您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本文小編為大家詳細介紹“Lucene索引刪除策略源碼分析”,內容詳細,步驟清晰,細節處理妥當,希望這篇“Lucene索引刪除策略源碼分析”文章能幫助大家解決疑惑,下面跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來學習新知識吧。
Lucene中,需要持久化的索引信息都要進行commit操作,然后會生成一個segments_N的索引文件記錄此次commit相關的索引信息。
一次commit生成segments_N之后,就對應了一個IndexCommit,IndexCommit只是一個接口,它定義了可以從IndexCommit中獲取哪些信息:
public abstract class IndexCommit implements Comparable<IndexCommit> {
// commit對應的segments_N
public abstract String getSegmentsFileName();
// commit關聯的所有的索引文件
public abstract Collection<String> getFileNames() throws IOException;
// 索引所在的Directory
public abstract Directory getDirectory();
// 刪除commit,后面會看到,刪除其實減少commit關聯的索引文件的引用計數
public abstract void delete();
// commit是否被刪除了
public abstract boolean isDeleted();
// commit關聯了幾個segment
public abstract int getSegmentCount();
// segments_N文件中的N
public abstract long getGeneration();
// commit可以記錄一些用戶自定義的信息
public abstract Map<String, String> getUserData() throws IOException;
// 用來讀取commit對應的索引數據
StandardDirectoryReader getReader() {
return null;
}
}IndexCommit有三個實現類:
CommitPoint
ReaderCommit
SnapshotCommitPoint
這個三個實現類都有對應的使用場景,在用到的時候我會再詳細介紹,本文中會涉及到SnapshotCommitPoint,后面會詳細介紹它。
在索引的生命周期中,可以有多次的commit操作,因此也會生成多個segments_N文件,對于這些文件是否要保留還是刪除,lucene中是通過IndexDeletionPolicy來管理的。我們先來看下IndexDeletionPolicy的接口定義:
public abstract class IndexDeletionPolicy {
protected IndexDeletionPolicy() {}
// 重新打開索引的時候,對所有commit的處理
public abstract void onInit(List<? extends IndexCommit> commits) throws IOException;
// 有新提交時對所有commit的處理
public abstract void onCommit(List<? extends IndexCommit> commits) throws IOException;
}從上面我可以看到,索引的刪除策略其實只在兩個地方進行應用,一個是加載索引的時候,打開一個舊索引時,根據當前設置的IndexDeletionPolicy進行處理。另一個是有新的commit產生時,借這個機會處理所有的commit。Lucene中提供的索引刪除策略一共有四種,不過可以分為三類:
NoDeletionPolicy索引刪除策略就是保留所有的commit信息,效果就是你有多少次commit就多少個segments_N文件,看個例子:
public class DeletionPolicyTest {
private static final Random RANDOM = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\code\\lucene-9.1.0-learning\\data").toPath());
WhitespaceAnalyzer analyzer = new WhitespaceAnalyzer();
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
indexWriterConfig.setUseCompoundFile(true);
indexWriterConfig.setIndexDeletionPolicy(NoDeletionPolicy.INSTANCE);
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, indexWriterConfig);
indexWriter.addDocument(getDoc(RANDOM.nextInt(10000),RANDOM.nextInt(10000)));
// 第一次commit,生成segments_1
indexWriter.commit();
indexWriter.addDocument(getDoc(RANDOM.nextInt(10000),RANDOM.nextInt(10000)));
// 第二次commit,生成segments_2
indexWriter.commit();
indexWriter.close();
}
private static Document getDoc(int... point) {
Document doc = new Document();
IntPoint intPoint = new IntPoint("point", point);
doc.add(intPoint);
return doc;
}
}上面的例子中有兩次commit,下圖是NoDeletionPolicy策略進行了兩次commit的索引目錄結構,可以看到生成了兩個segments_N文件:
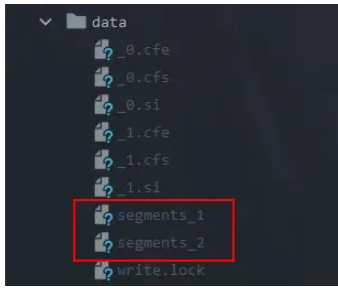
NoDeletionPolicy的代碼實現非常簡單,單例實現,并且在onCommit和onInit的時候都是空操作:
public final class NoDeletionPolicy extends IndexDeletionPolicy {
public static final IndexDeletionPolicy INSTANCE = new NoDeletionPolicy();
private NoDeletionPolicy() {
}
public void onCommit(List<? extends IndexCommit> commits) {}
public void onInit(List<? extends IndexCommit> commits) {}
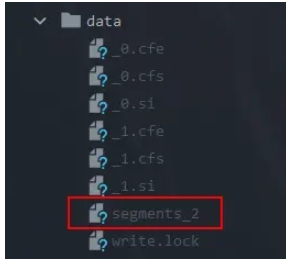
}KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy是Lucene默認的索引刪除策略,只保留最新的一次commit,從索引目錄看不管執行多少次commit只保留了N最大的segments_N文件,下圖是KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy策略進行了兩次commit的結果,KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy刪除策略只保留了segments_2。把上面示例代碼中的刪除策略替換成KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy,即可得到,注意需要先清空索引目錄:
KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy代碼實現也比較簡單,除了最后一個commit之外,其他的commit都刪除:
public final class KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy extends IndexDeletionPolicy {
public KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy() {}
public void onInit(List<? extends IndexCommit> commits) {
onCommit(commits);
}
// commits是從舊到新排序的
public void onCommit(List<? extends IndexCommit> commits) {
// 只保留最新的一個
int size = commits.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
commits.get(i).delete();
}
}
}快照相關的刪除策略有兩個,SnapshotDeletionPolicy和PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy,分別對應了不可持久化和可持久化的模式。不管是SnapshotDeletionPolicy還是PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy,他們都封裝了其他的IndexDeletionPolicy來執行刪除策略,他們只是提供了為當前最新的commit生成快照的能力。只要快照存在,則跟快照相關的所有索引文件都會被無條件保留。
public class SnapshotDeletionPolicyTest {
private static final Random RANDOM = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\code\\lucene-9.1.0-learning\\data").toPath());
WhitespaceAnalyzer analyzer = new WhitespaceAnalyzer();
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
indexWriterConfig.setUseCompoundFile(true);
SnapshotDeletionPolicy snapshotDeletionPolicy = new SnapshotDeletionPolicy(new KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy());
indexWriterConfig.setIndexDeletionPolicy(snapshotDeletionPolicy);
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, indexWriterConfig);
indexWriter.addDocument(getDoc(RANDOM.nextInt(10000),RANDOM.nextInt(10000)));
// 第一次commit,生成segments_1
indexWriter.commit();
indexWriter.addDocument(getDoc(RANDOM.nextInt(10000),RANDOM.nextInt(10000)));
// 第二次commit,生成segments_2
indexWriter.commit();
// segments_2當做快照,無條件保留
snapshotDeletionPolicy.snapshot();
indexWriter.addDocument(getDoc(RANDOM.nextInt(10000),RANDOM.nextInt(10000)));
// 第三次commit,生成segments_3
indexWriter.commit();
indexWriter.close();
}
private static Document getDoc(int... point) {
Document doc = new Document();
IntPoint intPoint = new IntPoint("point", point);
doc.add(intPoint);
return doc;
}
}在上面的例子中,我們使用SnapshotDeletionPolicy,SnapshotDeletionPolicy底層封裝的是KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy,我們進行了三次commit,理論上KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy只會保留最后一次,但是因為我們對第一次的commit進行了快照,所以第一次commit也被保留了:
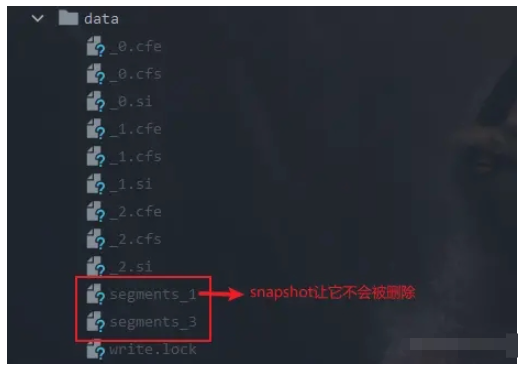
接下來我們看看SnapshotDeletionPolicy是怎么實現。SnapshotDeletionPolicy保證生成快照的commit不會被刪除的原理就是引用計數,SnapshotDeletionPolicy會記錄每個commit生成快照的次數,在刪除的時候,只會刪除引用計數為0的commit。
// key是IndexCommit的generation,value是對應的IndexCommit有多少個快照 // 需要注意的是,有被快照引用的才會記錄在refCounts中,也就是只要被記錄在refCounts中,引用次數至少是1 protected final Map<Long, Integer> refCounts = new HashMap<>(); // key是IndexCommit的generation,value是對應的IndexCommit protected final Map<Long, IndexCommit> indexCommits = new HashMap<>(); // SnapshotDeletionPolicy只是增加了支持快照的功能,刪除的邏輯是由primary參數對應的刪除策略提供的 private final IndexDeletionPolicy primary; // 最近一次提交的commit,只會對這個IndexCommit生成快照 protected IndexCommit lastCommit; // 是否初始化的標記,實例化后,必須先調用onInit方法 private boolean initCalled;
生成快照只會對當前最新的一個commit進行快照:
public synchronized IndexCommit snapshot() throws IOException {
