您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“@AliasFor注解如何使用”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“@AliasFor注解如何使用”吧!
@AliasFor注解基本上都是在spring源碼當中出現的,AliasFor是Spring提供的注解,Alias是別名的意思,For是為了,首先我們通過命名可以得出一個結論,他是為了別名而自定義的注解!
Spring中@AliasFor注解的作用有兩點:
將同一個注解類的屬性設置互為別名
將一個注解上的屬性值傳遞給另一個注解
但這并不是java原生支持的,需要通過Spring中提供的工具類:org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils或者org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotatedElementUtils來解析。AnnotatedElementUtils內部還是調用的AnnotationUtils。
源碼如下:它有三個屬性value和attribute以及annotation,@AliasFor注解注釋了自身,并且value和attribute互為別名,通過源碼很容易知道,當我們使用這個注解,
@AliasFor(value=“xxx”)和@AliasFor(attribute=“xxx”)是等價的。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
public @interface AliasFor {
@AliasFor("attribute")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String attribute() default "";
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
}Java 運行時讀取Annotation 需要通過反射,Spring 提供AnnotationUtils , AnnotationElementUtils 用于簡化操作,其他特點如下:
查詢Meta Annotation(注解的注解)
對@AliasFor 解析,生成指定注解的代理,并賦值。(注:定義其他Annotation 的別名)
Utils 調用涉及的元素:
Annotation: Annotation 元數據
AnnotatedElement: 被Annotation注解的對象,包括annotation , class , method等
Method: 類和接口中的方法信息
AnnotationUtils常用方法:
getAnnotation: 從某個類獲取某個annotation
findAnnotation: 從類或方法中查找某個annotation。
isAnnotationDeclaredLocally: 驗證annotation是否直接注釋在類上而不是集成來的。
isAnnotationInherited: 驗證annotation是否繼承于另一個class。
getAnnotationAttributes: 獲取annotation的所有屬性。
getValue: 獲取指定annotation的值.
getDefaultValue: 獲取指定annotation或annotation 屬性的默認值
AnnotatedElementUtils常用方法:
findMergedAnnotation:這個方法會合并@AliasFor傳遞的值
一共有兩個屬性
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface EnableCVS {
// 這里就算是改成@AliasFor(attribute = "address")測試結果也是一樣的
@AliasFor(value = "address")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor(value = "value")
String address() default "";
}然后使用自定義的注解@EnableCVS修飾
@Configuration
@EnableCVS(address = "hhh")
public class AppConfig {
}import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// spring提供的
EnableCVS annotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(AppConfig.class, EnableCVS.class);
System.out.println("AnnotationUtils:address:" + annotation.address());
System.out.println("AnnotationUtils:value:" + annotation.value());
// jdk原生
EnableCVS annotation1 = AppConfig.class.getAnnotation(EnableCVS.class);
System.out.println("AppConfig:address:" + annotation1.address());
System.out.println("AppConfig:value:" + annotation1.value());
}
}首先我們設置的注解是@EnableCVS(address = "hhh") ,只設置了address屬性,并沒有設置value屬性,會發現jdk原生方式獲取value的時候是拿不到值的,而spring提供的AnnotationUtils卻可以獲取到,而且獲取到的就是address的值!
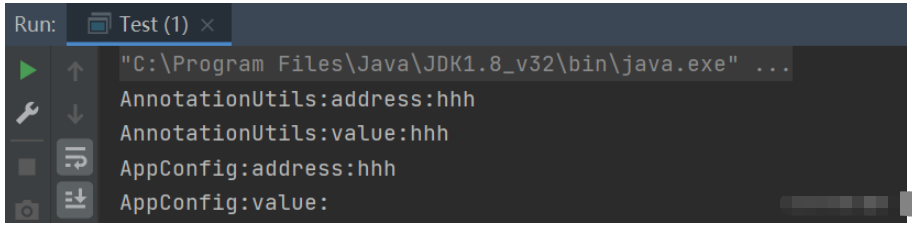
其實就可以理解為,一旦value值設置了如下注解@AliasFor(value = "address"),也就意味著通過AnnotationUtils來獲取value屬性值的時候,當value值沒有設置的時候,實際上會去獲取address屬性的值!
