您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
講這個之前,先來看一個例子:
void Test1 ()
{
int* p1 = new int(2);
//...
try
{
DoSomeThing();
}
catch(...)
{
delete p1 ;
throw;
}
//...
delete p1 ;
}這個例子,是通過C++異常處理機制,來管理動態開辟出來的內存,這是可以做到的。但是以后在開發軟件產品時,需要開辟動態內存,你都這樣處理,就顯得非常繁瑣,代碼量也會加大,有時候邏輯會理不清楚,于是有人提出能不能將“動態內存擁有權”這個問題的復雜性,從軟件產品本身的復雜性中分離出來,由專門的人或團隊來負責實現,實際上是非常有利于軟件的模塊化和復用性的。畢竟,從本質上來看,動態內存的擁有權和一款軟件產品本身所要解決的目標問題在相當大程度上是正交的,將其分解開來,分而治之從軟件工程學的角度來看實在是個不錯的選擇。也顯得非常繁瑣,那C++為了處理這個問題,提出了一個叫RAII(Resource Acquisition Is Initialization)。
RAII:資源分配即初始化,定義一個類來封裝資源的分配和釋放,在構造函數完成資源的分配和初始化,在析構函數完成資源的清理,可以保證資源的正確初始化和釋放。這個類具體到下面的智能指針。
智能指針:所謂智能指針就是智能\自動化管理動態開辟內存的釋放。
智能指針設計思想:首先提供一個類,然后用這個類去封裝原生指針,并且封裝類會提供客戶端代碼通常會施加在原生指針上的絕大多數操作接口。這樣,在保證跟原生指針相近的操作體驗的同時,簡化了動態內存的管理負擔。
在C++11之前,標準庫中,只有一個auto_ptr,下面是模擬實現auto_ptr舊版本.
/*舊版本*/
/*實現原理:通過擁有者的改變來最后確定是否析構對象*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class AutoPtr
{
public:
AutoPtr(T* ptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
{
_owner = true;
}
AutoPtr(AutoPtr<T>& ap)
:_ptr(ap._ptr),_owner(ap._owner)
{
ap._owner = false;
}
AutoPtr<T>& operator=(AutoPtr<T>& ap)
{
if(this != &ap)
{
if(_owner)
{
delete _ptr;
}
_ptr = ap._ptr;
_owner = ap._owner;
if(ap._owner)
{
ap._owner = false;
}
}
return *this;
}
~AutoPtr()
{
if(_owner)
{
delete _ptr;
}
}
public:
T& operator*()
{
return *_str;
}
T* operator ->()
{
return _str;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
bool _owner;
};
void Test1()
{
AutoPtr<int> ap1(new int(1));
AutoPtr<int> ap2(ap1);
AutoPtr<int> ap3(new int(3));
ap3 = ap2;
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}顯示結果:
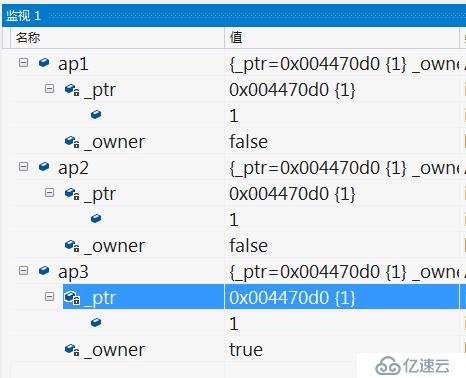
這樣看結果是對的,但是看下面這個Test2()
void Test2()
{
AutoPtr<int> ap1(new int(1));
AutoPtr<int> ap2(ap1);
AutoPtr<int> ap3(new int(3));
AutoPtr<int> ap4(ap3);
ap4 = ap1;
}顯示結果:
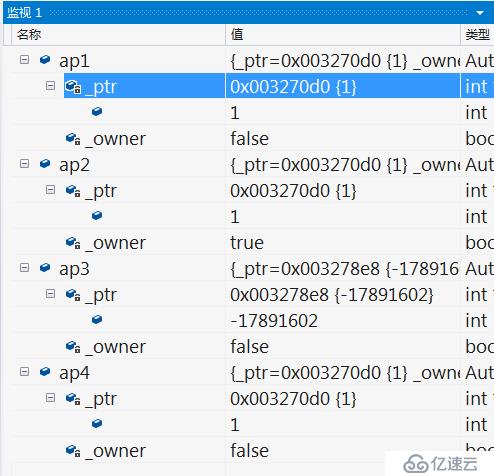
看上面就出現問題了,你把ap1 賦給 ap4 ,但是ap4的_owner 是 false ,這就是有問題的。到最后,ap4只是指向共有的那塊空間而已,沒有達到真正的管理,再看Test3()
