您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
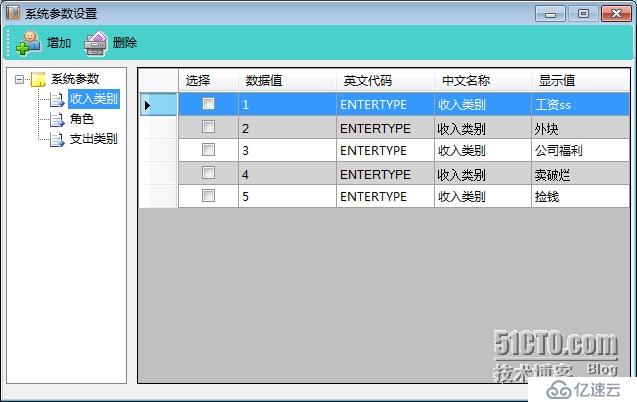
上一篇,我們看了用戶注冊,本片我們來看一下系統參數管理,C#版本的界面如下,我記得我在java實戰篇也寫過這個界面
那么今天我們來看一下Android中是如何實現這個東西。首先先來看一下Service端。
首先是新增加一個asmx。
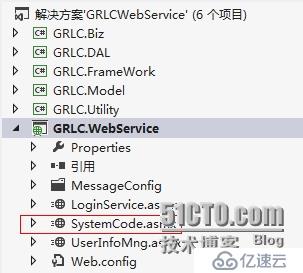
我們來看一下它內部提供的方法
[WebService(Namespace = "http://tempuri.org/")]
[WebServiceBinding(ConformsTo = WsiProfiles.None)]
[System.ComponentModel.ToolboxItem(false)]
// 若要允許使用 ASP.NET AJAX 從腳本中調用此 Web 服務,請取消注釋以下行。
// [System.Web.Script.Services.ScriptService]
public class SystemCode : System.Web.Services.WebService
{
[WebMethod(Description = "添加系統參數")]
public CommonResponse AddSystemCode(SystemCodeEntity systemCodeEntity,string userID)
{
return SystemCodeBiz.GetInstance().AddSystemCode(systemCodeEntity,userID);
}
[WebMethod(Description = "修改系統參數")]
public CommonResponse UpdateSystemCode(SystemCodeEntity systemCodeEntity, string userID)
{
return SystemCodeBiz.GetInstance().UpdateSystemCode(systemCodeEntity, userID);
}
[WebMethod(Description = "獲取系統參數列表", MessageName = "GetSytemCodeEntityList")]
public List<SystemCodeEntity> GetSytemCodeEntityList()
{
return SystemCodeBiz.GetInstance().GetSytemCodeEntityList();
}
[WebMethod(Description = "獲取系統參數列表", MessageName = "GetSytemCodeEntityListByEname")]
public List<SystemCodeEntity> GetSytemCodeEntityList(string ename)
{
return SystemCodeBiz.GetInstance().GetSytemCodeEntityList(ename);
}
}第一個方法是添加系統參數,第二個方法是修改系統參數,第三個方法是獲取系統參數列表,第四個方法是根據ename獲取系統參數列表。如果不知道什么是ename,請看第一篇。
OK,這四個方法對應的Biz層的代碼如下
namespace GRLC.Biz
{
public class SystemCodeBiz
{
static SystemCodeBiz systemCodeBiz = new SystemCodeBiz();
private SystemCodeBiz()
{ }
public static SystemCodeBiz GetInstance()
{
return systemCodeBiz;
}
const string moduleName = "SystemCodeModule";
private string GetMessageByName(string msgName)
{
return CommonFunction.GetMessageByModuleAndName(moduleName, msgName);
}
private string EnameExists
{
get
{
return this.GetMessageByName("EnameHasExists");
}
}
private string DataHasExists
{
get
{
return this.GetMessageByName("DataHasExists");
}
}
private string AddFailed
{
get
{
return this.GetMessageByName("AddFailed");
}
}
private string UpdateFailed
{
get
{
return this.GetMessageByName("UpdateFailed");
}
}
private string DisplayContentExists
{
get
{
return this.GetMessageByName("DisplayContentExists");
}
}
public CommonResponse AddSystemCode(SystemCodeEntity systemCodeEntity, string userID)
{
bool isEnameExists = SystemCodeDAL.GetInstance().CheckIfEnameExists(systemCodeEntity.Ename);
if (isEnameExists)
{
return new CommonResponse() { IsSuccess = false, ErrorMessage = EnameExists };
}
bool isDataExists = SystemCodeDAL.GetInstance().CheckIfDataExists(systemCodeEntity.Ename, systemCodeEntity.Cname);
if (isDataExists)
{
return new CommonResponse() { IsSuccess = false, ErrorMessage = DataHasExists };
}
bool isDisplayContentExists = SystemCodeDAL.GetInstance().CheckIfDisplayContentExists(systemCodeEntity.Ename, systemCodeEntity.DisplayContent);
int suc = SystemCodeDAL.GetInstance().AddSystemCode(systemCodeEntity, userID);
if (suc > 0)
{
return new CommonResponse() { IsSuccess = true };
}
else
{
return new CommonResponse() { IsSuccess = false, ErrorMessage = AddFailed };
}
}
public CommonResponse UpdateSystemCode(SystemCodeEntity systemCodeEntity, string userID)
{
bool isDisplayContentExists = SystemCodeDAL.GetInstance().CheckIfDisplayContentExists(systemCodeEntity.Ename, systemCodeEntity.DisplayContent);
if (isDisplayContentExists)
