溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
在Tensorflow卷積神經網絡實例這篇博客中,我們實現了一個簡單的卷積神經網絡,沒有復雜的Trick。接下來,我們將使用CIFAR-10數據集進行訓練。
CIFAR-10是一個經典的數據集,包含60000張32*32的彩色圖像,其中訓練集50000張,測試集10000張。CIFAR-10如同其名字,一共標注為10類,每一類圖片6000張。
本文實現了進階的卷積神經網絡來解決CIFAR-10分類問題,我們使用了一些新的技巧:
首先需要下載Tensorflow models Tensorflow models,以便使用其中的CIFAR-10數據的類.進入目錄models/tutorials/image/cifar10目錄,執行以下代碼
import cifar10
import cifar10_input
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import time
# 定義batch_size, 訓練輪數max_steps, 以及下載CIFAR-10數據的默認路徑
max_steps = 3000
batch_size = 128
data_dir = 'E:\\tmp\cifar10_data\cifar-10-batches-bin'
# 定義初始化weight的函數,定義的同時,對weight加一個L2 loss,放在集'losses'中
def variable_with_weight_loss(shape, stddev, w1):
var = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=stddev))
if w1 is not None:
weight_loss = tf.multiply(tf.nn.l2_loss(var), w1, name='weight_loss')
tf.add_to_collection('losses', weight_loss)
return var
# 使用cifar10類下載數據集,并解壓、展開到其默認位置
#cifar10.maybe_download_and_extract()
# 在使用cifar10_input類中的distorted_inputs函數產生訓練需要使用的數據。需要注意的是,返回的是已經封裝好的tensor,
# 且對數據進行了Data Augmentation(水平翻轉、隨機剪切、設置隨機亮度和對比度、對數據進行標準化)
images_train, labels_train = cifar10_input.distorted_inputs(data_dir=data_dir, batch_size=batch_size)
# 再使用cifar10_input.inputs函數生成測試數據,這里不需要進行太多處理
images_test, labels_test = cifar10_input.inputs(eval_data=True,
data_dir=data_dir,
batch_size=batch_size)
# 創建數據的placeholder
image_holder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 24, 24, 3])
label_holder = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size])
# 創建第一個卷積層
weight1 = variable_with_weight_loss(shape=[5, 5, 3, 64], stddev=5e-2,
w1=0.0)
kernel1 = tf.nn.conv2d(image_holder, weight1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
bias1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64]))
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(kernel1, bias1))
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME')
# LRN層對ReLU會比較有用,但不適合Sigmoid這種有固定邊界并且能抑制過大值的激活函數
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75)
# 創建第二個卷積層
weight2 = variable_with_weight_loss(shape=[5, 5, 64, 64], stddev=5e-2,
w1=0.0)
kernel2 = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, weight2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
bias2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[64]))
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(kernel2, bias2))
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75)
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME')
# 使用一個全連接層
reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, [batch_size, -1])
dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value
weight3 = variable_with_weight_loss(shape=[dim, 384], stddev=0.04, w1=0.004)
bias3 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[384]))
local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weight3) + bias3)
# 再使用一個全連接層,隱含節點數下降了一半,只有192個,其他的超參數保持不變
weight4 = variable_with_weight_loss(shape=[384, 192], stddev=0.04, w1=0.004)
bias4 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[192]))
local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weight4) + bias4)
# 最后一層,將softmax放在了計算loss部分
weight5 = variable_with_weight_loss(shape=[192, 10], stddev=1 / 192.0, w1=0.0)
bias5 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[10]))
logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weight5), bias5)
# 定義loss
def loss(logits, labels):
labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.int64)
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=labels,
name='cross_entropy_per_example')
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='cross_entropy')
tf.add_to_collection('losses', cross_entropy_mean)
return tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses'), name='total_loss')
# 獲取最終的loss
loss = loss(logits, label_holder)
# 優化器
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-3).minimize(loss)
# 使用tf.nn.in_top_k函數求輸出結果中top k的準確率,默認使用top 1,也就是輸出分數最高的那一類的準確率
top_k_op = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, label_holder, 1)
# 使用tf.InteractiveSession創建默認的session,接著初始化全部模型參數
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
# 啟動圖片數據增強線程
tf.train.start_queue_runners()
# 正式開始訓練
for step in range(max_steps):
start_time = time.time()
image_batch, label_batch = sess.run([images_train, labels_train])
_, loss_value = sess.run([train_op, loss], feed_dict={image_holder: image_batch, label_holder: label_batch})
duration = time.time() - start_time
if step % 10 == 0:
example_per_sec = batch_size / duration
sec_per_batch = float(duration)
format_str = 'step %d, loss=%.2f ,%.1f examples/sec, %.3f sec/batch'
print(format_str % (step, loss_value, example_per_sec, sec_per_batch))
num_examples = 10000
import math
num_iter = int(math.ceil(num_examples / batch_size))
true_count = 0
total_sample_count = num_iter * batch_size
step = 0
while step < num_iter:
image_batch, label_batch = sess.run([images_test, labels_test])
predictions = sess.run([top_k_op], feed_dict={image_holder: image_batch, label_holder: label_holder})
true_count += np.sum(predictions)
step += 1
precision = true_count / total_sample_count
print('precision @ 1 = %.3f'%precision)
運行結果:
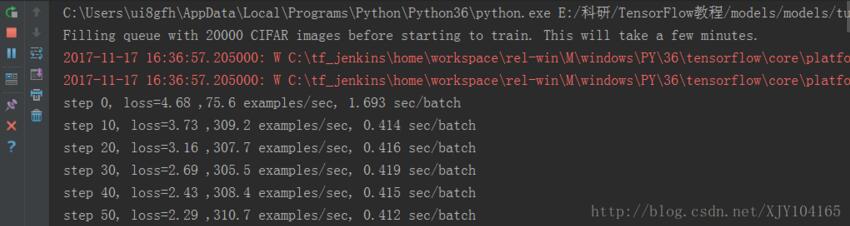
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。