void Test3()
{
AutoPtr<int> ap1(new int(1));
if(1)
{
AutoPtr<int> ap2(ap1);
}
*ap1 = 10;
}顯示結果:
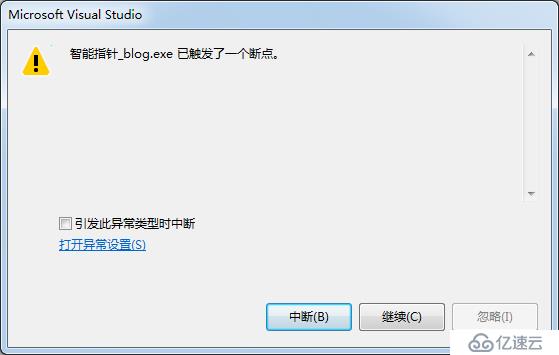
程序直接崩潰了,因為產生了野指針的訪問,訪問的那一塊空間已經釋放了,所以就會崩潰了,正是由于舊版本有這諸多的問題,C++改進了一下他,使他變得很“強大”,下來看模擬實現:
/*新版本*/
/*實現原理:管理權的轉交*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class AutoPtr
{
public:
AutoPtr(T* str)
:_str(str)
{}
AutoPtr(AutoPtr<T>& ap)
:_str(ap._str)
{
ap._str = NULL;
}
AutoPtr<T>& operator=(AutoPtr<T>& ap)
{
if(this != &ap)
{
delete _str;
_str = ap._str;
ap._str = NULL;
}
return *this;
}
~AutoPtr()
{
if(_str)
delete _str;
}
public:
T& operator*()
{
return *_str;
}
T* operator ->()
{
return _str;
}
private:
T* _str;
};
struct A
{
int _a;
};
void Test4()
{
AutoPtr<int>ap(new int(1));
AutoPtr<int>ap2(ap);
AutoPtr<int>ap3(new int(2));
AutoPtr<int>ap4(ap3);
ap4 = ap;
}
int main()
{
Test4();
return 0;
}顯示結果:
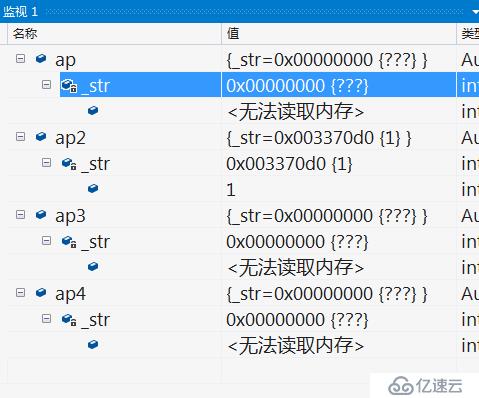
當然這個結果是正確的,但是你要這個AutoPtr又有什么用,你用對象之間拷貝構造新對象和對象之間相互賦值時,就是為了讓他們共同管理,但是現在,這就有點low了,既沒有達到那種共同管理,也在拷貝構造對象和相互賦值時,不清不楚,那么他就相當low。一些C++技術大牛,在開源庫函數boost庫(可移植的函數庫)中引出了新的智能指針,受到廣大編程愛好者的一致好評。于是在C++11標準引出了新的智能指針,unique_ptr,shared_ptr,weak_ptr。
模擬實現unique_ptr:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class UniquePtr
{
public:
UniquePtr(T* ptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
{}
~UniquePtr()
{
if(_ptr != NULL)
{
delete _ptr;
}
}
protected:
UniquePtr(UniquePtr<T>& up);
UniquePtr<T> operator=(UniquePtr<T>& up);
public:
T* operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T& operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
};
void Test1()
{
UniquePtr<int> up1(new int(1));
UniquePtr<int> up2(new int(2));
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}顯示結果:
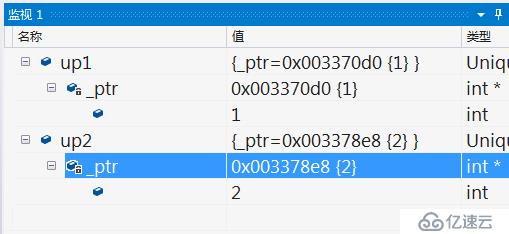
沒毛病,下來看test2():
void test2()
{
UniquePtr<int> up1(new int(1));
UniquePtr<int> up2(new int(2));
up2 = up1;
UniquePtr<int> up3(up1);
}顯示結果:
 在編譯的時候出現了問題,這是為什么呢?
