您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“SpringBoot yml配置文件如何讀取”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“SpringBoot yml配置文件如何讀取”吧!
YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language),一種數據序列化格式
優點:
容易閱讀
容易與腳本語言交互
以數據為核心,重數據輕格式
YANL文件擴展名
.yml(主流)
.yaml
幾種數據格式比較

大小寫敏感
屬性層級關系使用多行描述,每行結尾使用冒號結束
使用縮進表示層級關系,同層級左側對齊,只允許使用空格(不允許使用Tab鍵)
屬性值前面添加空格(屬性名與屬性值之間使用冒號+空格作為分隔)
#表示注釋
示例:
user:
name: zhangsan
age: 12
users:
-
name: lisi
age: 13
-
name: wangwu
age: 18
likes: [game,play,having]
users1: [{name:zhangsan,age:12},{name:lisi,age:12}]
字面值表示方式

數組表示方式:在屬性名書寫位置的下方使用減號作為數據開始符號,每行書寫一個數據,減號與數據鍵空格分隔

使用@Value讀取單個數據,屬性名引用方式:${一級屬性名.二級屬性名}
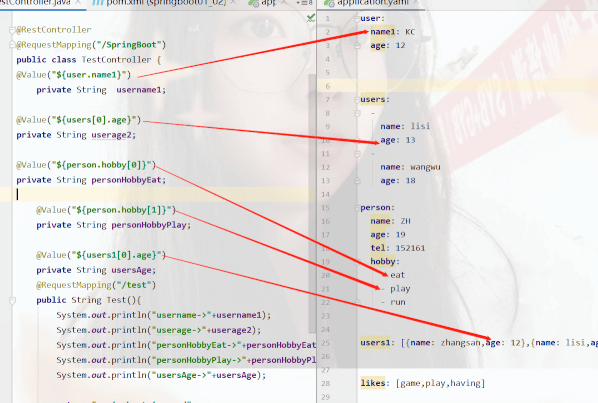
controller下
package com.springboot01_02.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/SpringBoot")
public class TestController {
@Value("${user.name1}")
private String username1;
@Value("${users[0].age}")
private String userage2;
@Value("${person.hobby[0]}")
private String personHobbyEat;
@Value("${person.hobby[1]}")
private String personHobbyPlay;
@Value("${users1[0].age}")
private String usersAge;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String Test(){
System.out.println("username->"+username1);
System.out.println("userage->"+userage2);
System.out.println("personHobbyEat->"+personHobbyEat);
System.out.println("personHobbyPlay->"+personHobbyPlay);
System.out.println("usersAge->"+usersAge);
return "springboot is good";
}
}yml配置文件
user:
name1: KC
age: 12
users:
-
name: lisi
age: 13
-
name: wangwu
age: 18
person:
name: ZH
age: 19
tel: 152161
hobby:
- eat
- play
- run
users1: [{name: zhangsan,age: 12},{name: lisi,age: 12}]
likes: [game,play,having]
運行結果:
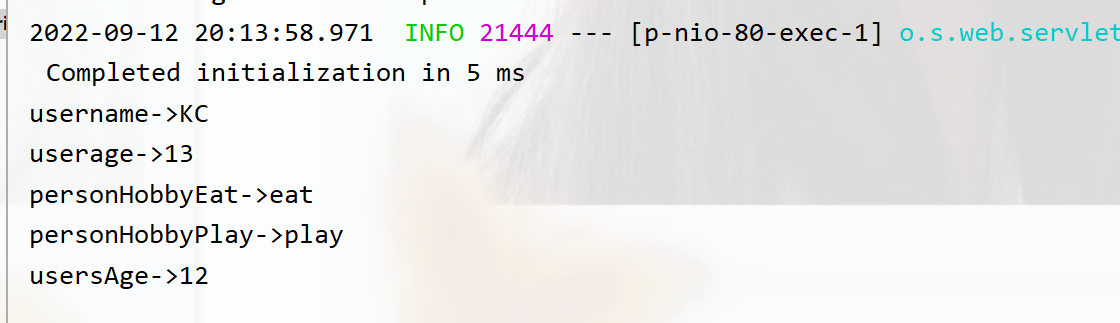
yaml數據讀取
在配置文件中可以使用屬性名引用方式引用屬性
在配置文件中
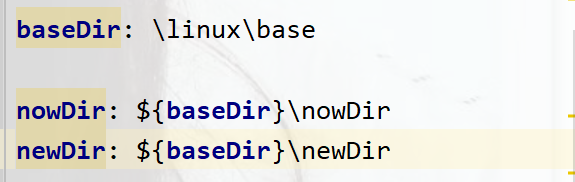
package com.springboot01_02.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/SpringBoot")
public class TestController {
@Value("${nowDir}")
private String nowDir1;
@Value("${tewDir}")
private String tewDir1;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String Test(){
