您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本文源碼:GitHub·點這里 || GitEE·點這里
下圖是常見的計算機文件系統的一部分。

文件系統是一個樹結構,樹上長有節點。樹的節點有兩種:
即文件夾,有內部樹結構,在圖中涂有顏色;
另一種是文件,即樹葉節點,沒有內部樹結構。
public class C01_InScene {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("F:\\tree") ;
fileTree(file, 0);
}
private static void fileTree(File file, int floor) {
// 判斷是否存在
if (file.exists()) {
if (floor > 0) {
// 循環打空格
for (int i = 0; i < floor; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
if (file.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("+" + file.getName());
// 列出所有文件及文件夾
File[] files = file.listFiles();
if (null != files) {
// 循環遞歸
for (File dirFile : files) {
fileTree(dirFile, floor + 1);
}
}
} else {
System.out.println("-" + file.getName());
}
}
}
}執行效果:+代表文件夾,-代表文件。
+tree
+dir1
+dir2
-dir2Leaf.txt
-leaf1.txt
-leaf2.txt
-OneLeaf.txt
-TwoLeaf.txt組合模式屬于對象的結構模式,有時又叫做“部分——整體”模式。組合模式將對象組織到樹結構中,可以用來描述整體與部分的關系。組合模式可以使客戶端將單純元素與復合元素同等看待。
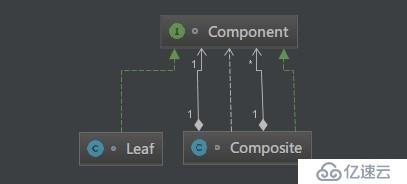
安全式的組合模式要求管理聚集的方法只出現在樹枝構件類中,而不出現在樹葉構件類中。涉及到三個角色:
它給組合的對象定義出公共的接口及其默認行為,可以用來管理所有的子對象。組合對象通常把它所包含的子對象當做類型為Component的對象。在安全式的組合模式里,構件角色并不定義出管理子對象的方法,這一定義由樹枝構件對象給出。
樹葉對象是沒有下級子對象的對象,定義出參加組合的原始對象的行為。
代表參加組合的有下級子對象的對象。樹枝構件類給出所有的管理子對象的方法,如add()、remove()以及getChild()。
public class C02_Security_Model {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Composite root = new Composite("服裝");
Composite composite1 = new Composite("男裝");
Leaf manCoat = new Leaf("上衣");
Leaf manBottom = new Leaf("下衣");
composite1.addChild(manCoat);
composite1.addChild(manBottom);
Composite composite2 = new Composite("女裝");
Leaf leaf1 = new Leaf("鞋子");
Leaf leaf2 = new Leaf("帽子");
root.addChild(leaf1);
root.addChild(leaf2);
root.addChild(composite1);
root.addChild(composite2);
root.printStruct("");
}
}
// 抽象構件角色類
interface Component {
/*
* 輸出組件自身的名稱
*/
void printStruct(String preStr);
}
// 樹枝構件角色類
class Composite implements Component{
// 用來存儲組合對象中包含的子組件對象
private List<Component> childComponents = new ArrayList<Component>();
// 輸出對象的名稱
private String name;
// 構造方法,傳入組合對象的名字
public Composite (String name){
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 聚集管理方法,增加一個子構件對象
* @param child 子構件對象
*/
public void addChild(Component child){
childComponents.add(child);
}
/**
* 聚集管理方法,刪除一個子構件對象
* @param index 子構件對象的下標
*/
public void removeChild(int index){
childComponents.remove(index);
}
/**
* 聚集管理方法,返回所有子構件對象
*/
public List getChild(){
return childComponents ;
}
/**
* 輸出對象的自身結構
* @param preStr 前綴,主要是按照層級拼接空格,實現向后縮進
*/
@Override
public void printStruct(String preStr) {
//先輸出自己
System.out.println(preStr+"+"+this.name);
//如果還包含有子組件,那么就輸出這些子組件對象
if (this.childComponents != null){
//添加兩個空格,表示向后縮進兩個空格
preStr = preStr+" ";
//輸出當前的子對象:使用函數遞歸的原理
for (Component c : childComponents) {
c.printStruct(preStr);
}
}
}
}
class Leaf implements Component{
// 輸出葉子對象的名稱
private String name;
// 構造方法,傳入葉子對象的名稱
public Leaf (String name){
this.name = name ;
}
/**
* 輸出葉子對象的結構,葉子對象沒有子對象,也就是輸出葉子對象的名字
* @param preStr 前綴,主要是按照層級拼接的空格,實現向后縮進
*/
@Override
public void printStruct(String preStr) {