@AliasFor(value = "address") String value() default "";
注意:如果@AliasFor注解當中兩個屬性互相設置了@AliasFor別名,并且使用自定義注解的時候,同時設置address和value的值,這時候通過AnnotationUtils#findAnnotation(Class<?>, annotationType)獲取屬性值,則會拋出異常!
示例如下:
@Configuration
@EnableCVS(value = "hhh",address = "222")
public class AppConfig {
}@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Scope("singleton")
@Component
@Inherited
public @interface SingletonComponent {
@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class, attribute = "value")
String value() default "";
}使用@SingletonComponent修飾
@SingletonComponent("simpleService")
public class SimpleSingletonService {
}import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotatedElementUtils;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
// 這個注解一定要加,不然getAllAnnocations方法獲取不到值
@ComponentScan
public class AnnotationUtilsDemo {
private static void annotationUtilsDemo() {
// 獲取類注解
SingletonComponent singletonComponentAnnocation = AnnotationUtils.
findAnnotation(SimpleSingletonService.class, SingletonComponent.class);
System.out.println("@SingletonComponent : " + singletonComponentAnnocation);
System.out.println("@SingletonComponent value: " + AnnotationUtils.getValue(singletonComponentAnnocation, "value"));
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------");
Scope scopeAnnocation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(SimpleSingletonService.class, Scope.class);
System.out.println("@Scope : " + scopeAnnocation);
System.out.println("@Scope value: " + AnnotationUtils.getValue(scopeAnnocation, "scopeName"));
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------");
// 獲取@AliasFor Marge 后的注解,直接調用 AnnotationUtils的方法不會組合@AliasFor的值,需要調用AnnotatedElementUtils
Component componentAnnocation = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(SimpleSingletonService.class, Component.class);
System.out.println("@Component : " + componentAnnocation);
System.out.println("@Component value: " + AnnotationUtils.getValue(componentAnnocation, "value"));
}
private static void getAllAnnocations() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AnnotationUtilsDemo.class);
// 獲取SingletonComponent注解修飾的類
Map<String, Object> beans = context.getBeansWithAnnotation(SingletonComponent.class);
for (Object bean : beans.values()) {
System.out.println("bean : " + bean);
// @SingletonComponent 繼承了 @Component 所以存在實例,@Component的value值就是通過@AliasFor注解傳遞過去的
Component componentAnnocation = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(bean.getClass(), Component.class);
System.out.println(componentAnnocation);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationUtilsDemo.annotationUtilsDemo();
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------");
AnnotationUtilsDemo.getAllAnnocations();
}
}Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:49763', transport: 'socket'
@SingletonComponent : @com.gzl.cn.springbootnacos.aa.SingletonComponent(value="simpleService")
@SingletonComponent value: simpleService
----------------------------------------------
@Scope : @org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope(proxyMode=DEFAULT, scopeName="singleton", value="singleton")
@Scope value: singleton
----------------------------------------------
@Component : @org.springframework.stereotype.Component(value="simpleService")
@Component value: simpleService
----------------------------------------------
bean : com.gzl.cn.springbootnacos.aa.SimpleSingletonService@1b759d6
@org.springframework.stereotype.Component(value="simpleService")
如下所示@SpringBootApplication并沒有定義新的屬性,而是復用其他注解已有的注解屬性,并對其進行組合形成新的注解從而到達到便捷的目的。
這樣的注解我們可以稱之為復合注解。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
String[] excludeName() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackages"
)
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackageClasses"
)
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "nameGenerator"
)
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;
@AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}所以在使用SpringBoot 時我們只需要@SpringBootApplication一個注解就能開啟自動配置,自動掃描的功能。
而不再需要使下面三個注解來達到同樣的目的。
@Configuration @ComponentSan @EnnableAutoConfiguration
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
String name() default "";
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
String[] params() default {};
String[] headers() default {};
String[] consumes() default {};
String[] produces() default {};
}到此,相信大家對“@AliasFor注解如何使用”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。