您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“elasticsearch節點間通信的transport啟動過程是什么”的相關知識,小編通過實際案例向大家展示操作過程,操作方法簡單快捷,實用性強,希望這篇“elasticsearch節點間通信的transport啟動過程是什么”文章能幫助大家解決問題。
transport顧名思義是集群通信的基本通道,無論是集群狀態信息,還是搜索索引請求信息,都是通過transport傳送。elasticsearch定義了tansport,tansportmessage,tansportchannel,tansportrequest,tansportresponse等所需的所有的基礎接口。這里將以transport為主,分析過程中會附帶介紹其它接口。首先看一下transport節點的定義,如下圖所示:
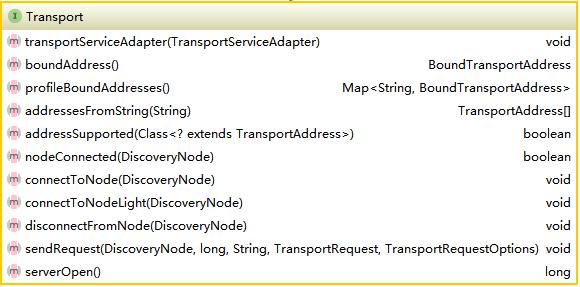
NettyTransport實現了該接口。分析NettyTransport前簡單說一下Netty的用法,Netty的使用需要三個模塊ServerBootStrap,ClientBootStrap(v3.x)及MessageHandler。ServerBootStrap啟動服務器,ClientBootStrap啟動客戶端并連接服務器,MessageHandler是message處理邏輯所在,也就是業務邏輯。其它詳細使用請參考Netty官方文檔。
NettyTransport每個在doStart()方法中啟動serverBootStrap,和ClientBootStrap,并綁定ip,代碼如下所示:
protected void doStart() throws ElasticsearchException {
clientBootstrap = createClientBootstrap();//根據配置啟動客戶端
……//省略了無關分代碼
createServerBootstrap(name, mergedSettings);//啟動server端
bindServerBootstrap(name, mergedSettings);//綁定ip
}每一個節點都需要發送和接收,因此兩者都需要啟動,client和server的啟動分別在相應的方法中,啟動過程就是netty的啟動過程,有興趣可以去看相應方法。bindServerBootstrap(name, mergedSettings)將本地ip和斷開綁定到netty同時設定好export host(export host的具體作業我也看明白也沒有看到相關的綁定,需要進一步研究)。
啟動client及server的過程中將messagehandler注入到channelpipeline中。至此啟動過程完成,但是client并未連接任何server,連接過程是在節點啟動后,才連接到其它節點的。
方法代碼如下所示:
public void connectToNode(DiscoveryNode node, boolean light) {
//transport的模塊必須要啟動
if (!lifecycle.started()) {
throw new ElasticsearchIllegalStateException("can't add nodes to a stopped transport");
}
//獲取讀鎖,每個節點可以和多個節點建立連接,因此這里用讀鎖
globalLock.readLock().lock();
try {
//以node.id為基礎獲取一個鎖,這保證對于每個node只能建立一次連接
connectionLock.acquire(node.id());
try {
if (!lifecycle.started()) {
throw new ElasticsearchIllegalStateException("can't add nodes to a stopped transport");
}
NodeChannels nodeChannels = connectedNodes.get(node);
if (nodeChannels != null) {
return;
}
try {
if (light) {//這里的light,就是對該節點只獲取一個channel,所有類型(5種連接類型下面會說到)都使用者一個channel
nodeChannels = connectToChannelsLight(node);
} else {
nodeChannels = new NodeChannels(new Channel[connectionsPerNodeRecovery], new Channel[connectionsPerNodeBulk], new Channel[connectionsPerNodeReg], new Channel[connectionsPerNodeState], new Channel[connectionsPerNodePing]);
try {
connectToChannels(nodeChannels, node);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.trace("failed to connect to [{}], cleaning dangling connections", e, node);
nodeChannels.close();
throw e;
}
}
// we acquire a connection lock, so no way there is an existing connection
connectedNodes.put(node, nodeChannels);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("connected to node [{}]", node);
}
transportServiceAdapter.raiseNodeConnected(node);
} catch (ConnectTransportException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "general node connection failure", e);
}
} finally {
connectionLock.release(node.id());
}
} finally {
globalLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}如果不是輕連接,每個server和clien之間都有5中連接,著5中連接承擔著不同的任務
protected void connectToChannels(NodeChannels nodeChannels, DiscoveryNode node) {
//五種連接方式,不同的連接方式對應不同的集群操作
ChannelFuture[] connectRecovery = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.recovery.length];
ChannelFuture[] connectBulk = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.bulk.length];
ChannelFuture[] connectReg = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.reg.length];
ChannelFuture[] connectState = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.state.length];
ChannelFuture[] connectPing = new ChannelFuture[nodeChannels.ping.length];
InetSocketAddress address = ((InetSocketTransportAddress) node.address()).address();
//嘗試建立連接
for (int i = 0; i < connectRecovery.length; i++) {
connectRecovery[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectBulk.length; i++) {
connectBulk[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectReg.length; i++) {
connectReg[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectState.length; i++) {
connectState[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectPing.length; i++) {
connectPing[i] = clientBootstrap.connect(address);
}
//獲取每個連接的channel存入到相應的channels中便于后面使用。
try {
for (int i = 0; i < connectRecovery.length; i++) {
connectRecovery[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectRecovery[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectRecovery[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.recovery[i] = connectRecovery[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.recovery[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectBulk.length; i++) {
connectBulk[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectBulk[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectBulk[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.bulk[i] = connectBulk[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.bulk[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectReg.length; i++) {
connectReg[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectReg[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectReg[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.reg[i] = connectReg[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.reg[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectState.length; i++) {
connectState[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectState[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectState[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.state[i] = connectState[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.state[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectPing.length; i++) {
connectPing[i].awaitUninterruptibly((long) (connectTimeout.millis() * 1.5));
if (!connectPing[i].isSuccess()) {
throw new ConnectTransportException(node, "connect_timeout[" + connectTimeout + "]", connectPing[i].getCause());
}
nodeChannels.ping[i] = connectPing[i].getChannel();
nodeChannels.ping[i].getCloseFuture().addListener(new ChannelCloseListener(node));
}
if (nodeChannels.recovery.length == 0) {
if (nodeChannels.bulk.length > 0) {
nodeChannels.recovery = nodeChannels.bulk;
} else {
nodeChannels.recovery = nodeChannels.reg;
}
}
if (nodeChannels.bulk.length == 0) {
nodeChannels.bulk = nodeChannels.reg;
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// clean the futures
for (ChannelFuture future : ImmutableList.<ChannelFuture>builder().add(connectRecovery).add(connectBulk).add(connectReg).add(connectState).add(connectPing).build()) {
future.cancel();
if (future.getChannel() != null && future.getChannel().isOpen()) {
try {
future.getChannel().close();
} catch (Exception e1) {
// ignore
}
}
}
throw e;
}
}關于“elasticsearch節點間通信的transport啟動過程是什么”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識點。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。