您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇“C++怎么實現兩個線程交替打印”文章的知識點大部分人都不太理解,所以小編給大家總結了以下內容,內容詳細,步驟清晰,具有一定的借鑒價值,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章能有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看這篇“C++怎么實現兩個線程交替打印”文章吧。
首先簡單搭一個框架,讓兩個線程先嘗試實現交替打印。
//實現兩個線程交替打印
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int n = 100;
int i = 0;
//創建兩個線程
thread t1([&n, &i](){
while (i < n)
{
cout << i << " ";
i++;
}
});
thread t2([&n, &i]() {
while (i < n)
{
cout << i << " ";
i++;
}
});
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
return 0;
}為了讓我們更加清楚是哪個線程打印了,我們需要獲取線程的ID。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int n = 100;
int i = 0;
//創建兩個線程
thread t1([&n, &i](){
while (i < n)
{
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
}
});
thread t2([&n, &i]() {
while (i < n)
{
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
}
});
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
return 0;
}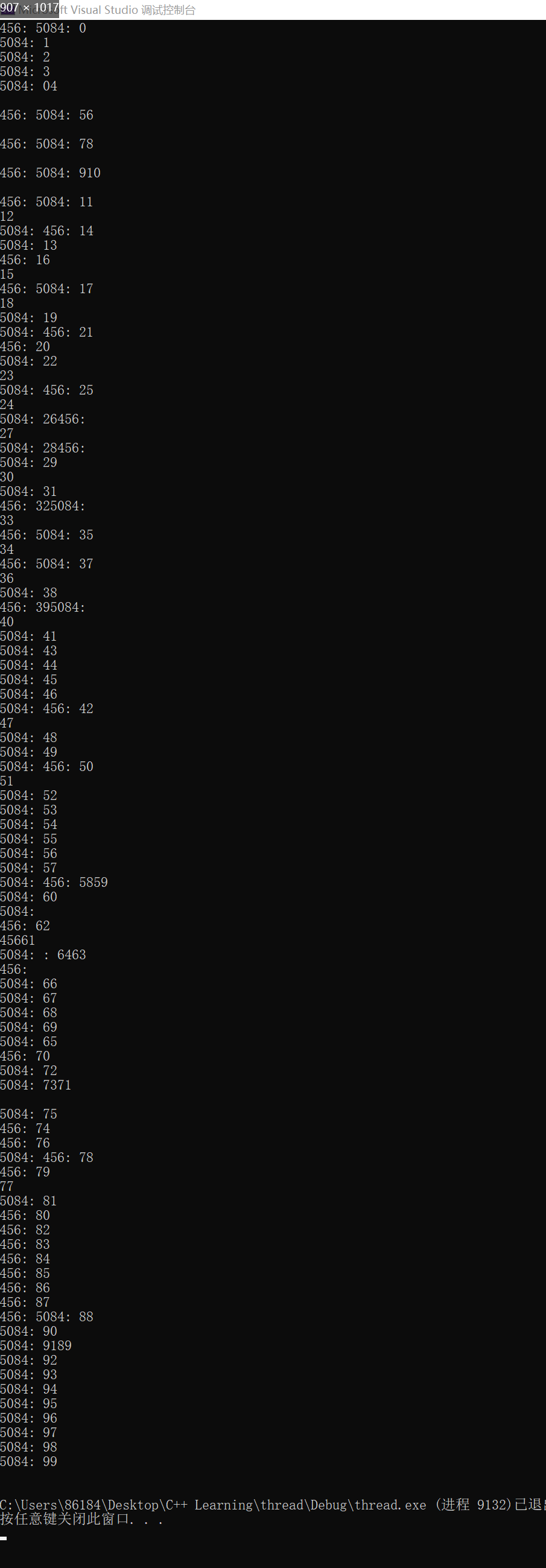
這顯然沒有完成兩個線程交替打印的目的,甚至數據的打印都非常地亂。這是因為i是臨界資源,多個線程爭搶訪問臨界資源可能會造成數據二義,線程是不安全的,需要保證任意時刻只有一個線程能夠訪問臨界資源。
所以創建一個互斥量,并在臨界區合適的地方加鎖和解鎖。由于線程的執行函數我使用了lambda表達式,為了讓兩個線程使用的是同一把鎖,把鎖創建在了main函數內,并在lambda表達式內使用了引用捕捉。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int n = 100;
int i = 0;
mutex mtx;
//創建兩個線程
thread t1([&n, &i, &mtx](){
while (i < n)
{
mtx.lock();
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
mtx.unlock();
}
});
thread t2([&n, &i, &mtx]() {
while (i < n)
{
mtx.lock();
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
mtx.unlock();
}
});
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
return 0;
}在C++中,一般不直接操作鎖,而是由類去管理鎖。
//第一個管理鎖的類 template <class Mutex> class lock_guard; //第二個管理鎖的類 template <class Mutex> class unique_lock;
lock_guar類,只有構造和析構函數。一般用于加鎖和解鎖,這里進行簡單的模擬:
//注意:為了使得加鎖和解鎖的是同一把鎖
//需要使用引用
template <class Lock>
class LockGuard
{
public:
LockGuard(Lock &lck)
:_lock(lck)
{
_lock.lock();
}
~LockGuard()
{
_lock.unlock();
}
private:
Lock &_lock;
};unique_lock的成員方法就不僅僅是析構函數和構造函數。詳見文檔unique_lock介紹和使用。
這里將鎖交給unique_lock類的對象進行管理。
int main(void)
{
int n = 100;
int i = 0;
mutex mtx;
//創建兩個線程
thread t1([&n, &i, &mtx, &cv, &flag](){
while (i < n)
