您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“java的排序算法有哪些”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在java的排序算法有哪些問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”java的排序算法有哪些”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!


import java.util.Arrays;//冒泡排序public class BubbleSort_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
//記錄比較次數
int count=0;
//i=0,第一輪比較
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) {
//第一輪,兩兩比較
for (int j = 0; j < a.length-1-i; j++) {
if (a[j]>a[j+1]) {
int temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
}
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
System.out.println("一共比較了:"+count+"次");//一共比較了:105次
}}冒泡排序的優化1:
import java.util.Arrays;public class BubbleSort1_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
int count=0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) {
boolean flag=true;
for (int j = 0; j < a.length-1-i; j++) {
if (a[j]>a[j+1]) {
int temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
flag=false;
}
count++;
}
if (flag) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));// [2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
System.out.println("一共比較了:"+count+"次");//一共比較了:95次
}}
import java.util.Arrays;//選擇排序:先定義一個記錄最小元素的下標,然后循環一次后面的,找到最小的元素,最后將他放到前面排序好的序列。public class SelectSort_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) {
int index=i;//標記第一個為待比較的數
for (int j = i+1; j < a.length; j++) { //然后從后面遍歷與第一個數比較
if (a[j]<a[index]) { //如果小,就交換最小值
index=j;//保存最小元素的下標
}
}
//找到最小值后,將最小的值放到第一的位置,進行下一遍循環
int temp=a[index];
a[index]=a[i];
a[i]=temp;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}}
import java.util.Arrays;//插入排序:定義一個待插入的數,再定義一個待插入數的前一個數的下標,然后拿待插入數與前面的數組一一比較,最后交換。public class InsertSort_03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { //長度不減1,是因為要留多一個位置方便插入數
//定義待插入的數
int insertValue=a[i];
//找到待插入數的前一個數的下標
int insertIndex=i-1;
while (insertIndex>=0 && insertValue <a[insertIndex]) {//拿a[i]與a[i-1]的前面數組比較
a[insertIndex+1]=a[insertIndex];
insertIndex--;
}
a[insertIndex+1]=insertValue;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}}
import java.util.Arrays;//希爾排序:插入排序的升級public class ShellSort_04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
int count=0;//比較次數
for (int gap=a.length / 2; gap > 0; gap = gap / 2) {
//將整個數組分為若干個子數組
for (int i = gap; i < a.length; i++) {
//遍歷各組的元素
for (int j = i - gap; j>=0; j=j-gap) {
//交換元素
if (a[j]>a[j+gap]) {
int temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+gap];
a[j+gap]=temp;
count++;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);//16
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}}參考這篇博客



import java.util.Arrays;//快速排序:冒泡排序的升華版public class QuickSort_05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int a[]={50,1,12,2};
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
quicksort(a,0,a.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void quicksort(int[] a, int low, int high) {
int i,j;
if (low>high) {
return;
}
i=low;
j=high;
int temp=a[low];//基準位,low=length時,會報異常,java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 4 ,所以必須在if判斷后面,就跳出方法。
while(i<j){
//先從右邊開始往左遞減,找到比temp小的值才停止
while ( temp<=a[j] && i<j) {
j--;
}
//再看左邊開始往右遞增,找到比temp大的值才停止
while ( temp>=a[i] && i<j) {
i++;
}
//滿足 i<j 就交換,繼續循環while(i<j)
if (i<j) {
int t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
}
//最后將基準位跟 a[i]與a[j]相等的位置,進行交換,此時i=j
a[low]=a[i];
a[i]=temp;
//左遞歸
quicksort(a, low, j-1);
//右遞歸
quicksort(a, j+1, high);
}}

