您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇“C++中怎么正確使用hashmap”文章的知識點大部分人都不太理解,所以小編給大家總結了以下內容,內容詳細,步驟清晰,具有一定的借鑒價值,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章能有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看這篇“C++中怎么正確使用hashmap”文章吧。
首先回顧一下hash沖突的解決方案有哪些。
open addressing是通過探測或者搜索數組的方法找到未使用的bucket來解決hash沖突的。
優點:
* 當hash沖突很小的時候,只需要訪問對應的bucket就能獲得對應的pair<key, value>,不需要再查找額外的數據結構,性能較好。
缺點:
* 對hash函數的要求比較高,否則當hash沖突很大的時,查找速度會很慢。
或者叫closed addressing,當發生hash沖突時需要通過額外的數據結構來處理,比如鏈表或者紅黑樹。
優點:
* hash沖突處理簡單,比如采用鏈表來解決hash沖突的話,添加節點的時候直接在鏈表后面添加即可。
* 對hash函數要求會低一點,即便沖突稍微大一點,也能把查找速度控制得比較好。
缺點:
* 由于需要額外的數據結構處理,性能在一般情況下不如Open addressing。
STL采用的是Separate chaining的方案。使用鏈表掛在bucket上解決沖突,當鏈表超過一定長度時轉換為紅黑樹。
一般的開源庫都會提供兩種memory layout,一種叫flat,另一種叫node。
flat實現是指存儲pair<key, value>的時候是直接存到對應的節點上。
優點:
* 對比node少一次尋址,對cache更加友好,查找速度會更高。
缺點:
* 對象不穩定,rehash的時候對象地址會修改,如果對象是個大結構的話rehash時的開銷會比node要大。
node實現是指在節點上只存儲pair<key, value>的地址。而pair<key, value>則存儲在另一塊內存上。
優點:
* 對象穩定,rehash的時候對象地址不修改,且rehash的效率不會被結構體影響。
缺點:
* 查找多一次尋址,對cache不友好,查找速度會比flat要慢。
STL用的是Node的實現。每個pair<key, value>都是stable的。
在hash沖突上,大部分的開源實現都選擇了Open addressing這種方式,畢竟理論性能會更好,而flat和node則是兩種實現都會提供。結合上面說的各種優缺點,我們可以簡單得出一套通用的方案。
首先考慮下面幾個點:
1. 是否可以一開始就可以確定好容量。
2. key的copy開銷是否很大。
3. value的copy開銷是否很大。
4. value的地址不穩定是否會影響代碼邏輯。
可以簡單歸納為以下四種情況:
情況1:value可以是不穩定的,而且容量是已知的,可以一開始確定。
推薦:使用flat實現,通過一開始reserve兩倍的size來減少rehash帶來的開銷。
情況2:value可以是不穩定的,容量未知,key和value的copy開銷很小。
推薦:使用flat實現。
情況3:value可以是不穩定的,容量未知,key的copy開銷很小但value的copy開銷很大。
推薦:使用flat實現,value使用unique_ptr包裹起來。
其他情況均使用node結構。
上面提到的規則基本可以適用大部分情況,但也不是沒有例外,比如筆者在用這套規則去測試robinhood的性能的時候發現行不通,robinhood在絕大部分情況下都是node的實現性能會更高,除非value是個十分簡單的結構。通過分析發現,這主要是因為以下兩個原因:
1.robinhood在emplace的時候會有移動pair<key, value>的操作,這使得如果pair<key, value>的copy代價很高,性能會大打折扣。
2.robinhood實現了自己的allocator來分配node的內存,使得調用malloc的次數大約為log(n)次,并且內存連續的情況會變多,對CPU Cache比一般的node實現要友好。
具體我們可以看看源代碼,首先是emplace的實現。
void nextWhileLess(InfoType* info, size_t* idx) const noexcept {
// unrolling this by hand did not bring any speedups.
while (*info < mInfo[*idx]) {
next(info, idx);
}
}
// Finds key, and if not already present prepares a spot where to pot the key & value.
// This potentially shifts nodes out of the way, updates mInfo and number of inserted
// elements, so the only operation left to do is create/assign a new node at that spot.
template <typename OtherKey>
std::pair<size_t, InsertionState> insertKeyPrepareEmptySpot(OtherKey&& key) {
for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i) {
size_t idx{};
InfoType info{};
// 找到對應key的info
keyToIdx(key, &idx, &info);
// 跳過distance大于自己的
nextWhileLess(&info, &idx);
// while we potentially have a match
while (info == mInfo[idx]) {
// distance相等的情況需要判key是不是已經存在了
if (WKeyEqual::operator()(key, mKeyVals[idx].getFirst())) {
// key already exists, do NOT insert.
