溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
1、連通圖和非連通圖
連通圖:任意的一個頂點到任意的另外一個頂點都有著相應的路徑所能夠到達。
非連通圖:只要找出了有一個頂點不能夠到達另外一個頂點。
2、遍歷
對于連通圖來說,通過DFS或BFS就可以完成遍歷;
對于非連通圖來說,就得從每個頂點出發進行搜索,每一次的從一個新的頂點出發訪問,每個頂點都要開始搜索一遍。
3、非連通圖的遍歷算法
(1)、不可取的算法:沒有必要將非連通圖生成森林,在由森林生成我們的遍歷樹,然后再進行樹形結構的訪問。
(2)、比較好的算法:直接調動我們之前編寫好的DFS()函數;只要沒有訪問的頂點,我們就由該頂點出發進行深度優先遍歷,這樣就最終把整個非連通圖就遍歷完成。
(3)強連通圖:針對有向圖,有A-->B的邊,一定也有B-->A的邊。
(4)、遍歷算法:
void components(){ //非連通圖的遍歷
int n = Graph<Type>::getCurVertex();
bool *visit = new bool[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
visit[i] = false;
}
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){ //對每個頂點都看一下,是否訪問過。4
if(!visit[i]){
DFS(getValue(i), visit);
}
}
delete []visit;
}4、完整代碼、測試代碼、測試結果
(1)、完整代碼
#ifndef _GRAPH_H_
#define _GRAPH_H_
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE 20
template<typename Type>
class Graph{
public:
bool isEmpty()const{
return curVertices == 0;
}
bool isFull()const{
if(curVertices >= maxVertices || curEdges >= curVertices*(curVertices-1)/2)
return true; //圖滿有2種情況:(1)、當前頂點數超過了最大頂點數,存放頂點的空間已滿
return false; //(2)、當前頂點數并沒有滿,但是當前頂點所能達到的邊數已滿
}
int getCurVertex()const{
return curVertices;
}
int getCurEdge()const{
return curEdges;
}
public:
virtual bool insertVertex(const Type &v) = 0; //插入頂點
virtual bool insertEdge(const Type &v1, const Type &v2) = 0; //插入邊
virtual bool removeVertex(const Type &v) = 0; //刪除頂點
virtual bool removeEdge(const Type &v1, const Type &v2) = 0; //刪除邊
virtual int getFirstNeighbor(const Type &v) = 0; //得到第一個相鄰頂點
virtual int getNextNeighbor(const Type &v, const Type &w) = 0; //得到下一個相鄰頂點
public:
virtual int getVertexIndex(const Type &v)const = 0; //得到頂點下標
virtual void showGraph()const = 0; //顯示圖
virtual Type getValue(int index)const = 0;
public:
virtual void DFS(const Type &v) = 0; //深度優先
virtual void BFS(const Type &v) = 0; //廣度優先
protected:
int maxVertices; //最大頂點數
int curVertices; //當前頂點數
int curEdges; //當前邊數
};
template<typename Type>
class GraphMtx : public Graph<Type>{ //鄰接矩陣繼承父類矩陣
#define maxVertices Graph<Type>::maxVertices //因為是模板,所以用父類的數據或方法都得加上作用域限定符
#define curVertices Graph<Type>::curVertices
#define curEdges Graph<Type>::curEdges
public:
GraphMtx(int vertexSize = VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE){ //初始化鄰接矩陣
maxVertices = vertexSize > VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE ? vertexSize : VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE;
vertexList = new Type[maxVertices]; //申請頂點空間
for(int i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //都初始化為0
vertexList[i] = 0;
}
edge = new int*[maxVertices]; //申請邊的行
for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //申請列空間
edge[i] = new int[maxVertices];
}
for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //賦初值為0
for(int j = 0; j < maxVertices; j++){
edge[i][j] = 0;
}
}
curVertices = curEdges = 0; //當前頂點和當前邊數
}
GraphMtx(Type (*mt)[4], int sz){ //通過已有矩陣的初始化
int e = 0; //統計邊數
maxVertices = sz > VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE ? sz : VERTEX_DEFAULT_SIZE;
