您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章將為大家詳細講解有關Canvas如何實現一個六邊形能力圖,小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲。
一、前言
六邊形能力圖如下,由 6 個 六邊形組成,每一個頂點代表其在某一方面的能力。這篇文章我們就來看看如何基于 canvas 去繪制這么一個六邊形能力圖。當然,你也可以基于其他開源的 js 方案來實現,如 EChars.js 等。
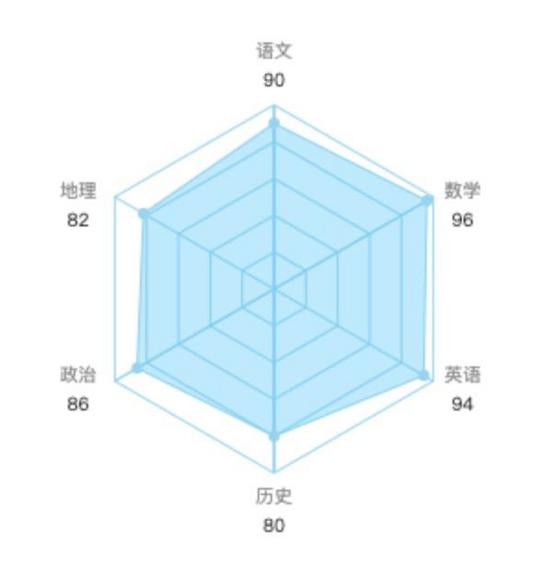
二、六邊形繪制基礎
六邊形能力圖有 6 個 六邊形組成,那我們只要繪制出一個,另外 5 個則依次減小六邊形的邊長即可。那我們首先來分析一下,如何繪制出一個六邊形。
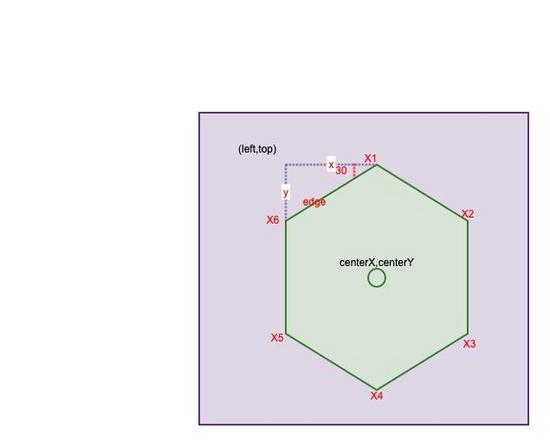
如上圖,繪制一個六邊形有以下幾個關鍵點:
1.紫色矩形區域我們可以看成是 canvas 的畫布。其大小可以認為是 (width,height)。center(centerX,centerY) 是其中心點,即 (width / 2, height / 2)。
2.繪制六邊形的關鍵是計算出它的 6 個頂點的坐標。而如上圖所示,這里面最關鍵的又是計算出六邊形所在矩形區域的左上角坐標(left,top)。對照上圖,(left,top) 的計算公式如下。
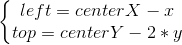
要計算出 (left,top) 需要先計算出 x,y 。而 x,y 的值與六邊形的邊長有關。
3.如上的 x,y 的計算公式為
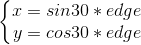
4.因此,X1(x1,y1),X2(x2,y2),X3(x3,y3),X4(x4,y4),X5(x5,y5),X6(x6,y6) 的坐標計算為
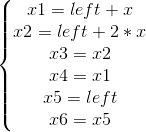

因此,得到繪制六邊形的代碼為:
function computeHexagonPoints(width, height, edge) {
let centerX = width / 2;
let centerY = height / 2;
let x = edge * Math.sqrt(3) / 2;
let left = centerX - x;
let x1,x2,x3,x4,x5,x6;
let y1,y2,y3,y4,y5,y6;
x5 = x6 = left;
x2 = x3 = left + x * 2;
x1 = x4 = left + x;
let y = edge / 2;
let top = centerY - 2 * y;
y1 = top;
y2 = y6 = top + y;
y3 = y5 = top + 3 * y;
y4 = top + 4 * y;
let points = new Array();
points[0] = [x1, y1];
points[1] = [x2, y2];
points[2] = [x3, y3];
points[3] = [x4, y4];
points[4] = [x5, y5];
points[5] = [x6, y6];
return points;
}三、繪制六維能力圖
3.1 繪制 6 個六邊形
基于 canvas 繪制,首先就是需要獲取 context。
_context = canvas.getContext('2d');而繪制的話,已經知道 6 個頂點了,那只需要將這 6 個點用連線的方式連接起來就可以了。主要用到 moveTo(x,y) 和 lineTo(x,y) 兩個方法。這里總共需要繪制 6 個六邊形,那只要按等比例減小 edge 的值就可以了。因此繪制六邊形能力圖的主要代碼如下。
function drawHexagonInner(edge) {
_context.strokeStyle = _color;
for (var i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
_allPoints[i] = computeHexagonPoints(_width, _height, edge - i * edge / 5);
_context.beginPath();
_context.moveTo(_allPoints[i][5][0],_allPoints[i][5][1]);
for (var j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
_context.lineTo(_allPoints[i][j][0],_allPoints[i][j][1]);
}
_context.closePath();
_context.stroke();
}
}代碼中還有 3 個相關的 API。beginPath() 和 closePath() 主要就是繪制得到一個封閉的路徑。stroke() 主要是得到一個鏤空的形狀。當然,相應的就有 fill() 得到填充的形狀。
3.2 繪制 3 條直線
繪制那 3 條直線也是比較簡單的,只要將 X1和X4 連接,將X2 和 X5 相連,將 X3 和 X6 相連。代碼如下:
function drawLines() {
_context.beginPath();
_context.strokeStyle = _color;
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
_context.moveTo(_allPoints[0][i][0],_allPoints[0][i][1]); //1-4
_context.lineTo(_allPoints[0][i+3][0],_allPoints[0][i+3][1]); //1-4
_context.stroke();
}
_context.closePath();
}3.3 繪制覆蓋圖
6 個頂點代表了六種能力,比如這里的各科成績,把六種能力封閉成一個閉合路徑并填充則稱為覆蓋圖。要繪制出覆蓋圖,這里需要計算出六個頂點。6 個頂點可以通過最外圍的六邊形的 6 個頂點和中心點來計算。簡單來說就是通過能力得分,在頂點到中心距離的占比來計算。計算公式如下。
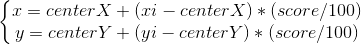
代碼如下
/**
* 畫覆蓋物
*/
function drawCover() {
let tmpCoverPoints = _allPoints[0];
_coverPoints = [];
console.log("coverPoints ",tmpCoverPoints)
let centerX = _width / 2;
let centerY = _height / 2;
for (let i = 0; i < tmpCoverPoints.length; i++) {
_coverPoints.push([
centerX + (tmpCoverPoints[i][0] - centerX) * (_data[i].score / 100.0),