System.out.println(preStr+"-"+name);
}
}+服裝
-鞋子
-帽子
+男裝
-上衣
-下衣
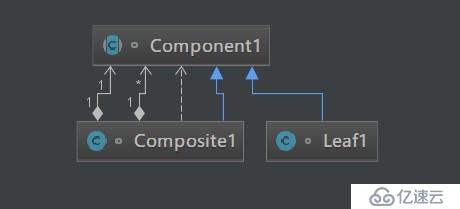
+女裝與安全式的組合模式不同的是,透明式的組合模式要求所有的具體構件類,不論樹枝構件還是樹葉構件,均符合一個固定接口。
public class C03_Transparent_Model {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Component1 root = new Composite1("服裝");
Component1 c1 = new Composite1("男裝");
Component1 c2 = new Composite1("女裝");
Component1 leaf1 = new Leaf1("襯衫");
Component1 leaf2 = new Leaf1("夾克");
Component1 leaf3 = new Leaf1("裙子");
Component1 leaf4 = new Leaf1("套裝");
root.addChild(c1);
root.addChild(c2);
c1.addChild(leaf1);
c1.addChild(leaf2);
c2.addChild(leaf3);
c2.addChild(leaf4);
root.printStruct("");
}
}
abstract class Component1 {
/**
* 輸出組件自身的名稱
*/
public abstract void printStruct(String preStr);
// 聚集管理方法,增加一個子構件對象
public void addChild(Component1 child){
/**
* 缺省實現,拋出異常,因為葉子對象沒有此功能
* 或者子組件沒有實現這個功能
*/
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("對象不支持此功能");
}
// 聚集管理方法,刪除一個子構件對象
public void removeChild(int index){
/**
* 缺省實現,拋出異常,因為葉子對象沒有此功能
* 或者子組件沒有實現這個功能
*/
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("對象不支持此功能");
}
// 聚集管理方法,返回所有子構件對象
public List<Component1> getChild(){
/**
* 缺省實現,拋出異常,因為葉子對象沒有此功能
* 或者子組件沒有實現這個功能
*/
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("對象不支持此功能");
}
}
class Composite1 extends Component1 {
// 用來存儲組合對象中包含的子組件對象
private List<Component1> childComponents = new ArrayList<Component1>();
// 輸出對象名稱
private String name ;
public Composite1 (String name){
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 聚集管理方法,增加一個子構件對象
* @param child 子構件對象
*/
public void addChild(Component1 child){
childComponents.add(child);
}
/**
* 聚集管理方法,刪除一個子構件對象
* @param index 子構件對象的下標
*/
public void removeChild(int index){
childComponents.remove(index);
}
// 聚集管理方法,返回所有子構件對象
public List<Component1> getChild(){
return childComponents ;
}
/**
* 輸出對象的自身結構
* @param preStr 前綴,主要是按照層級拼接空格,實現向后縮進
*/
@Override
public void printStruct(String preStr) {
// 首先輸出自己名稱
System.out.println(preStr+"+"+this.name);
// 如果還包含有子組件,那么就輸出這些子組件對象
preStr = preStr + " ";
if (this.childComponents != null) {
// 添加兩個空格,表示向后縮進
for (Component1 c : childComponents) {
////遞歸輸出每個子對象
c.printStruct(preStr);
}
}
}
}
class Leaf1 extends Component1 {
private String name;
public Leaf1 (String name){
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 輸出葉子對象的結構,葉子對象沒有子對象,也就是輸出葉子對象的名字
* @param preStr 前綴,主要是按照層級拼接的空格,實現向后縮進
*/
@Override
public void printStruct(String preStr) {
System.out.println(preStr+"-"+name);
}
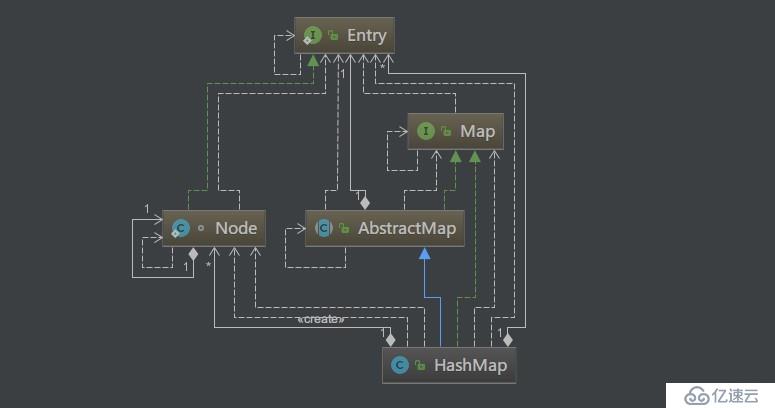
}
public V put(K var1, V var2) {
return this.putVal(hash(var1), var1, var2, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int var1, K var2, V var3, boolean var4, boolean var5) {
HashMap.Node[] var6 = this.table;
.......
}public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> var1) {
this.putMapEntries(var1, true);
}GitHub·地址
https://github.com/cicadasmile/model-arithmetic-parent
GitEE·地址
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/model-arithmetic-parent
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。