您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本文小編為大家詳細介紹“怎么使用numpy中的norm()函數求范數”,內容詳細,步驟清晰,細節處理妥當,希望這篇“怎么使用numpy中的norm()函數求范數”文章能幫助大家解決疑惑,下面跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來學習新知識吧。
函數:
norm(x, ord = None, axis = None, keepdims = False)
ord表示求什么類型的范數
import numpy as np x = [1,2,3,4] x1 = np.linalg.norm(x=x, ord=1) x2 = np.linalg.norm(x=x, ord=2) x3 = np.linalg.norm(x=x, ord=np.inf) print(x1) print(x2) print(x3)
運行結果:
axis=0表示對矩陣的每一列求范數,axis=1表示對矩陣的每一行求范數, keeptdims=True表示結果保留二維特性,keepdims=False表示結果不保留二維特性
import numpy as np x = np.array([[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5]]) x1 = np.linalg.norm(x=x, ord=1, axis=0, keepdims=True) x2 = np.linalg.norm(x=x, ord=1, axis=1, keepdims=True) x3 = np.linalg.norm(x=x, ord=1, axis=0, keepdims=False) x4 = np.linalg.norm(x=x, ord=1, axis=1, keepdims=False) print(x1) print(x2) print(x3) print(x4)
運行結果:
numpy.linalg.norm
numpy.linalg.norm(x,ord=None,axis=None,keepdims=False)
x: array_like
Input array. If
axisis None, x must be 1-D or 2-D, unlessordis None. If bothaxisandordare None, the 2-norm ofx.ravelwill be returned.
X是輸入的array, array的情況必須是以下三種情況之一:
axis未指定,ord指定。此時x必須是一維或二維數組
axis指定,x任意
axis未指定,ord未指定,此時x任意,返回值為x被展平后的一維向量x.ravel的二范數。
ord:{non-zero int, inf, -inf, ‘fro’, ‘nuc’}, optional
Order of the norm (see table under Notes). inf means numpy’s inf object. The default is None.
范數的階數,可以不指定。默認為None。inf代表無窮大,-inf為無窮小。
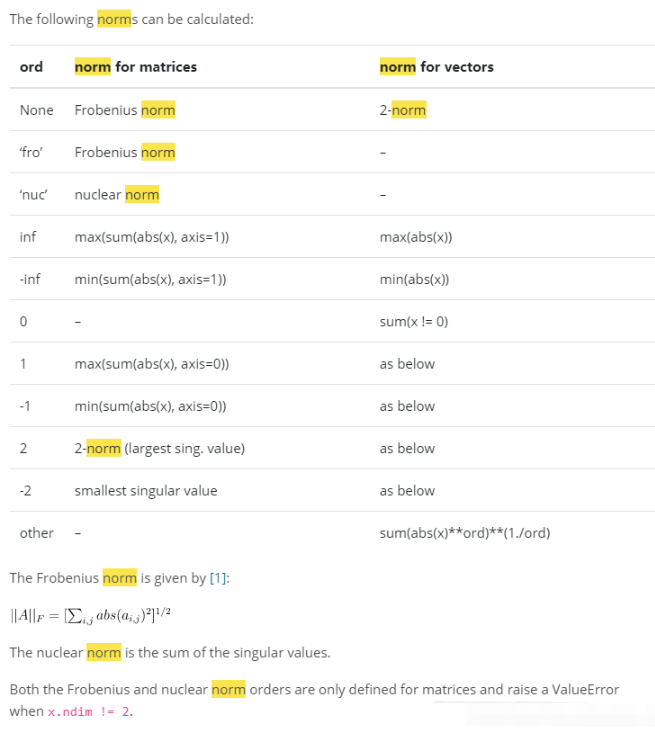
可選的階數見下圖:
axis:{None, int, 2-tuple of ints},optional
If
axisis an integer, it specifies theaxisof x along which to compute the vector norms. Ifaxisis a 2-tuple, it specifies the axes that hold 2-D matrices, and the matrix norms of these matrices are computed. If axis is None then either a vector norm (when x is 1-D) or a matrix norm (when x is 2-D) is returned. The default is None.
如果axis是整數,指定了一個維度,在該維度上按照向量進行范數計算。如果是一個二元整數組,指定了兩個維度,在指定的這兩個維度上可以構成矩陣。
對這些矩陣進行計算。如果沒有指定axis,那么對于一維輸入返回其向量形式的范數計算值,對于二維輸入返回其矩陣形式的范數。默認值為None
keepdims: bool, optional
If this is set to True, the axes which are normed over are left in the result as dimensions with size one. With this option the result will broadcast correctly against the original x.
如果keepdims=True,被指定計算范數的維度將在返回結果中保留,其size為1。計算結果會在該維度上進行broadcast
NOTE: 對于ord<1的各個范數,結果在嚴格意義不等于數學意義上的范數。但在數值計算層面仍然有效。

默認情況
當不指定ord時,即ord = None,對于矩陣,計算其Frobenius norm,對于向量,計算其2-norm
Frobenius范數
ord = 'fro'
其公式為:
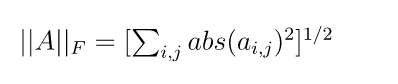
F范數只對矩陣存在。其值為對所有元素的絕對值的平方求和后開平方。
Nuclear范數(核范數)
ord = 'nuc'
只對矩陣存在,矩陣的核范數等于其所有奇異值的和。
無窮大范數
對于矩陣:max(sum(abs(x), axis=1)) ,每一行最終得到一個數,返回最大的數。
對于向量:max(abs(x)
無窮小范數
對于矩陣: min(sum(abs(x),axis=1)),每一行得到一個數,返回最小的數。
對于向量: min(abs(x))
0 范數
對于矩陣:不存在
對于向量:sum(x!=0) 所有非零元素的和
1 范數
對于矩陣:max(sum(abs(x)),axis=0,每一列得到一個數,返回最大值。
對于向量:sum(abs(x)**ord)**(1./ord)
-1 范數
對于矩陣:min(sum(abs(x)),axis=0,每一列得到一個數,返回最小值。
對于向量:sum(abs(x)**ord)**(1./ord)
2 范數
對于矩陣:最大的奇異值
對于向量:sum(abs(x)**ord)**(1./ord)
-2范數
對于矩陣:最小的奇異值
對于向量:sum(abs(x)**ord)**(1./ord)
其余int值對應的范數
對于矩陣: Undefined
對于向量:sum(abs(x)**ord)**(1./ord)
讀到這里,這篇“怎么使用numpy中的norm()函數求范數”文章已經介紹完畢,想要掌握這篇文章的知識點還需要大家自己動手實踐使用過才能領會,如果想了解更多相關內容的文章,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。