System.out.println("nowDir->"+nowDir1);
System.out.println("towDir->"+tewDir1);
return "springboot is good";
}
}運行結果:
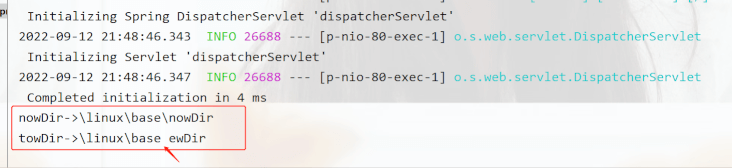
可以發現,要想讓轉義字符生效,就得加上雙引號不然還是以字符串的形式打印出
package com.springboot01_02.controller;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController@RequestMapping("/SpringBoot")public class TestController {//使用自動裝配將所有數據封裝到一個Environment中 @Autowired private Environment evn; @RequestMapping("/test") public String Test(){ System.out.println("----------------"); System.out.println(evn.getProperty("nowDir")); System.out.println(evn.getProperty("users1[0].age")); return "springboot is good"; }}運行結果:
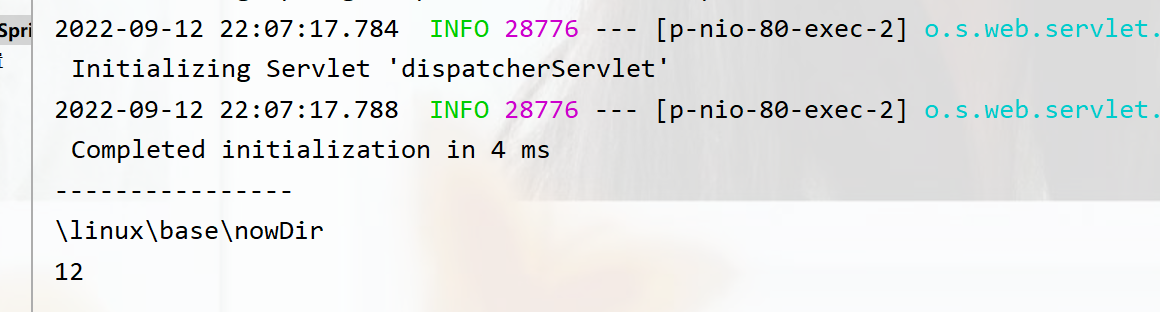
小結:
使用Environment對象封裝全部配置信息
使用@Autowired自動裝配數據到Environment對象中
application.yaml配置文件中的信息
#創建類,用于封裝下面的數據#有spring帶我們去加載數據到對象中,且告訴spring加載這組信息#使用時從spring中直接獲取信息使用datasource: driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost/love username: kongchao password: zenghui
自定義一個類
package com.springboot01_02.datesource;import lombok.Data;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;//1、定義數據類型模型封裝yaml文件中對應的數據//2、定義為spring管控的bean@Component//3、指定加載的數據@ConfigurationProperties("datasource")//4、設置getSet方法等@Datapublic class MyDateSource { private String driver; private String url; private String username; private String password;}使用了@Date,在pom.xml中導入lombok
<dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.16.10</version> </dependency>
測試類下
package com.springboot01_02.controller;import com.springboot01_02.datesource.MyDateSource;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController@RequestMapping("/SpringBoot")public class TestController {@Autowired private MyDateSource dateSource; @RequestMapping("/test") public String Test(){ System.out.println(dateSource); return "springboot is good"; }}運行訪問localhost/SpringBoot/test即可得到:

小結:
使用@ConfigurationProperties注解綁定配置信息到封裝類中
封裝類需要定義為Spring管理的bean(使用注解@Component),否則無法進行屬性注入
到此,相信大家對“SpringBoot yml配置文件如何讀取”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。