您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“Golang中的sync.Pool怎么用”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“Golang中的sync.Pool怎么用”吧!
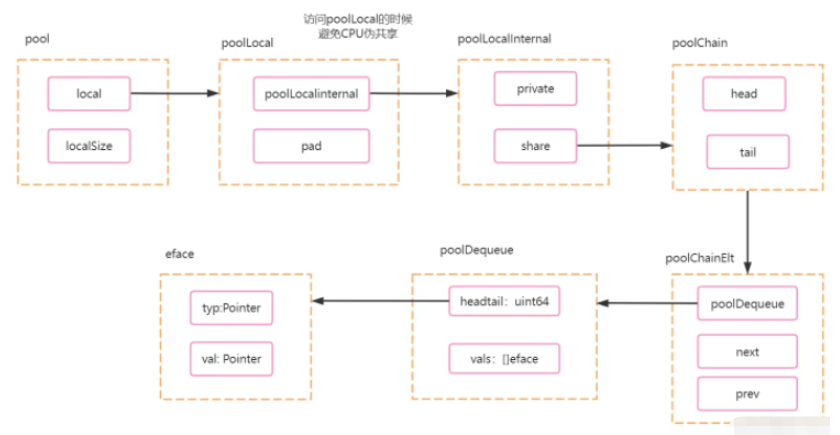
下面是相關源代碼,不過是已經刪減了對本次分析沒有用的代碼.
type Pool struct {
// GMP中,每一個P(協程調度器)會有一個數組,數組大小位localSize.
local unsafe.Pointer
// p 數組大小.
localSize uintptr
New func() any
}
// poolLocal 每個P(協程調度器)的本地pool.
type poolLocal struct {
poolLocalInternal
// 保證一個poolLocal占用一個緩存行
pad [128 - unsafe.Sizeof(poolLocalInternal{})%128]byte
}
type poolLocalInternal struct {
private any // Can be used only by the respective P. 16
shared poolChain // Local P can pushHead/popHead; any P can popTail. 8
}
type poolChain struct {
head *poolChainElt
tail *poolChainElt
}
type poolChainElt struct {
poolDequeue
next, prev *poolChainElt
}
type poolDequeue struct {
// head 高32位,tail低32位.
headTail uint64
vals []eface
}
// 存儲具體的value.
type eface struct {
typ, val unsafe.Pointer
}
Put 過程分析比較重要,因為這里會包含pool所有依賴相關分析.
總的分析學習過程可以分為下面幾個步驟:
1.獲取P對應的poolLocal
2.val如何進入poolLocal下面的poolDequeue隊列中的.
3.如果當前協程獲取到當前P對應的poolLocal之后進行put前,協程讓出CPU使用權,再次調度過來之后,會發生什么?
4.讀寫內存優化.
數組直接操作內存,而不經過Golang
充分利用uint64值的特性,將head和tail用一個值來進行表示,減少CPU訪問內存次數.
獲取P對應的poolLocal
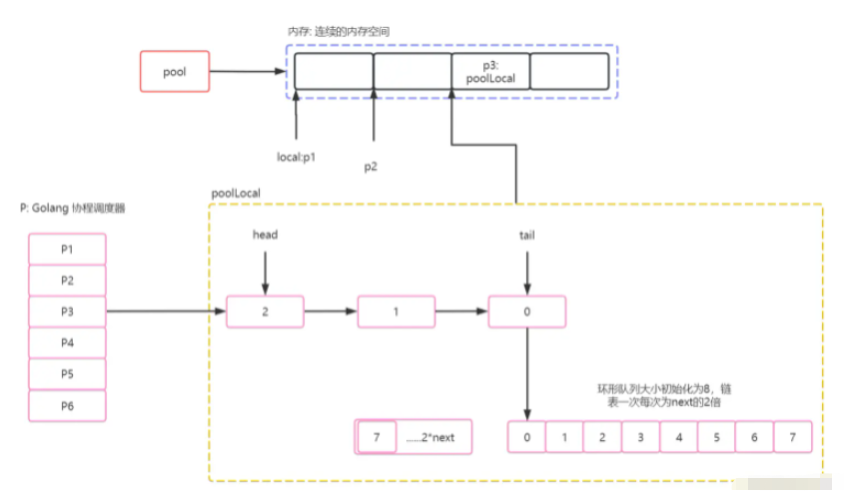
sync.Pool.local其實是一個指針,并且通過變量+結構體大小來劃分內存空間,從而將這片內存直接劃分為數組. Go 在Put之前會先對當前Goroutine綁定到當前P中,然后通過pid獲取其在local內存地址中的歧視指針,在獲取時是會進行內存分配的. 具體如下:
func (p *Pool) pin() (*poolLocal, int) {
// 返回運行當前協程的P(協程調度器),并且設置禁止搶占.
