您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本文小編為大家詳細介紹“Python Beautiful Soup模塊如何使用”,內容詳細,步驟清晰,細節處理妥當,希望這篇“Python Beautiful Soup模塊如何使用”文章能幫助大家解決疑惑,下面跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來學習新知識吧。
Beautiful Soup 是一個可以從HTML或XML文件中提取數據的Python庫.它能夠通過你喜歡的轉換器實現慣用的文檔導航,查找,修改文檔的方式.Beautiful Soup會幫你節省數小時甚至數天的工作時間.
# 引入 html_doc = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" rel="external nofollow" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" rel="external nofollow" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" rel="external nofollow" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser')
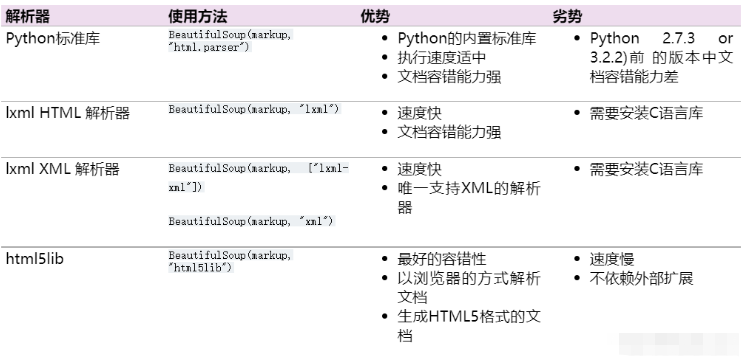
四種解析器
#獲取Tag,通俗點就是HTML中的一個個標簽
#獲取Tag,通俗點就是HTML中的一個個標簽
soup.title # 獲取整個title標簽字段:<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
soup.title.name # 獲取title標簽名稱 :title
soup.title.parent.name # 獲取 title 的父級標簽名稱:head
soup.p # 獲取第一個p標簽字段:<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
soup.p['class'] # 獲取第一個p中class屬性值:title
soup.p.get('class') # 等價于上面
soup.a # 獲取第一個a標簽字段
soup.find_all('a') # 獲取所有a標簽字段
soup.find(id="link3") # 獲取屬性id值為link3的字段
soup.a['class'] = "newClass" # 可以對這些屬性和內容等等進行修改
del bs.a['class'] # 還可以對這個屬性進行刪除
soup.find('a').get('id') # 獲取class值為story的a標簽中id屬性的值
soup.title.string # 獲取title標簽的值 :The Dormouse's story方法一:獲取單個屬性
soup.find_all('div',id="even") # 獲取所有id=even屬性的div標簽
soup.find_all('div',attrs={'id':"even"}) # 效果同上
方法二:
soup.find_all('div',id="even",class_="square") # 獲取所有id=even并且class=square屬性的div標簽
soup.find_all('div',attrs={"id":"even","class":"square"}) # 效果同上方法一:通過下標方式提取
for link in soup.find_all('a'):
print(link['href']) //等同于 print(link.get('href'))
方法二:利用attrs參數提取
for link in soup.find_all('a'):
print(link.attrs['href'])divs = soup.find_all('div') # 獲取所有的div標簽
for div in divs: # 循環遍歷div中的每一個div
a = div.find_all('a')[0] # 查找div標簽中的第一個a標簽
print(a.string) # 輸出a標簽中的內容
如果結果沒有正確顯示,可以轉換為list列表去除\n換行符等其他內容 stripped_strings
divs = soup.find_all('div')
for div in divs:
infos = list(div.stripped_strings) # 去掉空格換行等
bring(infos)prettify() 方法將Beautiful Soup的文檔樹格式化后以Unicode編碼輸出,每個XML/HTML標簽都獨占一行
markup = '<a href="http://example.com/" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >I linked to <i>example.com</i></a>' soup = BeautifulSoup(markup) soup.prettify() # '<html>\n <head>\n </head>\n <body>\n <a href="http://example.com/" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >\n...' print(soup.prettify()) # <html> # <head> # </head> # <body> # <a href="http://example.com/" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" > # I linked to # <i> # example.com # </i> # </a> # </body> # </html>
如果只想得到tag中包含的文本內容,那么可以調用 get_text() 方法,這個方法獲取到tag中包含的所有文版內容包括子孫tag中的內容,并將結果作為Unicode字符串返回:
markup = '<a href="http://example.com/" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >\nI linked to <i>example.com</i>\n</a>' soup = BeautifulSoup(markup) soup.get_text() u'\nI linked to example.com\n' soup.i.get_text() u'example.com'
讀到這里,這篇“Python Beautiful Soup模塊如何使用”文章已經介紹完畢,想要掌握這篇文章的知識點還需要大家自己動手實踐使用過才能領會,如果想了解更多相關內容的文章,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。