// see http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/unordered_map/insert
return std::make_pair(idx, InsertionState::key_found);
}
next(&info, &idx);
}
// unlikely that this evaluates to true
if (ROBIN_HOOD_UNLIKELY(mNumElements >= mMaxNumElementsAllowed)) {
if (!increase_size()) {
return std::make_pair(size_t(0), InsertionState::overflow_error);
}
continue;
}
// key not found, so we are now exactly where we want to insert it.
// 此時的位置原來的distance一定是小于當前的distance
auto const insertion_idx = idx;
auto const insertion_info = info;
if (ROBIN_HOOD_UNLIKELY(insertion_info + mInfoInc > 0xFF)) {
mMaxNumElementsAllowed = 0;
}
// find an empty spot
// 找到下一個空白的位置
while (0 != mInfo[idx]) {
next(&info, &idx);
}
// 如果當前的位置不是空白的,則把當前位置->下一個空白位置的所有元素往后移
if (idx != insertion_idx) {
shiftUp(idx, insertion_idx);
}
// put at empty spot
mInfo[insertion_idx] = static_cast<uint8_t>(insertion_info);
++mNumElements;
return std::make_pair(insertion_idx, idx == insertion_idx
? InsertionState::new_node
: InsertionState::overwrite_node);
}
// enough attempts failed, so finally give up.
return std::make_pair(size_t(0), InsertionState::overflow_error);
}
template <typename OtherKey, typename... Args>
std::pair<iterator, bool> try_emplace_impl(OtherKey&& key, Args&&... args) {
ROBIN_HOOD_TRACE(this)
auto idxAndState = insertKeyPrepareEmptySpot(key);
switch (idxAndState.second) {
case InsertionState::key_found:
break;
case InsertionState::new_node:
::new (static_cast<void*>(&mKeyVals[idxAndState.first])) Node(
*this, std::piecewise_construct, std::forward_as_tuple(std::forward<OtherKey>(key)),
std::forward_as_tuple(std::forward<Args>(args)...));
break;
case InsertionState::overwrite_node:
mKeyVals[idxAndState.first] = Node(*this, std::piecewise_construct,
std::forward_as_tuple(std::forward<OtherKey>(key)),
std::forward_as_tuple(std::forward<Args>(args)...));
break;
case InsertionState::overflow_error:
throwOverflowError();
break;
}
return std::make_pair(iterator(mKeyVals + idxAndState.first, mInfo + idxAndState.first),
InsertionState::key_found != idxAndState.second);
}這里robinhood有一個很神奇的操作,它在info里面存了一個distance,這個distance表示當前元素所在位置與初始位置的距離,簡單舉例,假設我插入了4個key,分別為a,b,c,d。
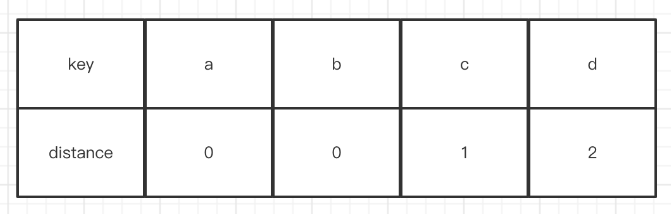
sequence1:插入a,hash(a) == 0,此時index0是空的,直接插入。它的distance(0, 0) == 0。
sequence2:插入b,hash(b) == 1,此時index1是空的,直接插入。它的distance(1, 1) == 0。
sequence3:插入c,hash(c) == 1,此時index1存在,那么找到下一個位置2插入,它的distance(1, 2) == 1。
sequence4:插入d,hash(d) == 1,此時index1和2都存在,找到位置3插入,它的distance(1, 3) == 2。
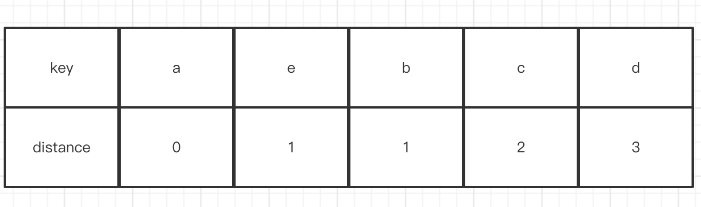
至于它的移動操作是怎么來的呢,假設基于上面的流程此時再加一個插入元素e的操作,并且這時候hash(e) == 0,首先是index0,發現這個位置兩者的distance是相同,所以跳過看下一個。而index1則滿足條件(新的距離>當前b這個key的距離),所以會把e放到index1這個位置,并且找到下一個空白的位置index4,然后把c, d這兩個元素后移,最終會變成下面這個圖。
分配內存這塊就比較簡單了。
T* allocate() {
T* tmp = mHead;
if (!tmp) {
tmp = performAllocation();
}
mHead = *reinterpret_cast_no_cast_align_warning<T**>(tmp);
return tmp; }
ROBIN_HOOD(NOINLINE) T* performAllocation() {
size_t const numElementsToAlloc = calcNumElementsToAlloc();
// alloc new memory: [prev |T, T, ... T]
size_t const bytes = ALIGNMENT + ALIGNED_SIZE * numElementsToAlloc;
ROBIN_HOOD_LOG("std::malloc " << bytes << " = " << ALIGNMENT << " + " << ALIGNED_SIZE
<< " * " << numElementsToAlloc)
add(assertNotNull<std::bad_alloc>(std::malloc(bytes)), bytes);
return mHead;
}
ROBIN_HOOD(NODISCARD) size_t calcNumElementsToAlloc() const noexcept {
auto tmp = mListForFree;
size_t numAllocs = MinNumAllocs;
while (numAllocs * 2 <= MaxNumAllocs && tmp) {
auto x = reinterpret_cast<T***>(tmp);
tmp = *x;
numAllocs *= 2;
}
return numAllocs;
}每次都分配比原來更多的內存,所以大概是分配log(n)次。
所以如果是用的robinhood,筆者建議除非你的pair<key, value>真的是非常簡單的結構,否則都是用node實現會好一點。或者你可以交給robinhood自己判斷,不顯示指定使用flat還是node,robinhood的模板會自動根據你的size去判斷去使用哪個實現。
using unordered_map =
detail::Table<sizeof(robin_hood::pair<Key, T>) <= sizeof(size_t) * 6 &&
