您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“@NonNull導致無法序列化如何解決”的相關知識,小編通過實際案例向大家展示操作過程,操作方法簡單快捷,實用性強,希望這篇“@NonNull導致無法序列化如何解決”文章能幫助大家解決問題。
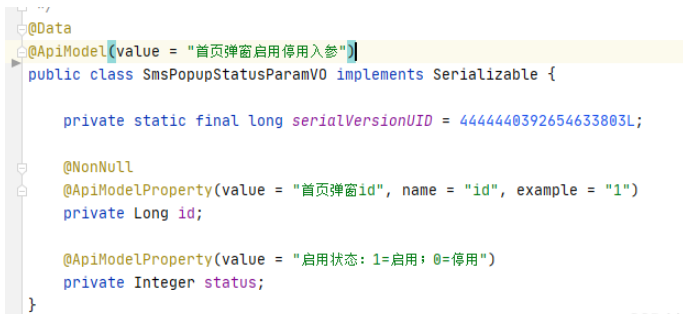
以上這個代碼在接參的時候報了一個缺少無參構造函數無法序列化的錯誤
將.class反編譯
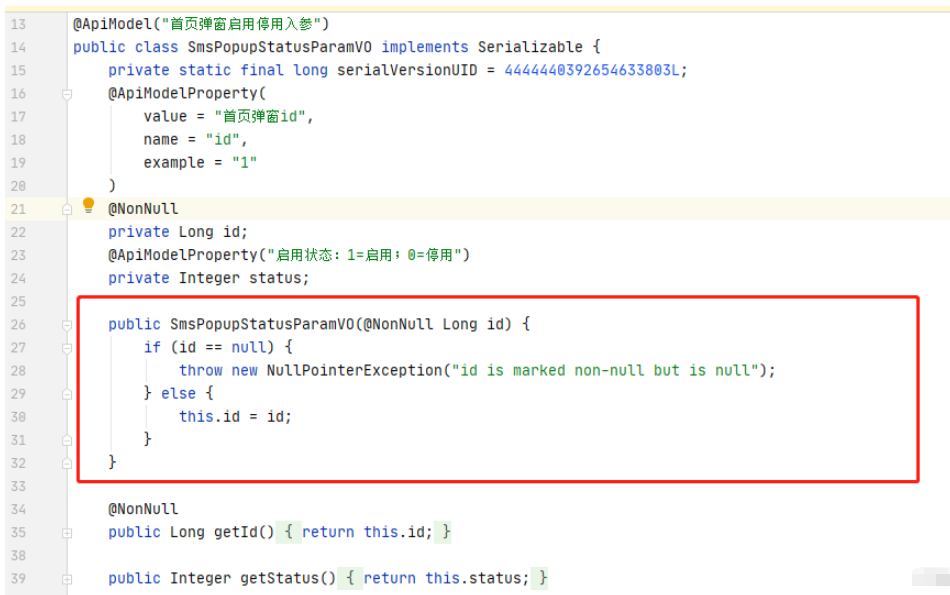
可以看到編譯后的源碼中生成了一個有參構造 明顯是 用來判空的 假設那么這個構造函數應該就是根據@NonNull生成的
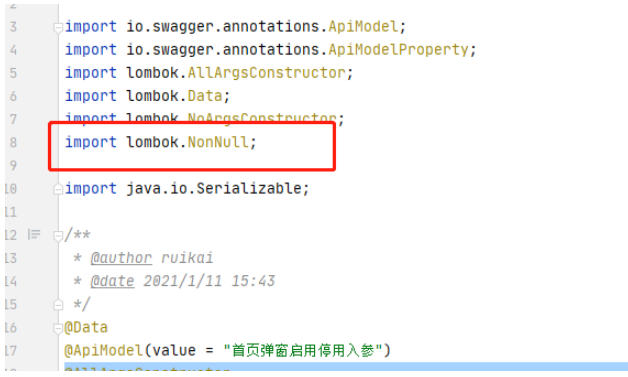
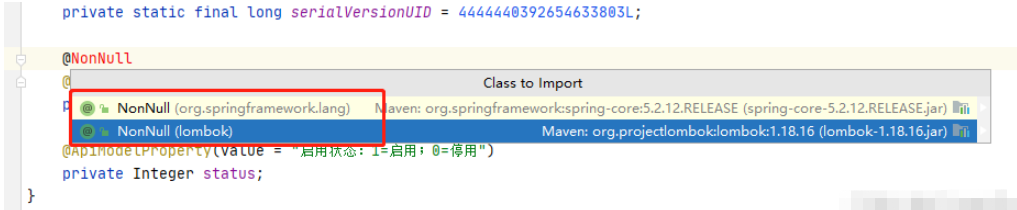
實際上我們治理應該添加的注解是NotNull才對
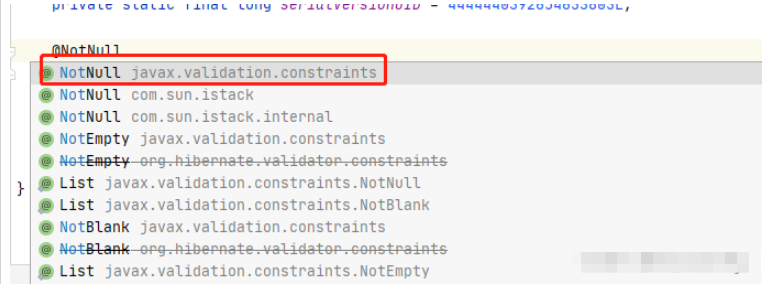
上面因為lombook根據@NonNull生成了一個有參構造函數,導致jdk不會添加默認的無參構造函數,沒有無參構造函數的話 序列化就會失敗.
一般Http接口,為了參數統一管理,定義一個VO用來接收POST過來的字段,常規做法是把參數解析成map,然后反序列化到VO中,早期定義的接口字段都非空,所以VO中都加了@NonNull注解;一直很和諧;
因為需求變化,接口字段需要增加兩個,為了版本兼容,新加的兩個字段需要可空;于是在VO中增加兩個字段,不用@NonNull修飾,但是反序列化后發現這兩個字段一直為空!怎么都不能從map中獲取到這兩個值!
版本:
JDK:1.8
lombok:1.18.12
fastjson:1.2.60
原代碼
package com.example.demo;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NonNull;
@Data
public class DemoRequestVO {
@NonNull
private String firstParam;
private String SecondParam;
private String thirdParam;
} public static void testDemo(){
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("firstParam","lllllll");
params.put("secondParam","45454645");
params.put("thirdParam","xx公司");
DemoRequestVO request = JSON.parseObject(JSON.toJSONString(params), DemoRequestVO.class);
System.out.println(request);
}分析原因
做兩方面猜測:
1: 注解提供者問題
2: Json反序列化問題
1: 先看下: 注解提供者 @NonNull
發現其是作用于RetentionPolicy.CLASS的
package lombok;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE, ElementType.TYPE_USE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
@Documented
public @interface NonNull {
}查看lombok源碼可以看到,NonNull注解提供者一共這么多
static {
NONNULL_ANNOTATIONS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(new String[] {
"androidx.annotation.NonNull",
"android.support.annotation.NonNull",
"com.sun.istack.internal.NotNull",
"edu.umd.cs.findbugs.annotations.NonNull",
"javax.annotation.Nonnull",
// "javax.validation.constraints.NotNull", // The field might contain a null value until it is persisted.