if (!initCalled) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"this instance is not being used by IndexWriter; be sure to use the instance returned from writer.getConfig().getIndexDeletionPolicy()");
}
if (lastCommit == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No index commit to snapshot");
}
// 新增lastCommit的引用計數
incRef(lastCommit);
return lastCommit;
}
protected synchronized void incRef(IndexCommit ic) {
long gen = ic.getGeneration();
Integer refCount = refCounts.get(gen);
int refCountInt;
if (refCount == null) { // 第一次被引用
indexCommits.put(gen, lastCommit);
refCountInt = 0;
} else {
refCountInt = refCount.intValue();
}
// 引用計數加+1
refCounts.put(gen, refCountInt + 1);
}public synchronized void release(IndexCommit commit) throws IOException {
long gen = commit.getGeneration();
releaseGen(gen);
}
protected void releaseGen(long gen) throws IOException {
if (!initCalled) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"this instance is not being used by IndexWriter; be sure to use the instance returned from writer.getConfig().getIndexDeletionPolicy()");
}
Integer refCount = refCounts.get(gen);
if (refCount == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("commit gen=" + gen + " is not currently snapshotted");
}
int refCountInt = refCount.intValue();
assert refCountInt > 0;
refCountInt--;
if (refCountInt == 0) { // 引用計數為0,直接從refCounts中移除
refCounts.remove(gen);
indexCommits.remove(gen);
} else {
refCounts.put(gen, refCountInt);
}
} public synchronized void onCommit(List<? extends IndexCommit> commits) throws IOException {
// 把commits中的所有IndexCommit都封裝成SnapshotCommitPoint,再使用primary執行onCommit方法
primary.onCommit(wrapCommits(commits));
// 更新最新的commit
lastCommit = commits.get(commits.size() - 1);
}
@Override
public synchronized void onInit(List<? extends IndexCommit> commits) throws IOException {
// 設置初始化的標記
initCalled = true;
primary.onInit(wrapCommits(commits));
for (IndexCommit commit : commits) {
if (refCounts.containsKey(commit.getGeneration())) {
indexCommits.put(commit.getGeneration(), commit);
}
}
if (!commits.isEmpty()) {
lastCommit = commits.get(commits.size() - 1);
}
}
private List<IndexCommit> wrapCommits(List<? extends IndexCommit> commits) {
List<IndexCommit> wrappedCommits = new ArrayList<>(commits.size());
for (IndexCommit ic : commits) {
// 把IndexCommit都封裝成 SnapshotCommitPoint
wrappedCommits.add(new SnapshotCommitPoint(ic));
}
return wrappedCommits;
}前面我們列出了SnapshotCommitPoint是IndexCommit的一個實現類,但是沒有詳細介紹,SnapshotCommitPoint除了能夠提供IndexCommit接口所提供的信息之外,最核心的是在刪除的時候,會先判斷IndexCommit是否被快照引用,只有沒有任何快照引用的IndexCommit才能刪除:
public void delete() {
synchronized (SnapshotDeletionPolicy.this) {
if (!refCounts.containsKey(cp.getGeneration())) {
cp.delete();
}
}
}需要注意的是SnapshotDeletionPolicy的快照信息是沒有持久化,我們重新打開SnapshotDeletionPolicyTest例子中生成的索引:
public class SnapshotDeletionPolicyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\code\\lucene-9.1.0-learning\\data").toPath());
WhitespaceAnalyzer analyzer = new WhitespaceAnalyzer();
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
indexWriterConfig.setUseCompoundFile(true);
SnapshotDeletionPolicy snapshotDeletionPolicy = new SnapshotDeletionPolicy(new KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy());
indexWriterConfig.setIndexDeletionPolicy(snapshotDeletionPolicy);
// 重新打開索引
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, indexWriterConfig);