std::is_nothrow_move_constructible<robin_hood::pair<Key, T>>::value &&
std::is_nothrow_move_assignable<robin_hood::pair<Key, T>>::value,
MaxLoadFactor100, Key, T, Hash, KeyEqual>;
template <bool IsFlat, size_t MaxLoadFactor100, typename Key, typename T, typename Hash,
typename KeyEqual>
class Table
: public WrapHash<Hash>,
public WrapKeyEqual<KeyEqual>,
detail::NodeAllocator<
typename std::conditional<
std::is_void<T>::value, Key,
robin_hood::pair<typename std::conditional<IsFlat, Key, Key const>::type, T>>::type,
4, 16384, IsFlat> {}這里附帶上一個簡單的benchmark測試robinhood和absl的性能,測試的key是uint32_t類型,value是個120size的結構。測試代碼如下
//
// Created by victorika on 2022/10/14.
//
#include "absl/container/flat_hash_map.h"
#include "absl/container/node_hash_map.h"
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#define ANKERL_NANOBENCH_IMPLEMENT
#include "riemann/3rd/nanobench/nanobench.h"
#include "robin_hood.h"
/**
* 測試結構
*/
struct TestStruct {
uint32_t* a;
std::vector<uint32_t> b, c, d;
std::string e, f, g;
uint32_t h, i, j;
};
void TestEmplace() {
ankerl::nanobench::Bench bench;
bench.minEpochIterations(50);
bench.title("Benchmarking rare value emplace");
bench.run("absl_flat", [&] {
absl::flat_hash_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
});
bench.run("absl_flat_and_set_value_pointer", [&] {
absl::flat_hash_map<uint32_t, std::unique_ptr<TestStruct>> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, std::make_unique<TestStruct>());
}
});
bench.run("absl_node", [&] {
absl::node_hash_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
});
bench.run("absl_flat_reserve", [&] {
absl::flat_hash_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m;
m.reserve(20000);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
});
bench.run("absl_flat_and_set_value_pointer_reserve", [&] {
absl::flat_hash_map<uint32_t, std::unique_ptr<TestStruct>> m;
m.reserve(20000);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, std::make_unique<TestStruct>());
}
});
bench.run("absl_node_reserve", [&] {
absl::node_hash_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m;
m.reserve(20000);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_flat", [&] {
robin_hood::unordered_flat_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_flat_and_set_value_pointer", [&] {
robin_hood::unordered_flat_map<uint32_t, std::unique_ptr<TestStruct>> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, std::make_unique<TestStruct>());
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_node", [&] {
robin_hood::unordered_node_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_flat_reserve", [&] {
robin_hood::unordered_flat_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m;
m.reserve(20000);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_flat_and_set_value_pointer_reserve", [&] {
robin_hood::unordered_flat_map<uint32_t, std::unique_ptr<TestStruct>> m;
m.reserve(20000);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, std::make_unique<TestStruct>());
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_node_reserve", [&] {
robin_hood::unordered_node_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m;
m.reserve(20000);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
});
}
void TestSearch() {
absl::flat_hash_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m1;
absl::flat_hash_map<uint32_t, std::unique_ptr<TestStruct>> m2;
absl::node_hash_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m3;
robin_hood::unordered_flat_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m4;
robin_hood::unordered_flat_map<uint32_t, std::unique_ptr<TestStruct>> m5;
robin_hood::unordered_node_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m6;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m1.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