vertexList = new Type[maxVertices]; //申請頂點空間
for(int i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //都初始化為0
vertexList[i] = 0;
}
edge = new int*[maxVertices]; //申請邊的行
for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //申請列空間
edge[i] = new Type[maxVertices];
}
for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++){ //賦初值為矩陣當中的值
for(int j = 0; j < maxVertices; j++){
edge[i][j] = mt[i][j];
if(edge[i][j] != 0){
e++; //統計列的邊數
}
}
}
curVertices = sz;
curEdges = e/2;
}
~GraphMtx(){}
public:
bool insertVertex(const Type &v){
if(curVertices >= maxVertices){
return false;
}
vertexList[curVertices++] = v;
return true;
}
bool insertEdge(const Type &v1, const Type &v2){
int maxEdges = curVertices*(curVertices-1)/2;
if(curEdges >= maxEdges){
return false;
}
int v = getVertexIndex(v1);
int w = getVertexIndex(v2);
if(v==-1 || w==-1){
cout<<"edge no exit"<<endl; //要插入的頂點不存在,無法插入
return false;
}
if(edge[v][w] != 0){ //當前邊已經存在,不能進行插入
return false;
}
edge[v][w] = edge[w][v] = 1; //因為是無向圖,對稱的,存在邊賦為1;
return true;
} //刪除頂點的高效方法
bool removeVertex(const Type &v){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
if(i == -1){
return false;
}
vertexList[i] = vertexList[curVertices-1];
int edgeCount = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < curVertices; k++){
if(edge[i][k] != 0){ //統計刪除那行的邊數
edgeCount++;
}
}
//刪除行
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; j++){
edge[i][j] = edge[curVertices-1][j];
}
//刪除列
for(j = 0; j < curVertices; j++){
edge[j][i] = edge[j][curVertices-1];
}
curVertices--;
curEdges -= edgeCount;
return true;
}
/* //刪除頂點用的是數組一個一個移動的方法,效率太低。
bool removeVertex(const Type &v){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
if(i == -1){
return false;
}
for(int k = i; k < curVertices-1; ++k){
vertexList[k] = vertexList[k+1];
}
int edgeCount = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; ++j){
if(edge[i][j] != 0)
edgeCount++;
}
for(int k = i; k < curVertices-1; ++k)
{
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; ++j)
{
edge[k][j] = edge[k+1][j];
}
}
for(int k = i; k < curVertices-1; ++k)
{
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; ++j)
{
edge[j][k] = edge[j][k+1];
}
}
curVertices--;
curEdges -= edgeCount;
return true;
}
*/
bool removeEdge(const Type &v1, const Type &v2){
int v = getVertexIndex(v1);
int w = getVertexIndex(v2);
if(v==-1 || w==-1){ //判斷要刪除的邊是否在當前頂點內
return false; //頂點不存在
}
if(edge[v][w] == 0){ //這個邊根本不存在,沒有必要刪
return false;
}
edge[v][w] = edge[w][v] = 0; //刪除這個邊賦值為0,代表不存在;
curEdges--;
return true;
}
int getFirstNeighbor(const Type &v){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
if(i == -1){
return -1;
}
for(int col = 0; col < curVertices; col++){
if(edge[i][col] != 0){
return col;
}
}
return -1;
}
int getNextNeighbor(const Type &v, const Type &w){
int i = getVertexIndex(v);
int j = getVertexIndex(w);
if(i==-1 || j==-1){
return -1;
}
for(int col = j+1; col < curVertices; col++){
if(edge[i][col] != 0){