{
unique_lock<mutex> LockManage(mtx);
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
}
});
thread t2([&n, &i, &mtx, &cv, &flag]() {
while (i < n)
{
unique_lock<mutex> LockManage(mtx);
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
}
});
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
return 0;
}
線程是安全了,但如果其中一個線程競爭鎖的能力比較強,那么可能會出現上面這種情況。
需要控制:一個線程執行一次后,如果再次去執行就不準許了,同時可以喚醒另一個進程去執行,如此循環往復達到交替打印的目的。所以可以增加一個條件變量,讓某個線程在該條件變量下的阻塞隊列等待。
C++庫中線程在條件變量下的等待函數第一個參數注意是管理鎖的類對象
int main(void)
{
int n = 100;
int i = 0;
mutex mtx;
condition_variable cv;
bool flag = false;
//創建兩個線程
thread t1([&n, &i, &mtx, &cv, &flag](){
while (i < n)
{
unique_lock<mutex> LockManage(mtx);
//!flag為真,那么獲取后不會阻塞,優先運行
cv.wait(LockManage, [&flag]() {return !flag; });
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
}
});
thread t2([&n, &i, &mtx, &cv, &flag]() {
while (i < n)
{
unique_lock<mutex> LockManage(mtx);
//flag為假,競爭到鎖后,由于條件不滿足,阻塞
cv.wait(LockManage, [&flag]() {return flag; });
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
}
});
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
return 0;
}這里flag以及lambda表達式的增加是非常巧妙的。flag的初始化值為false,讓線程t2在[&flag]() {return false; }下等待,那么t2線程就會先執行。

線程t1競爭到了鎖,但是由于不滿足條件,會繼續等待,所以就出現了上面的情況。
需要一個線程喚醒另一個線程之前,將flag的值進行修改。
int main(void)
{
int n = 100;
int i = 0;
mutex mtx;
condition_variable cv;
bool flag = false;
//創建兩個線程
thread t1([&n, &i, &mtx, &cv, &flag](){
while (i < n)
{
unique_lock<mutex> LockManage(mtx);
//!flag為真,那么獲取后不會阻塞,優先運行
cv.wait(LockManage, [&flag]() {return !flag; });
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
flag = true;
cv.notify_one();
}
});
thread t2([&n, &i, &mtx, &cv, &flag]() {
while (i < n)
{
unique_lock<mutex> LockManage(mtx);
//flag為假,競爭到鎖后,由于條件不滿足,阻塞
cv.wait(LockManage, [&flag]() {return flag; });
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": " << i << endl;
i++;
flag = false;
cv.notify_one();
}
});
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
return 0;
}最終,實現了兩個線程交替打印(一個線程打印奇數、一個線程打印偶數)
以上就是關于“C++怎么實現兩個線程交替打印”這篇文章的內容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小編分享的內容對大家有幫助,若想了解更多相關的知識內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。