{
return new CommonResponse() { IsSuccess = false, ErrorMessage = DisplayContentExists };
}
int suc = SystemCodeDAL.GetInstance().UpdateSystemCode(systemCodeEntity, userID);
if (suc > 0)
{
return new CommonResponse() { IsSuccess = true };
}
else
{
return new CommonResponse() { IsSuccess = false, ErrorMessage = UpdateFailed };
}
}
public List<SystemCodeEntity> GetSytemCodeEntityList()
{
return SystemCodeDAL.GetInstance().GetSytemCodeEntityList();
}
public List<SystemCodeEntity> GetSytemCodeEntityList(string ename)
{
List<SystemCodeEntity> systemCodeEntityList = this.GetSytemCodeEntityList();
if (systemCodeEntityList != null)
{
return systemCodeEntityList.Where(s => s.Ename == ename).OrderBy(s => s.Data).ToList();
}
return systemCodeEntityList;
}
}
}對應的DAL層的方法如下
namespace GRLC.DAL
{
public class SystemCodeDAL
{
static SystemCodeDAL systemCodeDAL = new SystemCodeDAL();
private SystemCodeDAL()
{ }
public static SystemCodeDAL GetInstance()
{
return systemCodeDAL;
}
public int AddSystemCode(SystemCodeEntity systemCodeEntity, string userID)
{
using (BonusEntities bonusEntities = new BonusEntities())
{
Codes code = new Codes();
code.ename = systemCodeEntity.Ename;
code.cname = systemCodeEntity.Cname;
code.data = systemCodeEntity.Data;
code.display_content = systemCodeEntity.DisplayContent;
code.create_time = DateTime.Now;
code.lastmodify_date = DateTime.Now;
code.lastmodifier = userID;
code.create_person = userID;
bonusEntities.Codes.Add(code);
return bonusEntities.SaveChanges();
}
}
public int UpdateSystemCode(SystemCodeEntity systemCodeEntity, string userID)
{
using (BonusEntities bonusEntities = new BonusEntities())
{
Codes code = new Codes();
code.ename = systemCodeEntity.Ename;
code.cname = systemCodeEntity.Cname;
code.data = systemCodeEntity.Data;
code.display_content = systemCodeEntity.DisplayContent;
code.lastmodify_date = DateTime.Now;
code.lastmodifier = userID;
bonusEntities.Entry(code).State = EntityState.Modified;
return bonusEntities.SaveChanges();
}
}
public bool CheckIfEnameExists(string ename)
{
using (BonusEntities bonusEntities = new BonusEntities())
{
return bonusEntities.Codes.Any(c => c.ename == ename);
}
}
public bool CheckIfDataExists(string ename, string data)
{
using (BonusEntities bonusEntities = new BonusEntities())
{
return bonusEntities.Codes.Any(c => c.ename == ename && c.data == data);
}
}
public bool CheckIfDisplayContentExists(string ename, string displayContent)
{
using (BonusEntities bonusEntities = new BonusEntities())
{
return bonusEntities.Codes.Any(c => c.ename == ename && c.display_content == displayContent);
}
}
public List<SystemCodeEntity> GetSytemCodeEntityList()
{
List<SystemCodeEntity> systemCodeEntityList = new List<SystemCodeEntity>();
using (BonusEntities bonusEntities = new BonusEntities())
{
SystemCodeEntity systemCodeEntity = null;
List<Codes> codeList = bonusEntities.Codes.ToList();
foreach (var code in codeList)
{
systemCodeEntity = new SystemCodeEntity();
systemCodeEntity.Cname = code.cname;
systemCodeEntity.Ename = code.ename;
systemCodeEntity.Data = code.data;
systemCodeEntity.DisplayContent = code.display_content;
systemCodeEntityList.Add(systemCodeEntity);
}
}
return systemCodeEntityList;
}
}
}OK,完了我們部署Service進行訪問
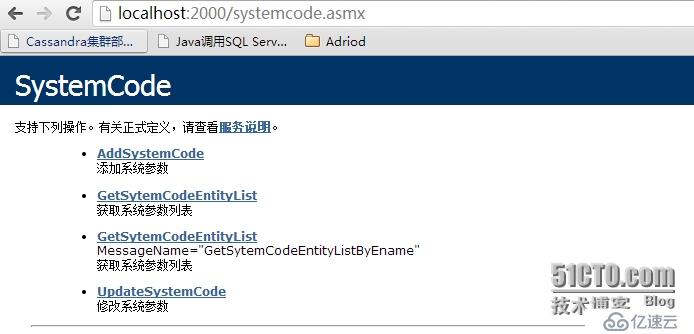
點擊第三個方法,如下,輸入ename,點擊調用

點擊調用返回的xml數據如下

OK,這證明我們的service沒問題。接下來看android部分,首先從index界面跳到系統參數界面
p_w_picpathBtnSystemCode=(ImageButton)this.findViewById(R.id.p_w_picpathBtnSystemCode);