"lombok.NonNull",
"org.checkerframework.checker.nullness.qual.NonNull",
"org.eclipse.jdt.annotation.NonNull",
"org.eclipse.jgit.annotations.NonNull",
"org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull",
"org.jmlspecs.annotation.NonNull",
"org.netbeans.api.annotations.common.NonNull",
"org.springframework.lang.NonNull",
}));再看下經過注解后編譯的CLASS
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package com.example.demo;
import lombok.NonNull;
public class DemoRequestVO {
@NonNull
private String firstParam;
private String SecondParam;
private String thirdParam;
public DemoRequestVO(@NonNull final String firstParam) {
if (firstParam == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("firstParam is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.firstParam = firstParam;
}
}
@NonNull
public String getFirstParam() {
return this.firstParam;
}
public String getSecondParam() {
return this.SecondParam;
}
public String getThirdParam() {
return this.thirdParam;
}
public void setFirstParam(@NonNull final String firstParam) {
if (firstParam == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("firstParam is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.firstParam = firstParam;
}
}
public void setSecondParam(final String SecondParam) {
this.SecondParam = SecondParam;
}
public void setThirdParam(final String thirdParam) {
this.thirdParam = thirdParam;
}
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof DemoRequestVO)) {
return false;
} else {
DemoRequestVO other = (DemoRequestVO)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
label47: {
Object this$firstParam = this.getFirstParam();
Object other$firstParam = other.getFirstParam();
if (this$firstParam == null) {
if (other$firstParam == null) {
break label47;
}
} else if (this$firstParam.equals(other$firstParam)) {
break label47;
}
return false;
}
Object this$SecondParam = this.getSecondParam();
Object other$SecondParam = other.getSecondParam();
if (this$SecondParam == null) {
if (other$SecondParam != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$SecondParam.equals(other$SecondParam)) {
return false;
}
Object this$thirdParam = this.getThirdParam();
Object other$thirdParam = other.getThirdParam();
if (this$thirdParam == null) {
if (other$thirdParam != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$thirdParam.equals(other$thirdParam)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(final Object other) {
return other instanceof DemoRequestVO;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $firstParam = this.getFirstParam();
int result = result * 59 + ($firstParam == null ? 43 : $firstParam.hashCode());
Object $SecondParam = this.getSecondParam();
result = result * 59 + ($SecondParam == null ? 43 : $SecondParam.hashCode());
Object $thirdParam = this.getThirdParam();
result = result * 59 + ($thirdParam == null ? 43 : $thirdParam.hashCode());
return result;
}
public String toString() {
return "DemoRequestVO(firstParam=" + this.getFirstParam() + ", SecondParam=" + this.getSecondParam() + ", thirdParam=" + this.getThirdParam() + ")";
}
}重點是看這個編譯后的class的構造方法:只有一個帶@NonNull注解參數的構造方法!!!
一般到這里都能想到反序列化后的為啥另外兩個未注解NonNull的為啥空值了;如果沒想到,也沒關系,咱們再來看看JSON反序列化的過程
2: json反序列化;
一系列遞進過程不再描述,重點看JavaBeanInfo類中的build方法,這個方法是真正把map反序化到javaBean的過程
public static JavaBeanInfo build(Class<?> clazz, Type type, PropertyNamingStrategy propertyNamingStrategy, boolean fieldBased, boolean compatibleWithJavaBean, boolean jacksonCompatible)
挑幾處重要的開看下:
取構造方法list
Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
Constructor<?> defaultConstructor = null;
if (!kotlin || constructors.length == 1) {
if (builderClass == null) {
defaultConstructor = getDefaultConstructor(clazz, constructors);
} else {
defaultConstructor = getDefaultConstructor(builderClass, builderClass.getDeclaredConstructors());
}
}賦值創建javaBean的構造
boolean is_public = (constructor.getModifiers() & 1) != 0;
if (is_public) {
String[] lookupParameterNames = ASMUtils.lookupParameterNames(constructor);
if (lookupParameterNames != null && lookupParameterNames.length != 0 && (creatorConstructor == null || paramNames == null || lookupParameterNames.length > paramNames.length)) {
paramNames = lookupParameterNames;
creatorConstructor = constructor;
}
}創建javaBean,看傳參; 只有一個構造方法;
if (!kotlin && !clazz.getName().equals("javax.servlet.http.Cookie")) {
return new JavaBeanInfo(clazz, builderClass, (Constructor)null, creatorConstructor, (Method)null, (Method)null, jsonType, fieldList);
}結論:
使用@NonNull注解,編譯后生成的CLASS構造方法只有一個,且只有被注解的字段才能構造時候賦值;此種做法是保證在編譯期可以判斷非空;
反序列化時候使用了這個構造方法,其他的值沒有被賦值;
1: 使用@NotNull代替
2: 如果修飾的是String類型,推薦使用@NotBlank,好處是可以判斷空字符串
3: 在自定義的VO中增加一個無參構造方法。
關于“@NonNull導致無法序列化如何解決”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識點。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。