您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了Behavior怎么實現復雜的視覺聯動效果的相關知識,內容詳細易懂,操作簡單快捷,具有一定借鑒價值,相信大家閱讀完這篇Behavior怎么實現復雜的視覺聯動效果文章都會有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看吧。
Behavior 是谷歌 Material 設計中重要的一員,用來實現復雜的視覺聯動效果。
使用 Behavior 的控件需要被包裹在 CoordinateLayout 內部。Behavior 就是一個接口。Behavior 實際上就是通過將 CoordinateLayout 的布局和觸摸事件傳遞給 Behavior 來實現的。
從設計模式上講,就一個 Behavior 而言,它是一種訪問者模式,相當于將 CoordinateLayout 的布局和觸摸過程對外提供的訪問器;而多個 Behavior 在 CoordinateLayout 內部的事件分發則是一種責任鏈機制,呈現出長幼有序的狀態。
以 layout 過程為例,
// androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout#onLayout
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
final int layoutDirection = ViewCompat.getLayoutDirection(this);
final int childCount = mDependencySortedChildren.size();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View child = mDependencySortedChildren.get(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE) {
continue;
}
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final Behavior behavior = lp.getBehavior();
// 這里
if (behavior == null || !behavior.onLayoutChild(this, child, layoutDirection)) {
onLayoutChild(child, layoutDirection);
}
}
}可見 Behavior 就是將子控件的布局通過 onLayoutChild() 方法對外回調了出來。控件的 behavior 優先攔截和處理 layout 事件。
那 Behavior 相比于我們直接覆寫觸摸事件的形式處理手勢有什么優點呢?
其優點在于,我們可以將頁面的布局、觸摸和滑動等事件封裝到 Behavior 接口的實現類中以達到交互邏輯的復用和解耦的目的。
Behavior 接口定義了許多方法,用于將 CoordinateLayout 的布局、測量和事件分發事件向外傳遞。這里我根據其作用將其歸納為以下幾組。
首先是 Behavior 和 LayoutParams 關聯和接觸綁定時回調的方法。它們被回調的世紀分別是,
onAttachedToLayoutParams:LayoutParams 的構造函數中回調
onDetachedFromLayoutParams:調用 LayoutParams 的 setBehavior,用一個新的 Behavior 覆蓋舊的 Behavior 時回調
public void onAttachedToLayoutParams(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams params) {}
public void onDetachedFromLayoutParams() {}然后是跟 scrim color 相關的方法,這些方法會在 CoordinateLayout 的繪制過程中被調用。主要是跟繪制相關的,即用來對指定的 child 進行著色。
這里的 child 是指該 Behavior 所關聯的控件,parent 就是指包裹這個 child 的最外層的 CoordinatorLayout. 后面的方法都是如此。
public int getScrimColor(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child) public float getScrimOpacity(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child) public boolean blocksInteractionBelow(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child)
然后一組方法是用來將 CoordinatorLayout 的測量和布局過程對外回調。不論是測量還是布局的回調方法,優先級都是回調方法優先。也就是回調方法可以通過返回 true 攔截 CoordinatorLayout 的邏輯。
另外,CoordinatorLayout 里使用 Behavior 的時候只會從直系子控件上讀取,所以,子控件的子控件上即便有 Behavior 也不會被攔截處理。所以,在一般使用 CoordinatorLayout 的時候,如果我們需要在某個控件上使用 Behavior,都是將其作為 CoordinatorLayout 的直系子控件。
還要注意,一個 CoordinatorLayout 的直系子控件包含多個 Behavior 的時候,這些 Behavior 被回調的先后順序和它們在 CoordinatorLayout 里布局的先后順序一致。也就是說,排序在前的子控件優先攔截和處理事件。這和中國古代的王位繼承制差不多。
public boolean onMeasureChild(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed, int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) public boolean onLayoutChild(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, int layoutDirection)
接下來的一組方法用來描述子控件之間的依賴關系。它的作用原理是,當 CoordinatorLayout 發生以下三類事件
NestedScroll 滾動事件,通過 onNestedScroll() 獲取(后面會分析這個事件工作原理)
PreDraw 事件,通過 ViewTreeObserver.OnPreDrawListener 獲取到該事件
控件被移除事件,通過 OnHierarchyChangeListener 獲取到該事件
的時候會使用 layoutDependsOn() 方法,針對 CoordinatorLayout 的每個子控件,判斷其他子控件與其是否構成依賴關系。如果構成了依賴關系,就回調其對應的 Behavior 的 onDependentViewChanged() 或者 onDependentViewRemoved() 方法。
public boolean layoutDependsOn(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View dependency) public boolean onDependentViewChanged(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View dependency) public void onDependentViewRemoved(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View dependency)