p_w_picpathBtnSystemCode.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(index.this,systemcode.class);
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
}
});SystemCode界面的代碼如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<ExpandableListView android:id="@+id/expandableListView"
android:dividerHeight="1dp"
android:divider="@color/yellow"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</ExpandableListView>
</LinearLayout>只有一個ExpandedListView。在后臺代碼中,我們首先會初始化數據
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.systemcode);
InitCodesInfo();
}我們看一下這個InitCodesInfo方法
private void InitCodesInfo() {
expandableListView = (ExpandableListView) findViewById(R.id.expandableListView);
List<Map<String, String>> groups = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
Map<String, String> root = new HashMap<String, String>();
root.put("root", "系統參數");
groups.add(root);
SoapObject soapChild = null;
List<String> enameList = new ArrayList<String>();
Map<String, String> leaf = null;
List<Map<String, String>> leafList = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
leaves = new ArrayList<List<Map<String, String>>>();
SoapObject soapObject = this.GetSystemCodeList();
for (int i = 0; i < soapObject.getPropertyCount(); i++) {
soapChild = (SoapObject) soapObject.getProperty(i);
String ename = soapChild.getProperty("Ename").toString();
String cname = soapChild.getProperty("Cname").toString();
if (!enameList.contains(ename)) {
leaf = new HashMap<String, String>();
leaf.put("Key", ename);
leaf.put("Name", cname);
leafList.add(leaf);
enameList.add(ename);
}
}
leaves.add(leafList);
SimpleExpandableListAdapter adapter = new SimpleExpandableListAdapter(
this, groups, R.layout.expandlist_group,
new String[] { "root" }, new int[] { R.id.textGroup }, leaves,
R.layout.expandlist_child, new String[] { "Key", "Name" },
new int[] { R.id.textChildID, R.id.textChildName });
expandableListView.setAdapter(adapter);
expandableListView.setOnChildClickListener(listener);
expandableListView.expandGroup(0);
}在這個方法中首先要看的是GetSystemCodeList方法,這個方法就是調用webservice提供的GetSytemCodeEntityList方法。我們看下代碼
private SoapObject GetSystemCodeList() {
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(NAMESPACE, METHOD_NAME);
SoapSerializationEnvelope soapEnvelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(
SoapEnvelope.VER11);
soapEnvelope.dotNet = true;
soapEnvelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);
HttpTransportSE httpTS = new HttpTransportSE(URL);
soapEnvelope.bodyOut = httpTS;
soapEnvelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);// 設置請求參數
try {
httpTS.call(SOAP_ACTION, soapEnvelope);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
SoapObject result = null;
try {
result = (SoapObject) soapEnvelope.getResponse();
} catch (SoapFault e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}NameSpace,MethodName等參數如下
final static String NAMESPACE = "http://tempuri.org/";
final static String METHOD_NAME = "GetSytemCodeEntityList";
final static String SOAP_ACTION = "http://tempuri.org/GetSytemCodeEntityList";
final static String URL = "http://10.0.2.2:2000/SystemCode.asmx?wsdl";OK,這個掉用完之后,就是構造數據了,我們先看一下圖
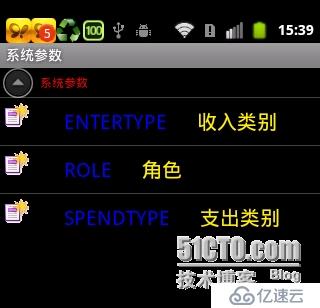
那么這個listView的數據正是由那個for循環實現的。因為我們只有一個根節點,所以我們只加了一個
root.put("root", "系統參數");
然后接下來我們要構造出下面的子節點,我們把ename當做key,把cname當做value加進HashMap<String, String>中。每一次循環,我們會得到一條數據加進Map<String,String>中,再把它加進List<Map<String,String>>中。最后將List<Map<String,String>>加進List<List<Map<String, String>>>中。數據構造好以后,就是展示了