m2.try_emplace(i, std::make_unique<TestStruct>());
m3.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
m4.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
m5.try_emplace(i, std::make_unique<TestStruct>());
m6.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
ankerl::nanobench::Bench bench;
bench.minEpochIterations(50);
std::vector<uint32_t> key_v;
key_v.resize(10000);
bench.title("Benchmarking rare value search");
bench.run("absl_flat_normal", [&] {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
auto it = m1.find(i);
key_v[i] = it->first;
}
});
bench.run("absl_flat_unique_ptr", [&] {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
auto it = m2.find(i);
key_v[i] = it->first;
}
});
bench.run("absl_node", [&] {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
auto it = m3.find(i);
key_v[i] = it->first;
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_flat_normal", [&] {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
auto it = m4.find(i);
key_v[i] = it->first;
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_unique_ptr", [&] {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
auto it = m5.find(i);
key_v[i] = it->first;
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_node", [&] {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
auto it = m6.find(i);
key_v[i] = it->first;
}
});
}
void TestIterator() {
absl::flat_hash_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m1;
absl::flat_hash_map<uint32_t, std::unique_ptr<TestStruct>> m2;
absl::node_hash_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m3;
robin_hood::unordered_flat_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m4;
robin_hood::unordered_flat_map<uint32_t, std::unique_ptr<TestStruct>> m5;
robin_hood::unordered_node_map<uint32_t, TestStruct> m6;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
m1.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
m2.try_emplace(i, std::make_unique<TestStruct>());
m3.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
m4.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
m5.try_emplace(i, std::make_unique<TestStruct>());
m6.try_emplace(i, TestStruct());
}
ankerl::nanobench::Bench bench;
bench.minEpochIterations(50);
std::vector<uint32_t> key_v;
key_v.resize(10000);
bench.title("Benchmarking rare value iterator");
bench.run("absl_flat_normal", [&] {
int i = 0;
for (auto &[key, value] : m1) {
key_v[i] = key;
}
});
bench.run("absl_flat_unique_ptr", [&] {
int i = 0;
for (auto &[key, value] : m2) {
key_v[i] = key;
}
});
bench.run("absl_node", [&]() {
int i = 0;
for (auto &[key, value] : m3) {
key_v[i] = key;
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_flat_normal", [&] {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
auto it = m4.find(i);
key_v[i] = it->first;
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_flat_unique_ptr", [&] {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
auto it = m5.find(i);
key_v[i] = it->first;
}
});
bench.run("robinhood_node", [&] {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
auto it = m6.find(i);
key_v[i] = it->first;
}
});
}
int main() {
std::cout << "size=" << sizeof(TestStruct) << std::endl;
TestEmplace();
TestSearch();
TestIterator();
}測試結果
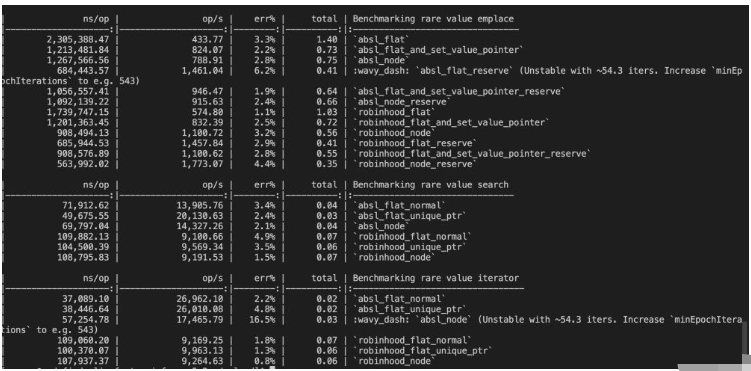
可以看到,在value copy rare的場景,absl的性能完全遵循上面提到的規則,而robinhood在這種情況下,emplace+construct+deconstruct是node更快,查找和遍歷幾乎和flat沒區別。橫向對比absl和robinhood兩者的話,在查找和遍歷上都是absl更快,emplace+construct+deconstruct在優化到極致的情況下兩者差不多,robinhood并沒有比absl快多少。當然,這只是簡單測試,針對key類型不同的場景可能兩者速度不太一樣,具體就需要更加詳細的benchmark了。
筆者也嘗試過極簡類型的場景,結論也沒有違背上面的規則,都是flat速度遠大于node。
建議:從兩者里面選擇的話,如果選型是用flat的話建議用absl,是node的話建議用robinhood。
以上就是關于“C++中怎么正確使用hashmap”這篇文章的內容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小編分享的內容對大家有幫助,若想了解更多相關的知識內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。