溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天小編給大家分享一下Python實現計算AUC的方式有哪些的相關知識點,內容詳細,邏輯清晰,相信大部分人都還太了解這方面的知識,所以分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后有所收獲,下面我們一起來了解一下吧。
AUC(Area Under Curve)被定義為ROC曲線下與坐標軸圍成的面積,顯然這個面積的數值不會大于1。又由于ROC曲線一般都處于y=x這條直線的上方,所以AUC的取值范圍在0.5和1之間。AUC越接近1.0,檢測方法真實性越高;等于0.5時,則真實性最低,無應用價值。
import numpy as np from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score y_true = [1,1,0,0,1,1,0] y_pred = [0.8,0.7,0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5,0.3] print(roc_auc_score(y_true, y_pred)) # 下面實現的是方法1 # https://blog.csdn.net/lieyingkub99/article/details/81266664?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-title-1&spm=1001.2101.3001.4242 def cal_auc1(y_true, y_pred): n_bins = 10 postive_len = sum(y_true) # M正樣本個數 negative_len = len(y_true) - postive_len # N負樣本個數 total_case = postive_len * negative_len # M * N樣本對數 pos_histogram = [0 for _ in range(n_bins)] # 保存每一個概率值下的正樣本個數 neg_histogram = [0 for _ in range(n_bins)] # 保存每一個概率值下的負樣本個數 bin_width = 1.0 / n_bins for i in range(len(y_true)): nth_bin = int(y_pred[i] / bin_width) # 概率值轉化為整數下標 if y_true[i] == 1: pos_histogram[nth_bin] += 1 else: neg_histogram[nth_bin] += 1 print(pos_histogram) print(neg_histogram) accumulated_neg = 0 satisfied_pair = 0 for i in range(n_bins): satisfied_pair += (pos_histogram[i] * accumulated_neg + pos_histogram[i] * neg_histogram[i] * 0.5) print(pos_histogram[i], neg_histogram[i], accumulated_neg, satisfied_pair) accumulated_neg += neg_histogram[i] return satisfied_pair / float(total_case) print(cal_auc1(y_true, y_pred)) # 下面實現的是方法2 # https://blog.csdn.net/lieyingkub99/article/details/81266664?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-title-1&spm=1001.2101.3001.4242 def cal_auc2(y_true, y_pred): n_bins = 10 postive_len = sum(y_true) # M正樣本個數 negative_len = len(y_true) - postive_len # N負樣本個數 total_case = postive_len * negative_len # M * N樣本對數 prob_rank = [0 for _ in range(n_bins)] # 保存每一個概率值的rank prob_num = [0 for _ in range(n_bins)] # 保存每一個概率值出現的次數 bin_width = 1.0 / n_bins raw_arr = [] for i in range(len(y_true)): raw_arr.append([y_pred[i], y_true[i]]) arr = sorted(raw_arr, key=lambda d: d[0]) # 按概率由低到高排序 for i in range(len(arr)): nth_bin = int(arr[i][0] / bin_width) # 概率值轉化為整數下標 prob_rank[nth_bin] = prob_rank[nth_bin] + i + 1 prob_num[nth_bin] = prob_num[nth_bin] + 1 satisfied_pair = 0 for i in range(len(arr)): if arr[i][1] == 1: nth_bin = int(arr[i][0] / bin_width) # 概率值轉化為整數下標 satisfied_pair = satisfied_pair + prob_rank[nth_bin] / prob_num[nth_bin] return (satisfied_pair - postive_len * (postive_len + 1) / 2 ) / total_case print(cal_auc2(y_true, y_pred)) # 根據roc曲線,找不同點算下面積, 需要點足夠多 def cal_auc3(y_true, y_pred): """Summary Args: raw_arr (TYPE): Description Returns: TYPE: Description """ raw_arr = [] for i in range(len(y_true)): raw_arr.append([y_pred[i], y_true[i]]) print(raw_arr) arr = sorted(raw_arr, key=lambda d:d[0], reverse=True) pos, neg = 0., 0. for record in arr: if record[1] == 1.: pos += 1 else: neg += 1 fp, tp = 0., 0. xy_arr = [] for record in arr: if record[1] == 1.: tp += 1 else: fp += 1 xy_arr.append([fp/neg, tp/pos]) print(xy_arr) auc = 0. prev_x = 0. prev_y = 0. for x, y in xy_arr: if x != prev_x: auc += ((x - prev_x) * (y + prev_y) / 2.) prev_x = x prev_y = y print(auc) import numpy as np from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score y_true = [1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0] y_pred = [0.8, 0.7, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.3] print(roc_auc_score(y_true, y_pred))
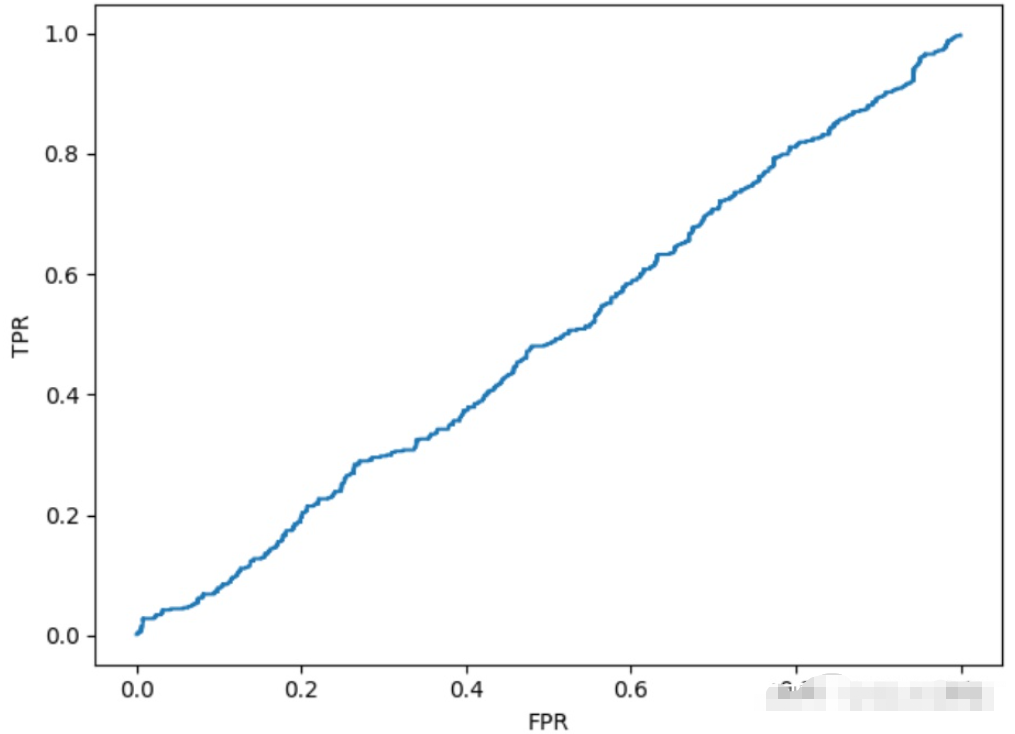
下面是小編為大家找到的另外三個計算AUC的代碼,會輸出三種方法各自的auc,以及通過面積計算AUC時的ROC曲線。
在通過面積計算AUC的方法中,沒有遍歷數據的預測概率作為分類閾值,而是對[0,1]區間等分得到一系列閾值。
# AUC的計算
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
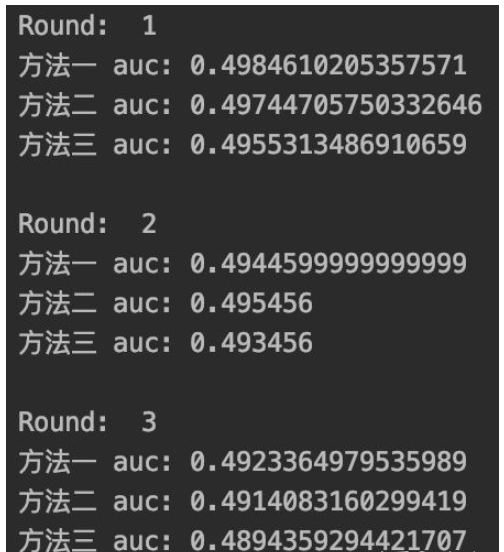
for e in range(3):
print("\nRound: ", e+1)
num = 1000
auc1 = auc2 = auc3 = 0.
# 準備數據
pred_prob = list(np.random.uniform(low=0,high=1, size=[num]))
labels = [int(prob>0.5) for prob in list(np.random.uniform(low=0,high=1, size=[num]))]
# 檢查數據
# print("pred_prob:\n", pred_prob)
# print("labels:\n", labels)
# 方法一,面積加和
roc_point = []
for i in range(num):
i = pred_prob[i]
TP = 0 # 真陽樣本數
FP = 0 # 假陽樣本數
TP_rate = 0. # 真陽率
FP_rate = 0. # 假陽率
pos_num = 0 # 預測真樣本數
# 計數過程
for ind, prob in enumerate(pred_prob):
if prob>i:
pos_num += 1
if prob>i and labels[ind]>0.5:
TP+=1
elif prob>i and labels[ind]<0.5:
FP+=1
if pos_num!=0:
TP_rate = TP / sum(labels)
FP_rate = FP / (num-sum(labels))
roc_point.append([FP_rate, TP_rate]) # 記錄ROC中的點
# 畫出ROC曲線
roc_point.sort(key=lambda x: x[0])
plt.plot(np.array(roc_point)[1:, 0], np.array(roc_point)[1: ,1])
plt.xlabel("FPR")
plt.ylabel("TPR")
plt.show()
# 計算每個小長方形的面積,求和即為auc
lastx = 0.
for x,y in roc_point:
auc1 += (x-lastx)*y # 底乘高
lastx = x
print("方法一 auc:", auc1)
# 方法二,利用AUC關于排列概率的定義計算
auc2 = 0
P_ind = [] # 正樣本下標
F_ind = [] # 負樣本下標
P_F = 0 # 正樣本分數高于負樣本的數量
F_P = 0 # 負樣本分數高于正樣本的數量
# 計數過程
for ind, val in enumerate(labels):
if val > 0.5:
P_ind.append(ind)
else:
F_ind.append(ind)
for Pi in P_ind:
for Fi in F_ind:
if pred_prob[Pi] > pred_prob[Fi]:
P_F += 1
else:
F_P += 1
auc2 = P_F/(len(P_ind)*len(F_ind))
print("方法二 auc:", auc2)
# 方法三,方法二的改進,簡化了計算,降低了時間復雜度
new_data = [[p, l] for p, l in zip(pred_prob, labels)]
new_data.sort(key=lambda x:x[0])
# 求正樣本rank之和
rank_sum = 0
for ind, [prob,label] in enumerate(new_data):
if label>0.5:
rank_sum+=ind
auc3 = (rank_sum - len(P_ind)*(1+len(P_ind))/2) / (len(P_ind)*len(F_ind))
print("方法三 auc:", auc3)運行結果
以上就是“Python實現計算AUC的方式有哪些”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家閱讀完這篇文章都有很大的收獲,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識,如果還想學習更多的知識,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。