您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“Java阻塞隊列BlockingQueue實例分析”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“Java阻塞隊列BlockingQueue實例分析”吧!
無限隊列(unbounded queue) 無容量限定,只隨存儲變化
有限隊列(bounded queue) 定義了最大容量
向無限隊列添加元素的所有操作都將永遠不會阻塞(也是線程安全的),因此它可以增長到非常大的容量。 使用無限阻塞隊列 BlockingQueue 設計生產者 - 消費者模型時最重要的是消費者應該能夠像生產者向隊列添加消息一樣快地消費消息 。否則可能內存不足而拋出 OutOfMemory 異常。
1.通常使用鏈表或數組實現
2.一般具有 FIFO(先進先出) 特性,也可以設計為雙端隊列
3.隊列的主要操作:入隊和出隊
定義:線程通信中,在任意時刻,無論并發有多高,在單個 JVM 上,同一時間永遠只有一個線程能對隊列進行入隊或出隊操作。BlockingQueue 可以在線程之間共享而無需任何顯式同步
阻塞隊列的類型:
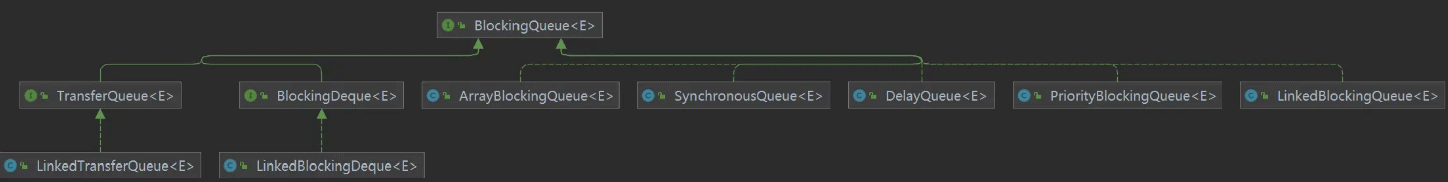
JAVA中的應用場景 : 線程池、SpringCloud-Eureka 三級緩存、Nacos、MQ、Netty 等
ArrayBlockingQueue : 由數組支持的有界隊列
應用場景: 線程池中有比較多的應用、生產者消費者模型
工作原理: 基于 ReentrantLock 保證線程安全,根據Condition實現隊列滿時的阻塞
LinkedBlockingQueue : 基于鏈表的無界隊列(理論上有界)
PriorityBlockingQueue : 由優先級堆支持的無界優先級隊列
DelayQueue : 由優先級堆支持的、基于時間的調度隊列,內部基于無界隊列PriorityQueue 實現,而無界隊列基于數組的擴容實現
使用方法: 入隊的對象必須要實現 Delayed 接口,而 Delayed 集成自 Comparable 接口
應用場景: 售賣電影票等
工作原理: 隊列內部會根據時間優先級進行排序。延遲類線程池周期執行。
它們都實現了BlockingQueue接口,都有put()和take()等方法,創建方式如下:
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<> (666);
添加元素:
| 方法 | 含義 |
|---|---|
| add() | 如果插入成功則返回 true,否則拋出 IllegalStateException 異常 |
| put() | 將指定的元素插入隊列,如果隊列滿了,會阻塞直到有空間插入 |
| offer() | 如果插入成功則返回 true,否則返回 false |
| offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 嘗試將元素插入隊列,如果隊列已滿,會阻塞直到有空間插入,阻塞有時間控制 |
檢索元素:
| 方法 | 含義 |
|---|---|
| take() | 獲取隊列的頭部元素并將其刪除,如果隊列為空,則阻塞并等待元素變為可用 |
| poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 檢索并刪除隊列的頭部,如有必要,等待指定的等待時間以使元素可用,如果超時,則返回 null |
實現:同步等待隊列(CLH)+ 條件等待隊列滿足條件的元素在CLH隊列中等待鎖,不滿足條件的隊列挪到條件等待隊列,滿足條件后再從 tail 插入 CLH 隊列
線程獲取鎖的條件: 在 CLH 隊列里等待的 Node 節點,并且 Node 節點的前驅節點是 Singal。條件等待隊列里的線程是無法獲取鎖的。
/**
* 構造方法
* 還有兩個構造函數,一個無fair參數,一個可傳入集合,創建時插入隊列
* @param capacity 固定容量
* @param fair 默認是false:訪問順序未指定; true:按照FIFO順序處理
*/
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair); // 根據fair創建對應的鎖
// 條件對象,配合容器能滿足業務
notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); // 出隊條件對象
notFull = lock.newCondition(); // 入隊條件對象
}
/**
* 入隊方法
* 在隊列的尾部插入指定的元素,如果隊列已滿,則等待空間可用
*/
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e); // 檢查put對象是否為空,空拋出異常
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly(); // 若未被中斷嘗試獲取鎖,詳見下文
try {
// 隊列中元素的數量 等于 排隊元素的長度
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await(); // 見下文
enqueue(e); // 元素入隊
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 出隊方法
* 獲取隊列的頭部元素并將其刪除,如果隊列為空,則阻塞并等待元素變為可用
*/
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly(); // 見下文
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await(); // 見下文
return dequeue(); // 元素出隊
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}令當前線程等待,直到收到信號或被中斷詳:與此 Condition 關聯的鎖被自動釋放,進入等待,并且處于休眠狀態,直到發生以下四種情況之一:
①其他線程調用這個Condition的 signal 方法,當前線程恰好被選為要被喚醒的線程;
②其他線程調用這個條件的 signalAll 方法
③其他線程中斷當前線程,支持中斷線程掛起;
④一個“虛假的喚醒”發生了。
在這些情況下,在此方法返回之前,當前線程必須重新獲得與此條件相關聯的鎖。當線程返回時,保證它持有這個鎖。
如果當前線程有以下兩種情況之一:
①在進入該方法時設置中斷狀態;
②在等待時被中斷,支持線程掛起的中斷 拋出InterruptedException
BlockingQueue 可以在線程之間共享而無需任何顯式同步,在生產者消費者之間,只需要將阻塞隊列以參數的形式進行傳遞即可。它內部的機制會自動保證線程的安全性。
生產者:實現了 Runnable 接口,每個生產者生產100種商品和1個中斷標記后完成線程任務
@Slf4j
@Slf4j
public class Producer implements Runnable{
// 作為參數的阻塞隊列
private BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue;
private final int stopTag;
/**
* 構造方法
* @param blockingQueue
* @param stopTag
*/
public Producer(BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue,int stopTag) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
this.stopTag = stopTag;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
generateNumbers();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
private void generateNumbers() throws InterruptedException {
// 每個生產者都隨機生產10種商品
