您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有關如何正確的使用ArrayList,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結了以下內容,希望大家根據這篇文章可以有所收獲。
ArrayList簡介
ArrayList 是一個數組隊列,相當于 動態數組。與Java中的數組相比,它的容量能動態增長。它繼承于AbstractList,實現了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable這些接口。
ArrayList 繼承了AbstractList,實現了List。它是一個數組隊列,提供了相關的添加、刪除、修改、遍歷等功能。
ArrayList 實現了RandmoAccess接口,即提供了隨機訪問功能。RandmoAccess是java中用來被List實現,為List提供快速訪問功能的。在ArrayList中,我們即可以通過元素的序號快速獲取元素對象;這就是快速隨機訪問。稍后,我們會比較List的“快速隨機訪問”和“通過Iterator迭代器訪問”的效率。
ArrayList 實現了Cloneable接口,即覆蓋了函數clone(),能被克隆。
ArrayList 實現java.io.Serializable接口,這意味著ArrayList支持序列化,能通過序列化去傳輸。和Vector不同,ArrayList中的操作不是線程安全的!所以,建議在單線程中才使用ArrayList,而在多線程中可以選擇Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList。
ArrayList構造函數
// 默認構造函數 ArrayList() // capacity是ArrayList的默認容量大小。當由于增加數據導致容量不足時,容量會添加上一次容量大小的一半。 ArrayList(int capacity) // 創建一個包含collection的ArrayList ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> collection)
ArrayList的API
// Collection中定義的API boolean add(E object) boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) void clear() boolean contains(Object object) boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) boolean equals(Object object) int hashCode() boolean isEmpty() Iterator<E> iterator() boolean remove(Object object) boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) int size() <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) Object[] toArray() // AbstractCollection中定義的API void add(int location, E object) boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection) E get(int location) int indexOf(Object object) int lastIndexOf(Object object) ListIterator<E> listIterator(int location) ListIterator<E> listIterator() E remove(int location) E set(int location, E object) List<E> subList(int start, int end) // ArrayList新增的API Object clone() void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) void trimToSize() void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
第2部分 ArrayList數據結構
ArrayList的繼承關系
java.lang.Object
java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
java.util.AbstractList<E>
java.util.ArrayList<E>
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}ArrayList與Collection關系如下圖:
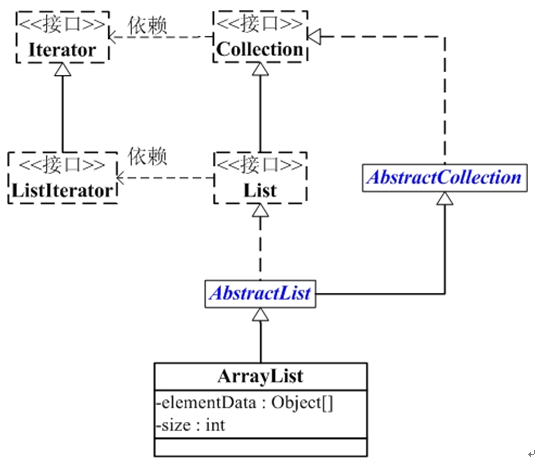
ArrayList包含了兩個重要的對象:elementData 和 size。
(1) elementData 是"Object[]類型的數組",它保存了添加到ArrayList中的元素。實際上,elementData是個動態數組,我們能通過構造函數 ArrayList(int initialCapacity)來執行它的初始容量為initialCapacity;如果通過不含參數的構造函數ArrayList()來創建ArrayList,則elementData的容量默認是10。elementData數組的大小會根據ArrayList容量的增長而動態的增長,具體的增長方式,請參考源碼分析中的ensureCapacity()函數。
(2) size 則是動態數組的實際大小。
第3部分 ArrayList源碼解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
為了更了解ArrayList的原理,下面對ArrayList源碼代碼作出分析。ArrayList是通過數組實現的,源碼比較容易理解。
package java.util;
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
// 序列版本號
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
// 保存ArrayList中數據的數組
private transient Object[] elementData;
// ArrayList中實際數據的數量
private int size;
// ArrayList帶容量大小的構造函數。
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
// 新建一個數組
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
// ArrayList構造函數。默認容量是10。
public ArrayList() {
this();
}
// 創建一個包含collection的ArrayList
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
// 將當前容量值設為 =實際元素個數
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (size < oldCapacity) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
// 確定ArrarList的容量。
// 若ArrayList的容量不足以容納當前的全部元素,設置 新的容量=“(原始容量x3)/2 + 1”
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 將“修改統計數”+1
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 若當前容量不足以容納當前的元素個數,設置 新的容量=“(原始容量x3)/2 + 1”
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object oldData[] = elementData;
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;
if (newCapacity < minCapacity)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
// 添加元素e
public boolean add(E e) {
// 確定ArrayList的容量大小
ensureCapacity(size + ); // Increments modCount!!