pid := runtime_procPin()
s := runtime_LoadAcquintptr(&p.localSize) // load-acquire
l := p.local // load-consume
// pid < 核心數. 默認走該邏輯.
if uintptr(pid) < s {
return indexLocal(l, pid), pid
}
// 設置的P大于本機CPU核心數.
return p.pinSlow()
}
// indexLocal 獲取當前P的poolLocal指針.
func indexLocal(l unsafe.Pointer, i int) *poolLocal {
// l p.local指針開始位置.
// 我猜測這里如果l為空,編譯階段會進行優化.
lp := unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(l) + uintptr(i)*unsafe.Sizeof(poolLocal{}))
// uintptr真實的指針.
// unsafe.Pointer Go對指針的封裝: 用于指針和結構體互相轉化.
return (*poolLocal)(lp)
}從上面代碼我們可以看到,Go通過runtime_procPin來設置當前Goroutine獨占P,并且直接通過頭指針+偏移量(數組結構體大小)來進行對內存劃分為數組.
Put 進入poolDequeue隊列:
Go在Push時,會通過headtail來獲取當前隊列內元素個數,如果滿了,則會重新構建一個環型隊列poolChainElt,并且設置為poolChain.head,并且賦值next以及prev.
通過下面代碼,我們可以看到,Go通過邏輯運算判斷隊列是否滿的設計時非常巧妙的,如果后續我們去開發組件,也是可以這么進行設計的。
func (c *poolChain) pushHead(val any) {
d := c.head
// 初始化.
if d == nil {
// Initialize the chain.
const initSize = 8 // Must be a power of 2
d = new(poolChainElt)
d.vals = make([]eface, initSize)
c.head = d
// 將新構建的d賦值給tail.
storePoolChainElt(&c.tail, d)
}
// 入隊.
if d.pushHead(val) {
return
}
// 隊列滿了.
newSize := len(d.vals) * 2
if newSize >= dequeueLimit {
// 隊列大小默認為2的30次方.
newSize = dequeueLimit
}
// 賦值鏈表前后節點關系.
// prev.
// d2.prev=d1.
// d1.next=d2.
d2 := &poolChainElt{prev: d}
d2.vals = make([]eface, newSize)
c.head = d2
// next .
storePoolChainElt(&d.next, d2)
d2.pushHead(val)
}
// 入隊poolDequeue
func (d *poolDequeue) pushHead(val any) bool {
ptrs := atomic.LoadUint64(&d.headTail)
head, tail := d.unpack(ptrs)
// head 表示當前有多少元素.
if (tail+uint32(len(d.vals)))&(1<<dequeueBits-1) == head {
return false
}
// 環型隊列. head&uint32(len(d.vals)-1) 表示當前元素落的位置一定在隊列上.
slot := &d.vals[head&uint32(len(d.vals)-1)]
typ := atomic.LoadPointer(&slot.typ)
if typ != nil {
return false
}
// The head slot is free, so we own it.
if val == nil {
val = dequeueNil(nil)
}
// 向slot寫入指針類型為*any,并且值為val.
*(*any)(unsafe.Pointer(slot)) = val
// headTail高32位++
atomic.AddUint64(&d.headTail, 1<<dequeueBits)
return true
}Get實現邏輯:
其實我們看了Put相關邏輯之后,我們可能很自然的就想到了Get的邏輯,無非就是遍歷鏈表,并且如果隊列中最后一個元素不為空,則會將該元素返回,并且將該插槽賦值為空值.
感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“Golang中的sync.Pool怎么用”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對Golang中的sync.Pool怎么用這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。