import java.util.Arrays;//歸并排序public class MergeSort_06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
//int a[]={5,2,4,7,1,3,2,2};
int temp[]=new int[a.length];
mergesort(a,0,a.length-1,temp);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void mergesort(int[] a, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
//分解
if (left<right) {
int mid=(left+right)/2;
//向左遞歸進行分解
mergesort(a, left, mid, temp);
//向右遞歸進行分解
mergesort(a, mid+1, right, temp);
//每分解一次便合并一次
merge(a,left,right,mid,temp);
}
}
/**
*
* @param a 待排序的數組
* @param left 左邊有序序列的初始索引
* @param right 右邊有序序列的初始索引
* @param mid 中間索引
* @param temp 做中轉的數組
*/
private static void merge(int[] a, int left, int right, int mid, int[] temp) {
int i=left; //初始i,左邊有序序列的初始索引
int j=mid+1;//初始化j,右邊有序序列的初始索引(右邊有序序列的初始位置即中間位置的后一位置)
int t=0;//指向temp數組的當前索引,初始為0
//先把左右兩邊的數據(已經有序)按規則填充到temp數組
//直到左右兩邊的有序序列,有一邊處理完成為止
while (i<=mid && j<=right) {
//如果左邊有序序列的當前元素小于或等于右邊的有序序列的當前元素,就將左邊的元素填充到temp數組中
if (a[i]<=a[j]) {
temp[t]=a[i];
t++;//索引向后移
i++;//i后移
}else {
//反之,將右邊有序序列的當前元素填充到temp數組中
temp[t]=a[j];
t++;//索引向后移
j++;//j后移
}
}
//把剩余數據的一邊的元素填充到temp中
while (i<=mid) {
//此時說明左邊序列還有剩余元素
//全部填充到temp數組
temp[t]=a[i];
t++;
i++;
}
while (j<=right) {
//此時說明左邊序列還有剩余元素
//全部填充到temp數組
temp[t]=a[j];
t++;
j++;
}
//將temp數組的元素復制到原數組
t=0;
int tempLeft=left;
while (tempLeft<=right) {
a[tempLeft]=temp[t];
t++;
tempLeft++;
}
}
}堆排序
第一步:構建初始堆buildHeap, 使用sink(arr,i, length)調整堆頂的值;
第二步:將堆頂元素下沉 目的是將最大的元素浮到堆頂來,然后使用sink(arr, 0,length)調整;
堆排序圖解:鏈接
public class Heap_Sort_07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
//構建堆
buildHeap(arr,length);
for ( int i = length - 1; i > 0; i-- ) {
//將堆頂元素與末位元素調換
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
//數組長度-1 隱藏堆尾元素
length--;
//將堆頂元素下沉 目的是將最大的元素浮到堆頂來
sink(arr, 0,length);
}
}
private static void buildHeap(int[] arr, int length) {
for (int i = length / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
sink(arr,i, length);
}
}
private static void sink(int[] arr, int index, int length) {
int leftChild = 2 * index + 1;//左子節點下標
int rightChild = 2 * index + 2;//右子節點下標
int present = index;//要調整的節點下標
//下沉左邊
if (leftChild < length && arr[leftChild] > arr[present]) {
present = leftChild;
}
//下沉右邊
if (rightChild < length && arr[rightChild] > arr[present]) {
present = rightChild;
}
//如果下標不相等 證明調換過了
if (present != index) {
//交換值
int temp = arr[index];
arr[index] = arr[present];
arr[present] = temp;
//繼續下沉
sink(arr, present, length);
}
}}參考鏈接
算法的步驟如下:
找出待排序的數組array中最大的元素max
統計數組中每個值為 i 的元素出現的次數,存入數組 count 的第 i 項
對所有的計數累加(從 count中的第一個元素開始,每一項和前一項相加)
反向填充目標數組:將每個元素 i 放在新數組的第 count [i] 項,每放一個元素就將 count [i] 減去

