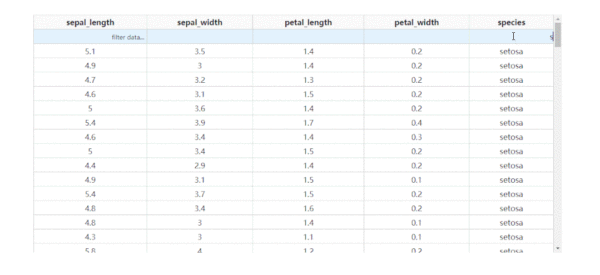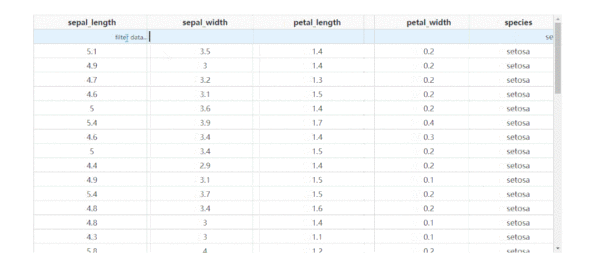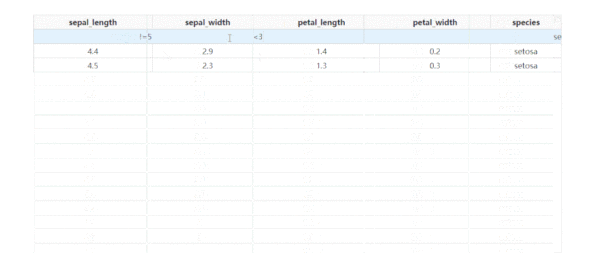
圖3
除了基于指定字段進行排序之外,dash_table還支持列的條件篩選,設置filter_action="native",就可以開啟基礎的按列條件篩選功能,此時每一列表頭下都會多出供用戶輸入篩選條件的單元格:
app3.py
import dash import dash_table import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc import seaborn as sns df = sns.load_dataset('iris') app = dash.Dash(__name__) app.layout = dbc.Container( [ dash_table.DataTable( data=df.to_dict('records'), columns=[ {'name': column, 'id': column} for column in df.columns ], # 自定義條件篩選單元格樣式 style_filter={ 'font-family': 'Times New Romer', 'background-color': '#e3f2fd' }, style_table={ 'height': '500px', 'overflow-y': 'auto' }, style_header={ 'font-family': 'Times New Romer', 'font-weight': 'bold', 'text-align': 'center' }, style_data={ 'font-family': 'Times New Romer', 'text-align': 'center' }, filter_action="native" ) ], style={ 'margin-top': '50px' } ) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run_server(debug=True)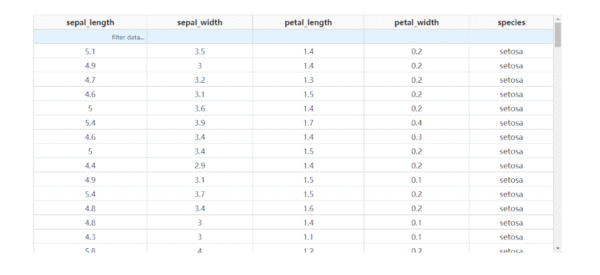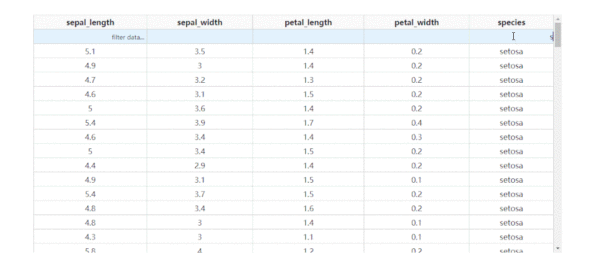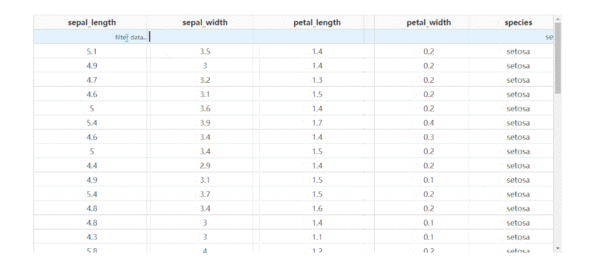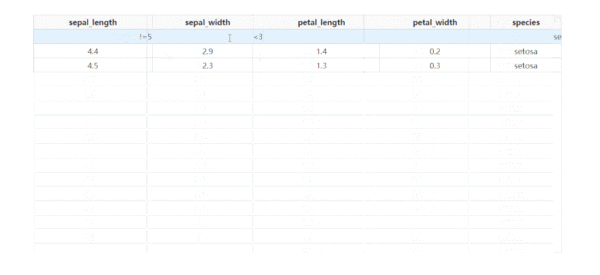
圖4
而dash_table中自帶的條件篩選語法很豐富,有條件的朋友可以前往https://dash.plotly.com/datatable/filtering了解更多。
而dash_table同樣可以實現后端篩選,和前面的后端排序類似,主要利用filter_query屬性的回調變化在后臺基于pandas等框架進行數據篩選,比較簡單,這里就不再贅述。
dash_table還自帶了將當前所渲染的表格內容直接下載為csv或xlsx格式文件的簡易功能,通過參數export_format設置導出的文件格式,但自帶的下載按鈕樣式比較丑,如果你對此有比較高的要求,還是建議結合之前的「上傳下載篇」自己設計相關功能:
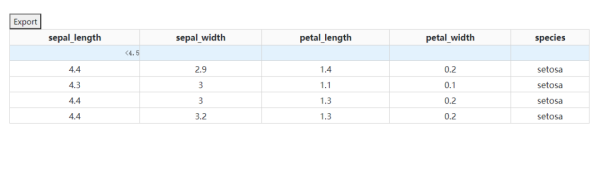
圖5
