您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
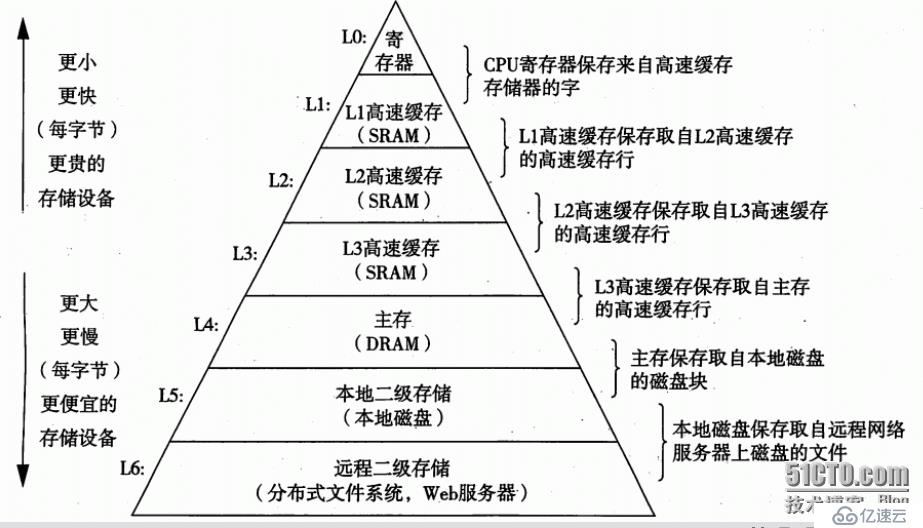
棧的管理可以用運鏈表,當然啦也可以用運數組,相比鏈表而數組管理起來更加方便,為什么呢???請睜大眼睛看下邊博主大人的總結 數組管理棧的優點: (1)插入刪除方便,數組直接將++_top或者--_top即可,而鏈表還要刪除節點置空指針,麻煩死啦; (2)效率高呀,數組一次能夠new T [_capacity]省事,而鏈表邊用邊new; (3)其實這里還牽扯到一個cpu的高速緩存利用率
static and queue.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class stack
{
public:
stack()
:_a(0)
,_top(0)
,_capacity(0)
{}
//剛開始寫這個函數的時候很傻比,哎,下次一定銘記
stack(const stack <T>& s)
:_a(new T[s._capacity])
,_top(s._top)
,_capacity(s._capacity)
{
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<s._top;i++)
{
_a[i]=s._a[i];
}
}
stack<T>& operator=(const stack<T>& s)
{
if(this!=&s)
{
delete [] _a;
_a=new T [s._capacity*sizeof(T)];
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<_top;i++)
{
a[i]=s._a[i];
}
_top=s._top;
_capacity=s._capacity;
}
return *this;
}
~stack()
{
if(_a!=NULL)
{
delete [] _a;
_a=NULL;
}
}
//棧擴容函數
void _checkcapacity()
{
//不能用realloc開辟因為它不會調用構造和析構函數
if(_top==_capacity)
{
_capacity=_capacity*2+3;
T* tmp=new T [_capacity];
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<_top;i++)
{
tmp[i]=_a[i];
}
delete [] _a;
_a=tmp;
}
}
void push(const T& x);
void pop();
T& top();
bool empty();
size_t size();
void print();
protected:
T * _a;
size_t _top;
size_t _capacity;
};
static and queue.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"stack and queue.h"
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void stack<T>::print()
{
while(!empty())
{
cout<<_top<<" ";
pop();
}
cout<<"over"<<endl;;
}
template<class T>
void stack<T>::push(const T& x)
{
_checkcapacity();
_a[_top++]=x;
}
template<class T>
void stack<T>::pop()
{
if(_top>0)
{
--_top;
}
}
template<class T>
T& stack<T>::top()
{
if(!empty())
{
return _a[_top-1];
}
}
template<class T>
bool stack<T>::empty()
{
return (_top==0);
}
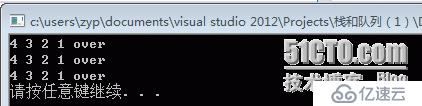
void TestStack()
{
stack<int> s1;
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);
stack<int> s2(s1);
stack<int> s3=s2;
s1.print();
s2.print();
s3.print();
/*cout<<s.top()<<endl;*/
}
int main()
{
TestStack();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。