// 添加e到ArrayList中
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
// 返回ArrayList的實際大小
public int size() {
return size;
}
// 返回ArrayList是否包含Object(o)
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
// 返回ArrayList是否為空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 正向查找,返回元素的索引值
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 反向查找,返回元素的索引值
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 反向查找(從數組末尾向開始查找),返回元素(o)的索引值
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 返回ArrayList的Object數組
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
// 返回ArrayList的模板數組。所謂模板數組,即可以將T設為任意的數據類型
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// 若數組a的大小 < ArrayList的元素個數;
// 則新建一個T[]數組,數組大小是“ArrayList的元素個數”,并將“ArrayList”全部拷貝到新數組中
if (a.length < size)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass());
// 若數組a的大小 >= ArrayList的元素個數;
// 則將ArrayList的全部元素都拷貝到數組a中。
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
// 獲取index位置的元素值
public E get(int index) {
RangeCheck(index);
return (E) elementData[index];
}
// 設置index位置的值為element
public E set(int index, E element) {
RangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = (E) elementData[index];
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
// 將e添加到ArrayList中
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacity(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
// 將e添加到ArrayList的指定位置
public void add(int index, E element) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);
ensureCapacity(size+1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
// 刪除ArrayList指定位置的元素
public E remove(int index) {
RangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = (E) elementData[index];
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
// 刪除ArrayList的指定元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 快速刪除第index個元素
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
// 從"index+1"開始,用后面的元素替換前面的元素。
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+, elementData, index,
numMoved);
// 將最后一個元素設為null
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
// 刪除元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
// 便利ArrayList,找到“元素o”,則刪除,并返回true。
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 清空ArrayList,將全部的元素設為null
public void clear() {
modCount++;
for (int i = ; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
// 將集合c追加到ArrayList中
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacity(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// 從index位置開始,將集合c添加到ArrayList
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacity(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// 刪除fromIndex到toIndex之間的全部元素。
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved);
// Let gc do its work
int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex);
while (size != newSize)
elementData[--size] = null;
}
private void RangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);
}
// 克隆函數
public Object clone() {
try {
ArrayList<E> v = (ArrayList<E>) super.clone();
// 將當前ArrayList的全部元素拷貝到v中
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError();
}
}
// java.io.Serializable的寫入函數
// 將ArrayList的“容量,所有的元素值”都寫入到輸出流中
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException{
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// 寫入“數組的容量”
s.writeInt(elementData.length);
// 寫入“數組的每一個元素”
for (int i=0; i<size; i++)
s.writeObject(elementData[i]);
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// java.io.Serializable的讀取函數:根據寫入方式讀出
// 先將ArrayList的“容量”讀出,然后將“所有的元素值”讀出
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
// 從輸入流中讀取ArrayList的“容量”
int arrayLength = s.readInt();
Object[] a = elementData = new Object[arrayLength];
// 從輸入流中將“所有的元素值”讀出
for (int i=0; i<size; i++)
a[i] = s.readObject();
}
}總結:
(01) ArrayList 實際上是通過一個數組去保存數據的。當我們構造ArrayList時;若使用默認構造函數,則ArrayList的默認容量大小是10。
(02) 當ArrayList容量不足以容納全部元素時,ArrayList會重新設置容量:新的容量=“(原始容量x3)/2 + 1”。
(03) ArrayList的克隆函數,即是將全部元素克隆到一個數組中。
(04) ArrayList實現java.io.Serializable的方式。當寫入到輸出流時,先寫入“容量”,再依次寫入“每一個元素”;當讀出輸入流時,先讀取“容量”,再依次讀取“每一個元素”。
第4部分 ArrayList遍歷方式
ArrayList支持3種遍歷方式
(01) 第一種,通過迭代器遍歷。即通過Iterator去遍歷。
Integer value = null;
Iterator iter = list.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
value = (Integer)iter.next();
}(02) 第二種,隨機訪問,通過索引值去遍歷。
由于ArrayList實現了RandomAccess接口,它支持通過索引值去隨機訪問元素。
Integer value = null;
int size = list.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
value = (Integer)list.get(i);
}(03) 第三種,for循環遍歷。如下:
Integer value = null;
for (Integer integ:list) {
value = integ;
}由此可見,遍歷ArrayList時,使用隨機訪問(即,通過索引序號訪問)效率最高,而使用迭代器的效率最低!