indexWriter.close();
}
}可以發現segments_1被刪除了,因為沒有持久化快照信息,所以根據KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy的刪除策略,只保留了最新的一個commit:

PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy主要是為了解決SnapshotDeletionPolicy無法持久化的問題。PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy持久化的時候會生成snapshots_N的索引文件,我們看個例子:
public class PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicyTest {
private static final Random RANDOM = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\code\\lucene-9.1.0-learning\\data").toPath());
WhitespaceAnalyzer analyzer = new WhitespaceAnalyzer();
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
indexWriterConfig.setUseCompoundFile(true);
PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy persistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy = new PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy(new KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy(), directory);
indexWriterConfig.setIndexDeletionPolicy(persistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy);
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, indexWriterConfig);
indexWriter.addDocument(getDoc(RANDOM.nextInt(10000),RANDOM.nextInt(10000)));
// 第一次commit,生成segments_1
indexWriter.commit();
// segments_1當做快照,無條件保留
persistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy.snapshot();
indexWriter.addDocument(getDoc(RANDOM.nextInt(10000),RANDOM.nextInt(10000)));
// 第二次commit,生成segments_2
indexWriter.commit();
indexWriter.addDocument(getDoc(RANDOM.nextInt(10000),RANDOM.nextInt(10000)));
// 第三次commit,生成segments_3
indexWriter.commit();
indexWriter.close();
}
private static Document getDoc(int... point) {
Document doc = new Document();
IntPoint intPoint = new IntPoint("point", point);
doc.add(intPoint);
return doc;
}
}上面的例子和我們在介紹SnapshotDeletionPolicy的時候邏輯一樣,只是把SnapshotDeletionPolicy換成了PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy,我們看結果:
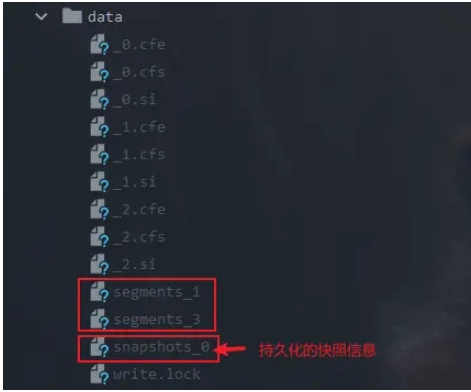
從上面結果圖中可以看到,segments_1和segments_3同樣被保留了,但是多了一個持久化的快照信息的文件snapshots_0,有了這個文件,索引重新打開的時候就可以恢復快照信息,segments_1還是會被保留,用下面的例子我們重新打開索引,可以發現segments_1還是被保留了:
public class PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\code\\lucene-9.1.0-learning\\data").toPath());
WhitespaceAnalyzer analyzer = new WhitespaceAnalyzer();
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
indexWriterConfig.setUseCompoundFile(true);
PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy persistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy = new PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy(new KeepOnlyLastCommitDeletionPolicy(), directory);
indexWriterConfig.setIndexDeletionPolicy(persistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy);
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, indexWriterConfig);
indexWriter.close();
}
}接下來我們看看PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy的實現,主要就是持久化和恢復快照信息的邏輯。
// 持久化快照信息的文件名snapshots_N中的N,從0開始 private long nextWriteGen; // 持久化的文件所在的目錄 private final Directory dir;
public PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy(IndexDeletionPolicy primary, Directory dir)
throws IOException {
this(primary, dir, OpenMode.CREATE_OR_APPEND);
}
public PersistentSnapshotDeletionPolicy(IndexDeletionPolicy primary, Directory dir, OpenMode mode)
throws IOException {
super(primary);
this.dir = dir;
if (mode == OpenMode.CREATE) { // 新建索引的模式,則需要清除所有的快照信息,索引模式以后再介紹