然后是與窗口變化和狀態保存與恢復相關的事件。
public WindowInsetsCompat onApplyWindowInsets(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull WindowInsetsCompat insets) public boolean onRequestChildRectangleOnScreen(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull Rect rectangle, boolean immediate) public void onRestoreInstanceState(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull Parcelable state) public Parcelable onSaveInstanceState(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child) public boolean getInsetDodgeRect(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull Rect rect)
這些事件一般不會用到。
以上是 Behavior 內定義的一些方法。Behavior 主要的用途還是用來做觸摸事件的分發。這里,我們來重點關注和觸摸事件分發相關的方法。
首先我們來回顧傳統的事件分發機制。當 window 將觸摸事件交給 DecorView 之后,觸摸事件在 ViewGroup 和 View 之間傳遞遵循如下模型,
// ViewGroup
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if ACTION_DOWN 事件并且 FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT 允許攔截 {
final boolean intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev) // 注意 onInterceptTouchEvent 的位置
}
boolean handled;
if !intercepted {
if child == null {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev)
} else {
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(ev)
}
}
return handled;
}
// View
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event) {
return true
}
if onTouchEvent(event) { // 注意 onTouchEvent 的位置
return true
}
return false
}所以,子控件可以通過調用父控件的 requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent() 方法不讓父控件攔截事件。但是這種攔截機制完全是基于默認的實現邏輯。如果父控件修改了 requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent() 方法或者 dispatchTouchEvent() 方法的邏輯,子控件的約束效果是無效的。
父控件通過 onInterceptTouchEvent() 攔截事件只能攔截部分事件。
相比于父控件,子控件的事件分發則簡單得多。首先是先將事件交給自定義的 mOnTouchListener 來處理,其沒有消費才將其交給默認的 onTouchEvent 來處理。在 onTouchEvent 里則會判斷事件的類型,比如點擊和長按之類的,而且可以看到系統源碼在判斷具體的事件類型的時候使用了 post Runnable 的方式。
在父控件中如果子控件沒有處理,則父控件將會走 View 的 dispatchTouchEvent() 邏輯,也就是去判斷事件的類型來消費了。
在 Behavior 中定義了兩個與觸摸事件分發相關的方法,
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull MotionEvent ev) public boolean onTouchEvent(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull MotionEvent ev)
對照上面的事件分發機制中 onInterceptTouchEvent 和 onTouchEvent 的邏輯,這里的 Behavior 的攔截邏輯是:CoordinatorLayout 按照 Behavior 的出現順序進行遍歷,先走 CoordinatorLayout 的 onInterceptTouchEvent,如果一個 Behavior 的 onInterceptTouchEvent 攔截了該事件,則會記錄攔截該事件的 View 并給其他 Behavior 的 onInterceptTouchEvent 發送給一個 Cancel 類型的觸摸事件。然后,在 CoordinatorLayout 的 onTouchEvent 方法中會執行該 View 對應的 Behavior 的 onTouchEvent 方法。
安卓在 5.0 上引入了 NestedScrolling 機制。之所以引入該事件是因為傳統的事件分發機制 MOVE 事件當父控件攔截了之后就無法再交給子 View. 而 NestedScrolling 機制可以指定在一個滑動事件中,父控件和子控件分別消費多少。比如,在一個向上的滑動事件中,我們需要 toolbar 先向上滑動 50dp,然后列表再向上滑動。此時,我們可以先讓 toolbar 消費 50dp 的事件,剩下的再交給列表處理,讓其向上滑動 6dp 的距離。
在 NestedScrolling 機制中定義了 NestedScrollingChild 和 NestedScrollingParent 兩個接口(為了支持更多功能后續又定義了 NestedScrollingChild2 和 NestedScrollingChild3 等接口)。外部容器通常實現 NestedScrollingParent 接口,而子控件通常實現 NestedScrollingChild 接口。在常規的事件分發機制中,子控件(比如 RecyclerView 或者 NestedScrollView )會在 Move 事件中找到父控件,如果該父控件實現了 NestedScrollingParent 接口,就會通知該父控件發生了滑動事件。然后,父控件可以對滑動事件進行進一步的分發。以 RecyclerView 為例,
// androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView#onTouchEvent
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
// ...
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
// ...
if (dispatchNestedPreScroll(
canScrollHorizontally ? dx : 0,
canScrollVertically ? dy : 0,
mReusableIntPair, mScrollOffset, TYPE_TOUCH
)) {
// ...