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int product = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000,1100);
log.info("生產者{}號,生產了商品,編號為{}",Thread.currentThread().getId(),product);
blockingQueue.put(product);
}
// 生產終止標記
blockingQueue.put(stopTag);
log.info("生產者{}號,生產了第終止標記編號{}",Thread.currentThread().getId(),Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
}消費者:消費者拿到終止消費標記終止消費,否則消費商品,拿到終止標記后完成線程任務
@Slf4j
public class Consumer implements Runnable{
// 作為參數的阻塞隊列
private BlockingQueue<Integer> queue;
private final int stopTage;
public Consumer(BlockingQueue<Integer> queue, int stopTage) {
this.queue = queue;
this.stopTage = stopTage;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
Integer product = queue.take();
if (product.equals(stopTage)) {
log.info("{}號消費者,停止消費,因為拿到了停止消費標記",Thread.currentThread().getId());
return;
}
log.info("{}號消費者,拿到的商品編號:{}",Thread.currentThread().getId(),product);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}客戶端類: 創建與計算機 CPU 核數相同的線程數,與 16個生產者
public class ProductConsumerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 阻塞隊列容量
int blockingQueueSize = 10;
// 生產者數量
int producerSize = 16;
// 消費者數量 = 計算機線程核數 8
int consumerSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
// 終止消費標記
int stopTag = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(blockingQueueSize);
// 創建16個生產者線程
for (int i = 0; i < producerSize; i++) {
new Thread(new Producer(blockingQueue, stopTag)).start();
}
// 創建8個消費者線程
for (int j = 0; j < consumerSize; j++) {
new Thread(new Consumer(blockingQueue, stopTag)).start();
}
}
}定義: Java 延遲隊列提供了在指定時間才能獲取隊列元素的功能,隊列頭元素是最接近過期的元素。沒有過期元素的話,使用 poll() 方法會返回 null 值,超時判定是通過getDelay(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)方法的返回值小于等于 0 來判斷。延時隊列不能存放空元素。
/**
* 電影票類,實現了Delayed接口,重寫 compareTo 和 getDelay方法
*/
public class MovieTicket implements Delayed {
//延遲時間
private final long delay;
//到期時間
private final long expire;
//數據
private final String msg;
//創建時間
private final long now;
public long getDelay() {
return delay;
}
public long getExpire() {
return expire;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public long getNow() {
return now;
}
/**
* @param msg 消息
* @param delay 延期時間
*/
public MovieTicket(String msg , long delay) {
this.delay = delay;
this.msg = msg;
expire = System.currentTimeMillis() + delay; //到期時間 = 當前時間+延遲時間
now = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* @param msg
*/
public MovieTicket(String msg){
this(msg,1000);
}
public MovieTicket(){
this(null,1000);
}
/**
* 獲得延遲時間 用過期時間-當前時間,時間單位毫秒
* @param unit
* @return
*/
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(this.expire
- System.currentTimeMillis() , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
/**
* 用于延遲隊列內部比較排序 當前時間的延遲時間 - 比較對象的延遲時間
* 越早過期的時間在隊列中越靠前
* @param delayed
* @return
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed delayed) {
return (int) (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
- delayed.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
}測試類:
public static void main(String[] args) {
DelayQueue<MovieTicket> delayQueue = new DelayQueue<MovieTicket>();
MovieTicket ticket = new MovieTicket("電影票1",10000);
delayQueue.put(ticket);
MovieTicket ticket1 = new MovieTicket("電影票2",5000);
delayQueue.put(ticket1);
MovieTicket ticket2 = new MovieTicket("電影票3",8000);
delayQueue.put(ticket2);
log.info("message:--->入隊完畢");
while( delayQueue.size() > 0 ){
try {
ticket = delayQueue.take();
log.info("電影票出隊:{}",ticket.getMsg());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}從運行結果可以看出隊列是延遲出隊,間隔和我們所設置的時間相同
感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“Java阻塞隊列BlockingQueue實例分析”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對Java阻塞隊列BlockingQueue實例分析這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。