clearPriorSnapshots();
}
// 加載快照信息
loadPriorSnapshots();
if (mode == OpenMode.APPEND && nextWriteGen == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("no snapshots stored in this directory");
}
}public synchronized IndexCommit snapshot() throws IOException {
// 使用SnapshotDeletionPolicy來生成快照
IndexCommit ic = super.snapshot();
// 標記持久化是否成功,不成功的話需要刪除快照
boolean success = false;
try {
// 持久化最新的快照信息
persist();
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) { // 持久化失敗,刪除快照
try {
super.release(ic);
} catch (
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
Exception e) {
// Suppress so we keep throwing original exception
}
}
}
return ic;
}public synchronized void release(IndexCommit commit) throws IOException {
// 使用SnapshotDeletionPolicy來釋放快照
super.release(commit);
// 持久化快照信息是否成功
boolean success = false;
try {
// 持久化最新的快照信息
persist();
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) { // 持久化失敗,重新加回快照信息
try {
incRef(commit);
} catch (
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
Exception e) {
// Suppress so we keep throwing original exception
}
}
}
}private synchronized void persist() throws IOException {
// 快照文件名
String fileName = SNAPSHOTS_PREFIX + nextWriteGen;
boolean success = false;
try (IndexOutput out = dir.createOutput(fileName, IOContext.DEFAULT)) {
CodecUtil.writeHeader(out, CODEC_NAME, VERSION_CURRENT);
out.writeVInt(refCounts.size());
for (Entry<Long, Integer> ent : refCounts.entrySet()) { // 持久化所有的引用信息
out.writeVLong(ent.getKey());
out.writeVInt(ent.getValue());
}
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
IOUtils.deleteFilesIgnoringExceptions(dir, fileName);
}
}
dir.sync(Collections.singletonList(fileName));
if (nextWriteGen > 0) {
String lastSaveFile = SNAPSHOTS_PREFIX + (nextWriteGen - 1);
// 刪除前一個快照文件,因為每次持久化都是把當前的快照信息全量持久化,所以只需要保留最新的一個就可以
// 這里有可能刪除失敗,所以在啟動加載的時候會再次嘗試把舊版本的文件都刪掉
IOUtils.deleteFilesIgnoringExceptions(dir, lastSaveFile);
}
nextWriteGen++;
}private synchronized void loadPriorSnapshots() throws IOException {
long genLoaded = -1;
IOException ioe = null;
List<String> snapshotFiles = new ArrayList<>();
for (String file : dir.listAll()) {
if (file.startsWith(SNAPSHOTS_PREFIX)) { // 找到快照文件
long gen = Long.parseLong(file.substring(SNAPSHOTS_PREFIX.length()));
if (genLoaded == -1 || gen > genLoaded) { // 找到gen最大的快照文件
snapshotFiles.add(file);
Map<Long, Integer> m = new HashMap<>();
IndexInput in = dir.openInput(file, IOContext.DEFAULT);
try {
CodecUtil.checkHeader(in, CODEC_NAME, VERSION_START, VERSION_START);
int count = in.readVInt();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
long commitGen = in.readVLong();
int refCount = in.readVInt();
m.put(commitGen, refCount);
}
} catch (IOException ioe2) {
// 保存第一個捕獲到的異常
if (ioe == null) {
ioe = ioe2;
}
} finally {
in.close();
}
genLoaded = gen;
// 清除舊數據
refCounts.clear();
// 保留最新的
refCounts.putAll(m);
}
}
}
if (genLoaded == -1) { // 沒有加載快照文件
if (ioe != null) { // 加載過程中捕獲到異常了,直接拋出
throw ioe;
}
} else { // 把舊版本的快照文件都刪掉
if (snapshotFiles.size() > 1) {
String curFileName = SNAPSHOTS_PREFIX + genLoaded;
for (String file : snapshotFiles) {
if (!curFileName.equals(file)) {
IOUtils.deleteFilesIgnoringExceptions(dir, file);
}
}
}
nextWriteGen = 1 + genLoaded;
}
}讀到這里,這篇“Lucene索引刪除策略源碼分析”文章已經介紹完畢,想要掌握這篇文章的知識點還需要大家自己動手實踐使用過才能領會,如果想了解更多相關內容的文章,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。