在編譯的時候出現了問題,這是為什么呢?
protected: UniquePtr(UniquePtr<T>& up); UniquePtr<T> operator=(UniquePtr<T>& up);
由于在類中只聲名拷貝構造函數和賦值運算符重載,不實現,防止調用默認的拷貝構造函數和賦值運算符重載造成淺拷貝的問題,加上保護限制,防止在被繼承時,對其進行重寫。避免了auto_ptr出現的問題,我unique_ptr就是不讓被復制和賦值,他是一種防拷貝(你就是霸道)的實現,沒有像auto_ptr那樣轉移管理權,直接就是我的就是我的,你們其他人邊去,但是我們也想要實現向原生指針那樣共同管理,那就可以shared_ptr,模擬實現shared_ptr:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class SharedPtr
{
public:
SharedPtr(T* ptr)
:_ptr(ptr),_pcount(new int(1))
{
cout<<"SharedPtr(T* ptr)"<<endl;
}
~SharedPtr()
{
cout<<"~SharedPtr()"<<endl;
_Release();
}
SharedPtr(SharedPtr<T>& sp)
:_ptr(sp._ptr),_pcount(sp._pcount)
{
cout<<"SharedPtr(SharedPtr<T>& sp)"<<endl;
++(*_pcount);
}
SharedPtr<T>& operator= (SharedPtr<T> sp)//傳值,賦值前調用拷貝構造函數
{
cout<<"SharedPtr<T>& operator="<<endl;
swap(_ptr, sp._ptr);
swap(_pcount, sp._pcount);
return *this;
}
public:
/*接口函數*/
T& operator*()//提供*接口
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()//提供->接口
{
return _ptr;
}
public:
int UseCount()
{
return *_pcount;
}
T* GetPtr()
{
return _ptr;
}
protected:
void _Release()
{
if(--(*_pcount) == 0)
{
delete _ptr;
delete _pcount;
}
}
private:
T* _ptr;
int* _pcount;
};
int main()
{
SharedPtr<int> sp(new int(1));
SharedPtr<int> sp1(sp);
SharedPtr<int> sp2(new int(2));
SharedPtr<int> sp3(new int(3));
sp3 = sp2;
int count = sp2.UseCount();
return 0;
}顯示結果:
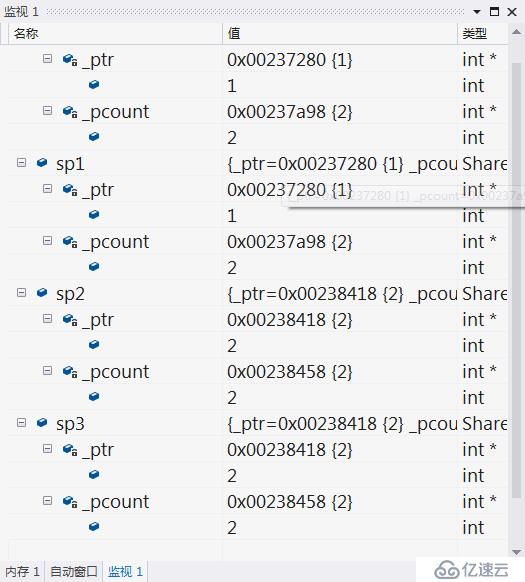
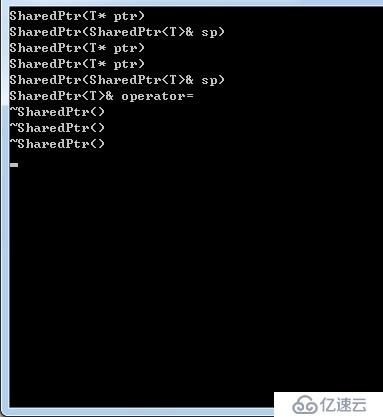
第一次構造函數:
SharedPtr<int> sp(new int(1));
第一次拷貝構造函數:
SharedPtr<int> sp1(sp);
第二次,第三次構造函數:
SharedPtr<int> sp2(new int(2)); SharedPtr<int> sp3(new int(3));
第二次拷貝構造函數,第一次賦值:
sp3 = sp2;
因為賦值時,采用傳值方式,所以調用拷貝構造函數。
第一次析構函數,析構臨時拷貝構造出來的臨時對象。
第二次析構函數,析構sp3,sp2(是共同管理一塊內存的)。
第三次析構函數,析構sp,sp1(是共同管理一塊內存的)。
 完美...
完美...
是不是新的智能指針完美的解決auto_ptr的問題呢,對,是的。所以在以后需要使用智能指針的時候,不要用auto_ptr,因為他們完美的詮釋原生指針,當不需要復制,賦值時,應該首選unique_ptr,需要復制和賦值就需要選擇shared_ptr.
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。