}
}
}
}這里 dispatchNestedPreScroll() 就是滑動事件的分發邏輯,它最終會走到 ViewParentCompat 的 onNestedPreScroll() 方法,并在該方法中向上交給父控件進行分發。代碼如下,
public static void onNestedPreScroll(ViewParent parent, View target, int dx, int dy,
int[] consumed, int type) {
if (parent instanceof NestedScrollingParent2) {
((NestedScrollingParent2) parent).onNestedPreScroll(target, dx, dy, consumed, type);
} else if (type == ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 21) {
parent.onNestedPreScroll(target, dx, dy, consumed);
} else if (parent instanceof NestedScrollingParent) {
((NestedScrollingParent) parent).onNestedPreScroll(target, dx, dy, consumed);
}
}
}在 CoordinatorLayout 中,與 NestedScrolling 機制相關的方法主要分成 scroll 和 fling 兩類。
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View directTargetChild, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes, @NestedScrollType int type) public void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View directTargetChild, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes, @NestedScrollType int type) public void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View target, @NestedScrollType int type) public void onNestedScroll(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @NestedScrollType int type, @NonNull int[] consumed) public void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed, @NestedScrollType int type)
public boolean onNestedFling(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View target, float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean consumed) public boolean onNestedPreFling(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View target, float velocityX, float velocityY)
以 scroll 類型的事件為例,其工作的原理:
CoordinatorLayout 中會對子控件進行遍歷,然后將對應的事件傳遞給子控件的 Behavior (若有)的對應方法。對于滑動類型的事件,在滑動事件傳遞的時候先傳遞 onStartNestedScroll 事件,用來判斷某個 View 是否攔截滑動事件。而在 CoordinatorLayout 中,會交給 Beahvior 判斷是否處理該事件。然后 CoordinatorLayout 會講該 Behavior 是否攔截該事件的狀態記錄到對應的 View 的 LayoutParam. 然后,當 CoordinatorLayout 的 onNestedPreScroll 被調用的時候,會讀取 LayoutParame 上的狀態以決定是否調用該 Behavior 的 onNestedPreScroll 方法。另外,只有當一個 CoordinatorLayout 包含的所有的 Behavior 都不處理該滑動事件的時候,才判定 CoordinatorLayout 不處理該滑動事件。
偽代碼如下,
// CoordinatorLayout
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(View child, View target, int axes, int type) {
boolean handled = false;
for 遍歷子 view {
Behavior viewBehavior = view.getLayoutParams().getBehavior()
final boolean accepted = viewBehavior.onStartNestedScroll();
handled |= accepted;
// 根據 accepted 給 view 的 layoutparams 置位
view.getLayoutParams().setNestedScrollAccepted(accepted)
}
return handled;
}
// CoordinatorLayout
public void onStopNestedScroll(View target, int type) {
for 遍歷子 view {
// 讀取 view 的 layoutparams 的標記位
if view.getLayoutParams().isNestedScrollAccepted(type) {
Behavior viewBehavior = view.getLayoutParams().getBehavior()
// 將事件交給 behavior
viewBehavior.onStopNestedScroll(this, view, target, type)
}
}
}在消費事件的時候是通過覆寫 onNestedPreScroll() 等方法,以該方法為例,
public void onNestedPreScroll(View target, int dx, int dy, int[] consumed, int type) {}這里的 dx 和 dy 是滾動在水平和方向上的總的值,我們消費的值通過 consumed 指定。比如 dy 表示向上一共滾動了 50dp,而我們的 toolbar 需要先向上滾動 44dp,那么我們就將 44dp 的數值賦值給 consumed 數組(方法簽名中的數組是按引用傳遞的)。這樣父控件就可以將剩下的 6dp 交給列表,所以列表最終會向上滾動 6dp.
按照上述 Behavior 的實現方式,一個 Behavior 是可以攔截到 CoordinatorLayout 內所有的 View 的 NestedScrolling 事件的。因而,我們可以在一個 Behavior 內部對 CoordinatorLayout 內的所有的 NestedScrolling 事件進行統籌攔截和調度。用一個圖來表示整體分發邏輯,如下,
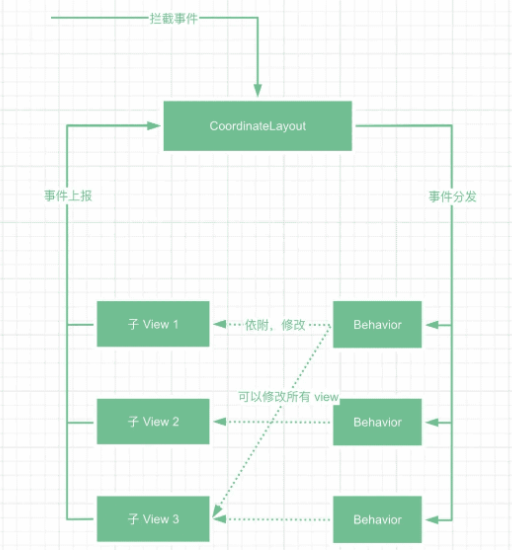
這里需要注意,按照我們上面的分析,CoordinatorLayout 收集到的事件 NestedScrolling 事件,如果一個控件并沒有實現 NestedScrollingChild 接口,或者更嚴謹得說,沒有將滾動事件傳遞給 CoordinatorLayout,那么 Behavior 就無法接受到滾動事件。但是對于普通的觸摸事件 Behavior 是可以攔截到的。
關于“Behavior怎么實現復雜的視覺聯動效果”這篇文章的內容就介紹到這里,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家對“Behavior怎么實現復雜的視覺聯動效果”知識都有一定的了解,大家如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。