通過設置參數fixed_rows={'headers': True},我們可以實現下滑查看表格的過程中,始終保持表頭被凍結:
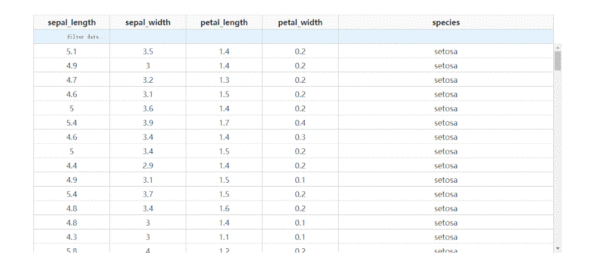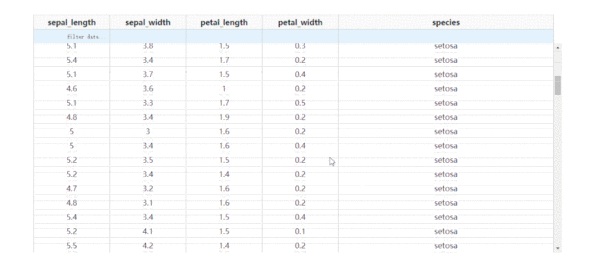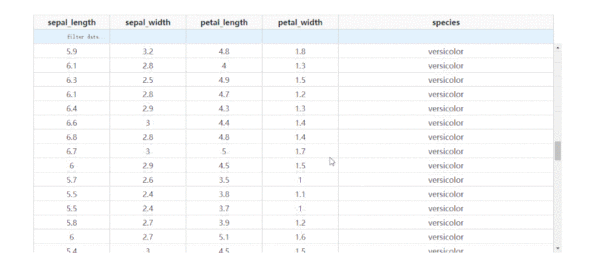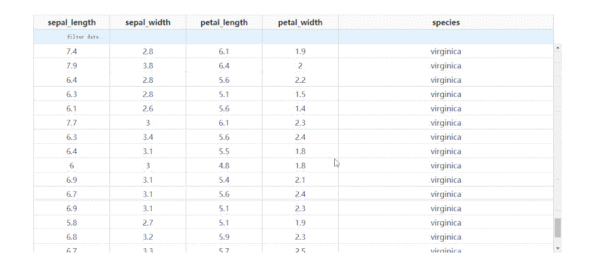
圖6
在學習完今天的內容之后,我們來結合之前「上傳下載篇」中提到的下載功能,來制作一個簡單的對指定數據庫中的數據表進行快速條件篩選并下載的工具,其中DataTable的derived_virtual_data屬性記錄了經過排序、條件篩選等操作后當前顯示的表格數據:
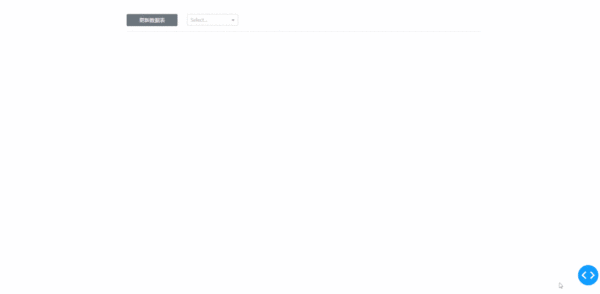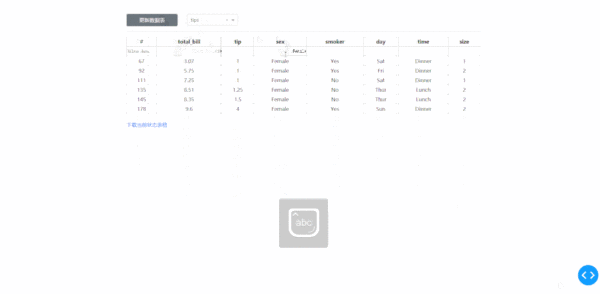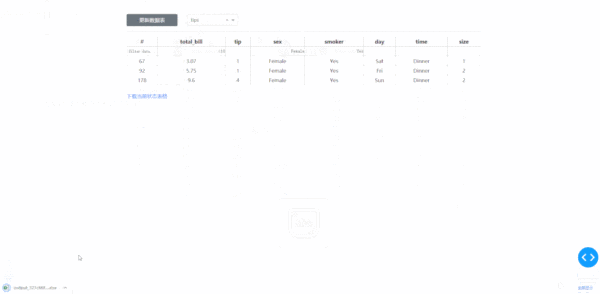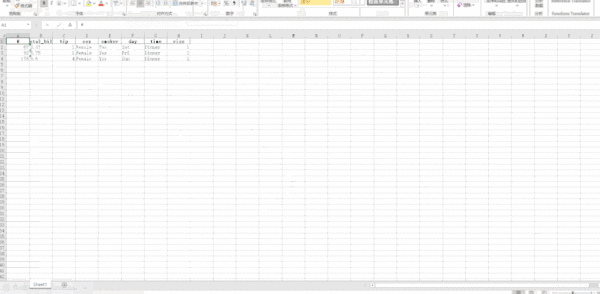
圖7
app4.py
import dash import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc import dash_core_components as dcc import dash_html_components as html import dash_table from dash.dependencies import Input, Output from flask import send_from_directory import os import uuid from sqlalchemy import create_engine import pandas as pd try: os.mkdir("downloads") except FileExistsError: pass engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:mysql@localhost/DASH') app = dash.Dash(__name__) @app.server.route('/download/<file>') def download(file): return send_from_directory('downloads', file) app.layout = dbc.Container( [ dbc.Row( [ dbc.Col(dbc.Button('更新數據表', id='refresh-tables', style={'width': '100%'}), width=2), dbc.Col(dcc.Dropdown(id='table-select', style={'width': '100%'}), width=2) ] ), html.Hr(), dash_table.DataTable( id='dash-table', editable=True, page_size=15, style_header={ 'font-family': 'Times New Romer', 'font-weight': 'bold', 'text-align': 'center' }, style_data={ 'font-family': 'Times New