SimpleExpandableListAdapter adapter = new SimpleExpandableListAdapter(
this, groups, R.layout.expandlist_group,
new String[] { "root" }, new int[] { R.id.textGroup }, leaves,
R.layout.expandlist_child, new String[] { "Key", "Name" },
new int[] { R.id.textChildID, R.id.textChildName });
expandableListView.setAdapter(adapter);
expandableListView.setOnChildClickListener(listener);
expandableListView.expandGroup(0);第一個參數是頁面本身對象,第二個參數是根節點的數據,第三個參數是展示根節點的布局文件
一個是根節點的布局文件expandlist_group.xml,內容如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView android:id="@+id/textGroup" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:paddingLeft="40px"
android:paddingTop="6px" android:paddingBottom="6px" android:textSize="12sp"
android:textColor="@color/red"
android:text="No data">
</TextView>
</LinearLayout>另一個是子節點的布局文件expandlist_child.xml,內容如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ImageView android:id="@+id/civ" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/main_system_code"
android:maxWidth="20dp" android:maxHeight="20dp" android:padding="5dp" />
<TextView android:id="@+id/textChildID" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:paddingLeft="30px"
android:textColor="@color/blue"
android:paddingTop="10px"
android:paddingBottom="10px"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView android:id="@+id/textChildName" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:textColor="@color/yellow"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:paddingLeft="30px"
android:text="No data" />
</LinearLayout>第四個參數是根節點的key值root,如果你有很多的根節點,那么這里可以有多個。第五個參數是設置用expandlist_group.xml布局模版中哪個控件來顯示根節點的內容。第六個參數是子節點的數據,第七個參數是要展示子節點內容的布局模版。第八個參數是設置要顯示的字段,第九個參數每個參數對應的展示控件。OK,最終運行出來的效果如上圖所示。
OK,接下來我們看看點擊某個子節點,展示其詳細內容的界面的部分。先看一下跳轉
private OnChildClickListener listener = new OnChildClickListener() {
public boolean onChildClick(ExpandableListView parent, View v,
int groupPosition, int childPosition, long id) {
Object ename = leaves.get(0).get(childPosition).values().toArray()[1];
Intent intent = new Intent();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("ename", ename.toString());
intent.putExtras(bundle);
intent.setClass(systemcode.this, systemcodedetail.class);
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
finish();
return false;
}
};我們首先會拿到ename,這個ename在這里的話,因為leaves集合中只有一項。所以在這里是get(0)。
然后我們根據position,即第一行就是0,第二行就是1。根據position我們拿到點擊的行的數據values。那么values[1]就是ename,values[0]就是cname。
拿到ename直接傳到systemcodedetail界面。systemcodedetailUI代碼如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/ls"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ListView android:id="@+id/codelistView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>其后臺接收到ename之后會初始化數據
private void InitData() {
Bundle bundle = getIntent().getExtras();
String enameValue = bundle.getString("ename");
List<Map<String, Object>> dataList = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
Map<String, Object> dataMap = null;
SoapObject soapObject = this.GetSystemCodeListByEname(enameValue);
for (int i = 0; i < soapObject.getPropertyCount(); i++) {
SoapObject soapObj = (SoapObject) soapObject.getProperty(i);
dataMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
String displayContent = soapObj.getProperty("DisplayContent")
.toString();
String cname = soapObj.getProperty("Cname").toString();
String data = soapObj.getProperty("Data").toString();