centerX + (tmpCoverPoints[i][1] - centerY) * (_data[i].score / 100.0)
]);
}
console.log("newCoverPoints ",_coverPoints)
_context.beginPath();
_context.fillStyle = 'rgba(90,200,250,0.4)';
_context.moveTo(_coverPoints[5][0],_coverPoints[5][1]); //5
for (var j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
_context.lineTo(_coverPoints[j][0],_coverPoints[j][1]);
}
_context.stroke();
_context.closePath();
_context.fill();
}/**
* 描點
* @param pointRadius
*/
function drawPoints(pointRadius) {
_context.fillStyle = _color;
for (let i = 0; i < _coverPoints.length; i++) {
_context.beginPath();
_context.arc(_coverPoints[i][0],_coverPoints[i][1],pointRadius,0,Math.PI*2);
_context.closePath();
_context.fill();
}
}3.4 最后來繪制文本
繪制文本也是用的最外圍的 6 個頂點的坐標。而用的 API 是 fillText(text,x,y),其中 x,y 代碼文字繪制起點,但注意,不是文字所在矩形框的左上角,應該在左下角的大概位置。準確來說是文字的基線位置,這個在其他的GUI系統中也是一樣,當然這里不追求那么細節了,就認為是左下角位置吧。
因此,對于不同側的文字,其起點坐標也是不一樣。如左側的文字至少應該是左側的頂點 x 減去文字的寬度。再比如,上下兩側的文字與頂點中相對居中對齊的,因此計算方法是 x 減去文字寬度的一半。代碼的實現分為了上下左右來進行不同的繪制。
代碼如下,看著有點長,但其實是很簡單的。
/**
* 繪制上側的文字
* @param text
* @param pos
*/
function drawUpText(item, pos) {
let nameMeasure = _context.measureText(item.name);
let scoreMeasure = _context.measureText(item.score);
_context.fillStyle = '#8E8E8E';
_context.fillText(item.name, pos[0] - nameMeasure.width / 2,pos[1] - 26);
_context.fillStyle = '#212121';
_context.fillText(item.score, pos[0] - scoreMeasure.width / 2,pos[1] - 10);
}/**
* 繪制下側的文字
* @param text
* @param pos
*/
function drawDownText(item, pos) {
let nameMeasure = _context.measureText(item.name);
let scoreMeasure = _context.measureText(item.score);
_context.fillStyle = '#8E8E8E';
_context.fillText(item.name, pos[0] - nameMeasure.width / 2,pos[1] + 16);
_context.fillStyle = '#212121';
_context.fillText(item.score, pos[0] - scoreMeasure.width / 2,pos[1] + 32);
}/**
* 繪制左側的文字
* @param text
* @param pos
*/
function drawLeftText(item, pos) {
let nameMeasure = _context.measureText(item.name);
let scoreMeasure = _context.measureText(item.score);
_context.fillStyle = '#8E8E8E';
_context.fillText(item.name, pos[0] - nameMeasure.width - 10,pos[1]);
_context.fillStyle = '#212121';
_context.fillText(item.score, pos[0] - 10 - (nameMeasure.width + scoreMeasure.width) / 2,pos[1] + 16);
}/**
* 繪制右側的文字
* @param text
* @param pos
*/
function drawRightText(item, pos) {
let nameMeasure = _context.measureText(item.name);
let scoreMeasure = _context.measureText(item.score);
_context.fillStyle = '#8E8E8E';
_context.fillText(item.name, pos[0] - nameMeasure.width + 26,pos[1]);
_context.fillStyle = '#212121';
_context.fillText(item.score, pos[0] + 26 - (nameMeasure.width + scoreMeasure.width) / 2,pos[1] + 16);
}/**
* 繪制所有文本
*/
function drawText() {
_context.fillStyle = '#8E8E8E';
_context.strokeStyle = _color;
let textPos = _allPoints[0];
for (let i = 0; i < textPos.length; i++) {
let item = _data[i];
let pos = textPos[i];
if(i == 0) {
drawUpText(item, pos);
} else if(i == 1 || i == 2) {
drawRightText(item, pos);
} else if(i == 3) {
drawDownText(item, pos);
} else if(i == 4 || i == 5) {
drawLeftText(item, pos);
}
}
}關于“Canvas如何實現一個六邊形能力圖”這篇文章就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,使各位可以學到更多知識,如果覺得文章不錯,請把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。