import java.util.Arrays;public class CountSort_08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = { 4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1 };
// 找到數組中最大的值 ---> max:8
int max = findMaxElement(array);
int[] sortedArr = countingSort(array, max + 1);
System.out.println("計數排序后的數組: " + Arrays.toString(sortedArr));
}
private static int findMaxElement(int[] array) {
int max = array[0];
for (int val : array) {
if (val > max)
max = val;
}
return max;
}
private static int[] countingSort(int[] array, int range) { //range:8+1
int[] output = new int[array.length];
int[] count = new int[range];
//初始化: count1數組
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
count[array[i]]++;
}
//計數: count2數組,累加次數后的,這里用count2區分
for (int i = 1; i < range; i++) {
count[i] = count[i] + count[i - 1];
}
//排序:最后數組
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i];
count[array[i]]--;
}
return output;
}}參考鏈接
桶排序可以看成是計數排序的升級版,它將要排的數據分到多個有序的桶里,每個桶里的數據再單獨排序,再把每個桶的數據依次取出,即可完成排序。
桶排序:將值為i的元素放入i號桶,最后依次把桶里的元素倒出來。
桶排序序思路:
設置一個定量的數組當作空桶子。
尋訪序列,并且把項目一個一個放到對應的桶子去。
對每個不是空的桶子進行排序。
從不是空的桶子里把項目再放回原來的序列中。
public class BucketSort_09 {
public static void sort(int[] arr){
//最大最小值
int max = arr[0];
int min = arr[0];
int length = arr.length;
for(int i=1; i<length; i++) {
if(arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
} else if(arr[i] < min) {
min = arr[i];
}
}
//最大值和最小值的差
int diff = max - min;
//桶列表
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> bucketList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++){
bucketList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
//每個桶的存數區間
float section = (float) diff / (float) (length - 1);
//數據入桶
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++){
//當前數除以區間得出存放桶的位置 減1后得出桶的下標
int num = (int) (arr[i] / section) - 1;
if(num < 0){
num = 0;
}
bucketList.get(num).add(arr[i]);
}
//桶內排序
for(int i = 0; i < bucketList.size(); i++){
//jdk的排序速度當然信得過
Collections.sort(bucketList.get(i));
}
//寫入原數組
int index = 0;
for(ArrayList<Integer> arrayList : bucketList){
for(int value : arrayList){
arr[index] = value;
index++;
}
}
}}我們假設有一個待排序數組[53,3,542,748,14,214],那么如何使用基數排序對其進行排序呢?
首先我們有這樣的十個一維數組,在基數排序中也叫桶。用桶排序實現。
第一輪,以元素的個位數進行區分:[542,53,3,14,214,748]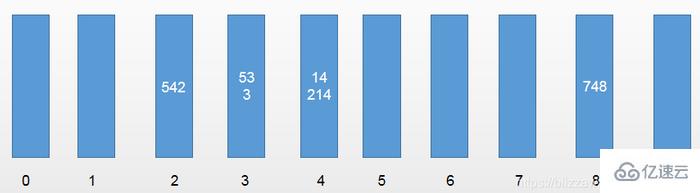
第二輪,以元素的十位數進行區分:[3,14,214,542,748,53]
第三輪,以元素的百位數進行區分:[3,14,53,214,542,748]
import java.util.Arrays;public class RaixSort_10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 53, 3, 542, 748, 14, 214 };
// 得到數組中最大的數
int max = arr[0];// 假設第一個數就是數組中的最大數
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
// 得到最大數是幾位數
// 通過拼接一個空串將其變為字符串進而求得字符串的長度,即為位數
int maxLength = (max + "").length();
// 定義一個二維數組,模擬桶,每個桶就是一個一維數組
// 為了防止放入數據的時候桶溢出,我們應該盡量將桶的容量設置得大一些
int[][] bucket = new int[10][arr.length];
// 記錄每個桶中實際存放的元素個數
// 定義一個一維數組來記錄每個桶中每次放入的元素個數
int[] bucketElementCounts = new int[10];
// 通過變量n幫助取出元素位數上的數
for (int i = 0, n = 1; i < maxLength; i++, n *= 10) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
// 針對每個元素的位數進行處理
int digitOfElement = arr[j] / n % 10;
// 將元素放入對應的桶中
// bucketElementCounts[digitOfElement]就是桶中的元素個數,初始為0,放在第一位
bucket[digitOfElement][bucketElementCounts[digitOfElement]] = arr[j];
// 將桶中的元素個數++
// 這樣接下來的元素就可以排在前面的元素后面
bucketElementCounts[digitOfElement]++;
}
// 按照桶的順序取出數據并放回原數組
int index = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < bucket.length; k++) {
// 如果桶中有數據,才取出放回原數組
if (bucketElementCounts[k] != 0) {
// 說明桶中有數據,對該桶進行遍歷
for (int l = 0; l < bucketElementCounts[k]; l++) {
// 取出元素放回原數組
arr[index++] = bucket[k][l];
}
}
// 每輪處理后,需要將每個bucketElementCounts[k]置0
bucketElementCounts[k] = 0;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));//[3, 14, 53, 214, 542, 748]
}}基數排序是用空間換時間的經典算法,當數據足夠多時,達到幾千萬級別時內存空間可能不夠用了,發生堆內存溢出

到此,關于“java的排序算法有哪些”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。