Romer', 'text-align': 'center' }, style_data_conditional=[ { # 對選中狀態下的單元格進行自定義樣式 "if": {"state": "selected"}, "background-color": "#b3e5fc", "border": "none" }, ], filter_action="native" ), html.Br(), html.A(id='download-url', target="_blank") ], style={ 'margin-top': '50px' } ) @app.callback( Output('table-select', 'options'), Input('refresh-tables', 'n_clicks') ) def refresh_tables(n_clicks): if n_clicks: return [ { 'label': table, 'value': table } for table in pd.read_sql_query('SHOW TABLES', con=engine)['Tables_in_dash'] ] return dash.no_update @app.callback( [Output('dash-table', 'data'), Output('dash-table', 'columns')], Input('table-select', 'value') ) def render_dash_table(value): if value: df = pd.read_sql_table(value, con=engine) return df.to_dict('records'), [ {'name': column, 'id': column} for column in df.columns ] else: return [], [] @app.callback( [Output("download-url", "href"), Output("download-url", "children")], [Input("dash-table", "derived_virtual_data"), Input("dash-table", "filter_query")], prevent_initial_call=True ) def download_table(derived_virtual_data, filter_query): if derived_virtual_data: print(derived_virtual_data) filename = f"output_{uuid.uuid1()}.xlsx" pd.DataFrame(derived_virtual_data).to_excel("downloads/" + filename, index=False) return "/download/" + filename, "下載當前狀態表格" return "", "" if __name__ == '__main__': app.run_server(debug=True)以上就是如何用Python輕松開發數據庫取數下載工具,小編相信有部分知識點可能是我們日常工作會見到或用到的。希望你能通過這篇文章學到更多知識。更多詳情敬請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。