dataMap.put("displaycontent", displayContent);
dataMap.put("cname", cname);
dataMap.put("data", data);
dataList.add(dataMap);
}
SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(this, dataList,
R.layout.systemcodedetailtemplate, new String[] { "cname",
"data", "displaycontent" }, new int[] { R.id.labCname,
R.id.labData,R.id.labDisplay });
this.codeListView.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);
}他獲取數據的方法是GetSystemCodeListByEname
private SoapObject GetSystemCodeListByEname(String ename) {
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(NAMESPACE, METHOD_NAME);
PropertyInfo pi = new PropertyInfo();
pi.setName("ename");
pi.setType(String.class);
pi.setValue(ename);
request.addProperty(pi);
SoapSerializationEnvelope soapEnvelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(
SoapEnvelope.VER11);
soapEnvelope.dotNet = true;
soapEnvelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);
HttpTransportSE httpTS = new HttpTransportSE(URL);
soapEnvelope.bodyOut = httpTS;
soapEnvelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);// 設置請求參數
try {
httpTS.call(SOAP_ACTION, soapEnvelope);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
SoapObject result = null;
try {
result = (SoapObject) soapEnvelope.getResponse();
} catch (SoapFault e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}其對應的NameSpace,Method_Name參數如下
final static String NAMESPACE = "http://tempuri.org/";
final static String METHOD_NAME = "GetSytemCodeEntityListByEname";
final static String SOAP_ACTION = "http://tempuri.org/GetSytemCodeEntityListByEname";
/* final static String URL = "http://10.0.2.2:2000/SystemCode.asmx?wsdl";*/
final static String URL = "http://172.19.73.18:2000/SystemCode.asmx?wsdl";OK,在初始化方法中,我們構造出了List<Map<String, Object>>集合。
然后通過下面的方法呈現數據到界面
SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(this, dataList,
R.layout.systemcodedetailtemplate, new String[] { "cname",
"data", "displaycontent" }, new int[] { R.id.labCname,
R.id.labData,R.id.labDisplay });
this.codeListView.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);第一個參數當前Activity對象,第二個參數是數據源。第三個參數是展示數據的布局模版。如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="75dp"
android:paddingLeft="10dp" android:paddingRight="10dp">
<ImageView android:id="@+id/img" android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_width="60dp" android:src="@drawable/userregister"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" />
<LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:gravity="center_vertical" android:layout_toRightOf="@id/img"
android:paddingLeft="8dp">
<TextView android:id="@+id/labCname" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textColor="#cbcaca"
android:textSize="12dp" />
<TextView android:id="@+id/labData" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textColor="#cbcaca"
android:textSize="12dp" />
<TextView android:id="@+id/labDisplay" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textColor="#cbcaca"
android:textSize="12dp" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content">
<Button android:id="@+id/btnUpdate" android:text="@string/btnUpdate"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
<Button android:id="@+id/btnDelete" android:text="@string/btnDelete"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>OK,這個布局使用了相對布局和線性布局的嵌套。第四個參數是指要顯示的字段。第五個參數是指分別顯示這些字段的控件。OK,跑起來看看效果

效果還湊合,至于修改和刪除嘛,請留意下節。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。