return col;
}
}
return -1;
}
public:
void showGraph()const{
if(curVertices == 0){
cout<<"Nul Graph"<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < curVertices; i++){
cout<<vertexList[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
for(i = 0; i < curVertices; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < curVertices; j++){
cout<<edge[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<vertexList[i]<<endl;
}
}
int getVertexIndex(const Type &v)const{
for(int i = 0; i < curVertices; i++){
if(vertexList[i] == v){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public:
Type getValue(int index)const{
return vertexList[index];
}
void DFS(const Type &v){
int n = Graph<Type>::getCurVertex();
bool *visit = new bool[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
visit[i] = false;
}
DFS(v, visit);
delete []visit;
}
void BFS(const Type &v){
int n = Graph<Type>::getCurVertex();
bool *visit = new bool[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
visit[i] = false;
}
cout<<v<<"-->";
int index = getVertexIndex(v);
visit[index] = true;
queue<int> q; //隊列中存放的是頂點下標;
q.push(index);
int w;
while(!q.empty()){
index = q.front();
q.pop();
w = getFirstNeighbor(getValue(index));
while(w != -1){
if(!visit[w]){
cout<<getValue(w)<<"-->";
visit[w] = true;
q.push(w);
}
w = getNextNeighbor(getValue(index), getValue(w));
}
}
delete []visit;
}
void components(){ //非連通圖的遍歷
int n = Graph<Type>::getCurVertex();
bool *visit = new bool[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
visit[i] = false;
}
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(!visit[i]){
DFS(getValue(i), visit);
}
}
delete []visit;
}
protected:
void DFS(const Type &v, bool *visit){
cout<<v<<"-->";
int index = getVertexIndex(v);
visit[index] = true;
int w = getFirstNeighbor(v);
while(w != -1){
if(!visit[w]){
DFS(getValue(w), visit);
}
w = getNextNeighbor(v, getValue(w));
}
}
private:
Type *vertexList; //存放頂點的數組
int **edge; //存放邊關系的矩陣
};
#endif(2)、測試代碼
#include"Graph3.h"
int main(void){
GraphMtx<char> gm;
gm.insertVertex('A');
gm.insertVertex('B');
gm.insertVertex('C'); //B的第一個鄰接頂點是C,
gm.insertVertex('D');
gm.insertVertex('E');
gm.insertVertex('F');
gm.insertVertex('G');
gm.insertVertex('H');
gm.insertVertex('I');
gm.insertVertex('J');
gm.insertVertex('K');
gm.insertVertex('L');
gm.insertVertex('M');
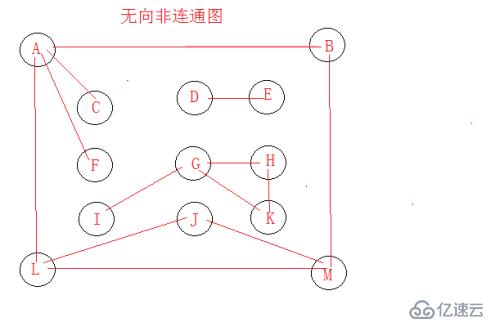
gm.insertEdge('A','B');
gm.insertEdge('A','C');
gm.insertEdge('A','F');
gm.insertEdge('A','L');
gm.insertEdge('B','M');
gm.insertEdge('L','J');
gm.insertEdge('L','M');
gm.insertEdge('J','M');
gm.insertEdge('D','E');
gm.insertEdge('G','H');
gm.insertEdge('G','I');
gm.insertEdge('G','K');
gm.insertEdge('H','K');
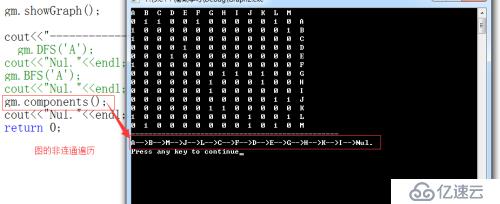
gm.showGraph();
cout<<"------------------------------------------------"<<endl;
gm.DFS('A');
cout<<"Nul."<<endl;
gm.BFS('A');
cout<<"Nul."<<endl;
gm.components();
cout<<"Nul."<<endl;
return 0;
}(3)、測試結果
測試圖的模型:
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。