第5部分 toArray()異常
當我們調用ArrayList中的 toArray(),可能遇到過拋出“java.lang.ClassCastException”異常的情況。下面我們說說這是怎么回事。
ArrayList提供了2個toArray()函數:
Object[] toArray() <T> T[] toArray(T[] contents)
調用 toArray() 函數會拋出“java.lang.ClassCastException”異常,但是調用 toArray(T[] contents) 能正常返回 T[]。
toArray() 會拋出異常是因為 toArray() 返回的是 Object[] 數組,將 Object[] 轉換為其它類型(如如,將Object[]轉換為的Integer[])則會拋出“java.lang.ClassCastException”異常,因為Java不支持向下轉型。具體的可以參考前面ArrayList.java的源碼介紹部分的toArray()。
解決該問題的辦法是調用 <T> T[] toArray(T[] contents) , 而不是 Object[] toArray()。
調用 toArray(T[] contents) 返回T[]的可以通過以下幾種方式實現。
// toArray(T[] contents)調用方式一
public static Integer[] vectorToArray1(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
Integer[] newText = new Integer[v.size()];
v.toArray(newText);
return newText;
}
// toArray(T[] contents)調用方式二。最常用!
public static Integer[] vectorToArray2(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
Integer[] newText = (Integer[])v.toArray(new Integer[0]);
return newText;
}
// toArray(T[] contents)調用方式三
public static Integer[] vectorToArray3(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
Integer[] newText = new Integer[v.size()];
Integer[] newStrings = (Integer[])v.toArray(newText);
return newStrings;
}第6部分 ArrayList示例
本文通過一個實例(ArrayListTest.java),介紹 ArrayList 中常用API的用法。
import java.util.*;
/*
* @desc ArrayList常用API的測試程序
*
*
*/
public class ArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 創建ArrayList
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
// 將“”
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
list.add("4");
// 將下面的元素添加到第1個位置 list.add(0, "5");
// 獲取第1個元素
System.out.println("the first element is: "+ list.get(0));
// 刪除“3”
list.remove("3");
// 獲取ArrayList的大小
System.out.println("Arraylist size=: "+ list.size());
// 判斷list中是否包含"3"
System.out.println("ArrayList contains 3 is: "+ list.contains(3));
// 設置第2個元素為10
list.set(1, "10");
// 通過Iterator遍歷ArrayList
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
System.out.println("next is: "+ iter.next());
}
// 將ArrayList轉換為數組
String[] arr = (String[])list.toArray(new String[]);
for (String str:arr)
System.out.println("str: "+ str);
// 清空ArrayList
list.clear();
// 判斷ArrayList是否為空
System.out.println("ArrayList is empty: "+ list.isEmpty());
}
}運行結果:
the first element is: 5 Arraylist size=: 4 ArrayList contains 3 is: false next is: 5 next is: 10 next is: 2 next is: 4 str: 5 str: 10 str: 2 str: 4 ArrayList is empty: true
看完上述內容,你們對如何正確的使用ArrayList有進一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識或者相關內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。