您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本文小編為大家詳細介紹“Java雙指針法怎么使用”,內容詳細,步驟清晰,細節處理妥當,希望這篇“Java雙指針法怎么使用”文章能幫助大家解決疑惑,下面跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來學習新知識吧。
通常用在線性的數據結構中,比如鏈表和數組。
指針其實就是數據的索引或者鏈表的結點。兩個指針朝著左右兩個方向移動,直到滿足搜索條件。 雙指針可分為同向雙指針、異向雙指針、快慢指針、滑動窗口。根據需求選擇雙指針的模型,比如 刪除數組或鏈表中重復的元素,同向雙指針(線性表前提是有序的); 快慢指針一般用在鏈表中,比如求鏈表的中點、判斷鏈表是否有環、判斷鏈表換的起點、環的長度、以及鏈表的倒數第K個元素; 比如在二分查找中用的就是異向雙指針; 滑動窗口其實就是在數組或者鏈表某個區間上的操作,比如求最長/最短子字符串或是特定子字符串的長度要求。
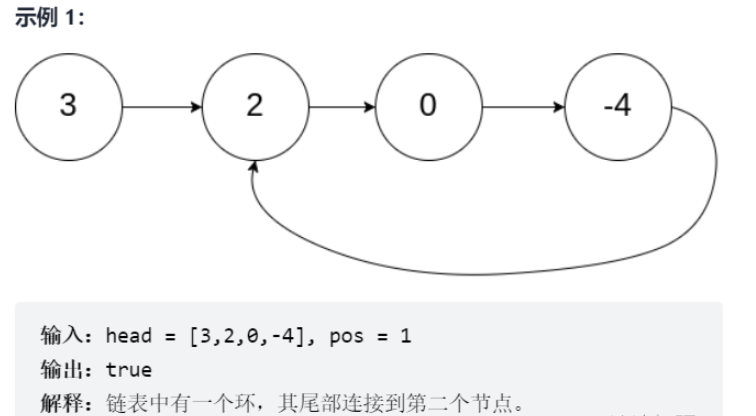
力扣141題
給你一個鏈表的頭節點 head ,判斷鏈表中是否有環。
如果鏈表中有某個節點,可以通過連續跟蹤 next 指針再次到達,則鏈表中存在環。 為了表示給定鏈表中的環,評測系統內部使用整數 pos 來表示鏈表尾連接到鏈表中的位置(索引從 0 開始)。注意:pos 不作為參數進行傳遞 。僅僅是為了標識鏈表的實際情況。
如果鏈表中存在環 ,則返回 true 。 否則,返回 false 。
代碼實現
public class Solution {
//快慢指針法
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode low = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
low = low.next;
//此時相遇了
if(fast == low){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}力扣876題
給定一個頭結點為 head 的非空單鏈表,返回鏈表的中間結點。
如果有兩個中間結點,則返回第二個中間結點。

代碼實現
//快慢指針法
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode low = head,fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
//慢指針走一步
low = low.next;
//快指針走兩步
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//奇數,fast.next = null時,low即為所求
//偶數,fsat == null時,low即為所求
return low;
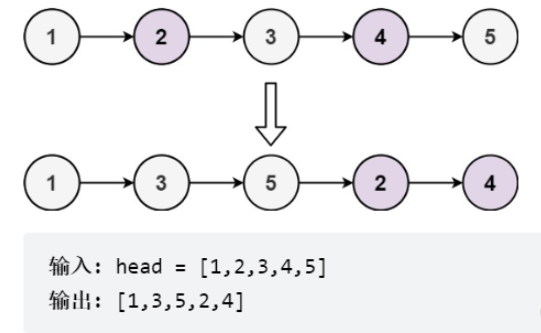
}力扣328題
給定單鏈表的頭節點 head ,將所有索引為奇數的節點和索引為偶數的節點分別組合在一起,然后返回重新排序的列表。
第一個節點的索引被認為是 奇數 , 第二個節點的索引為 偶數 ,以此類推。
代碼實現
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
ListNode fastHead = head.next;
ListNode lowTail = head;//奇數鏈表
ListNode fastTail = fastHead;//偶數鏈表
while(fastTail != null && fastTail.next != null){
//更新奇數節點時,奇數節點的后一個節點需要指向偶數節點的后一個節點
lowTail.next = fastTail.next;
lowTail = lowTail.next;
// 更新偶數節點時,偶數節點的后一個節點需要指向奇數節點的后一個節點
fastTail.next = lowTail.next;
fastTail = fastTail.next;
}
//合并兩個鏈表
lowTail.next = fastHead;
return head;
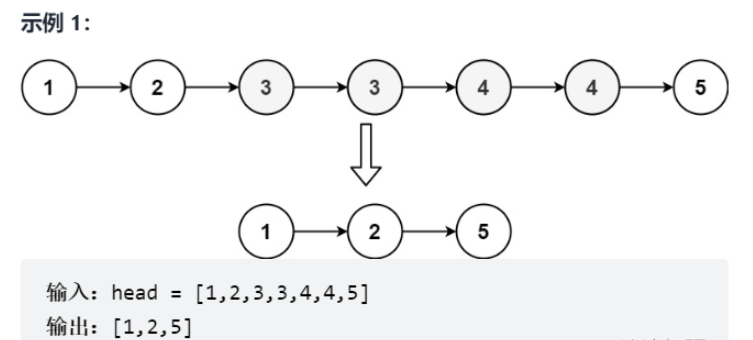
}力扣82題
給定一個已排序的鏈表的頭 head , 刪除原始鏈表中所有重復數字的節點,只留下不同的數字 。返回 已排序的鏈表
代碼實現
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
//虛擬頭節點法
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummyHead;
ListNode cur = prev.next;
while(cur != null){
//引入next指針
ListNode next = cur.next;
if(next == null){
//只有一個元素
return dummyHead.next;
}
if(cur.val != next.val){
//cur不是重復節點,三指針都移動
cur = cur.next;
prev = prev.next;
}else{
//讓next指針一直向后移動,直到與cur.val不相等的節點位置
while(next != null && cur.val == next.val){
next = next.next;
}
// 此時next指向了第一個不重復的元素
// 此時prev - next之間所有重復元素全部刪除
prev.next = next;
cur = next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}力扣15題
給你一個包含 n 個整數的數組 nums,判斷 nums 中是否存在三個元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?請你找出所有和為 0 且不重復的三元組。
注意:答案中不可以包含重復的三元組。

代碼實現
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
// 枚舉 a
for (int first = 0; first < n; ++first) {
// 需要和上一次枚舉的數不相同
if (first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first - 1]) {
continue;
}
// c 對應的指針初始指向數組的最右端
int third = n - 1;
int target = -nums[first];
// 枚舉 b
for (int second = first + 1; second < n; ++second) {
// 需要和上一次枚舉的數不相同
if (second > first + 1 && nums[second] == nums[second - 1]) {
continue;
}
// 需要保證 b 的指針在 c 的指針的左側
while (second < third && nums[second] + nums[third] > target) {
--third;
}
// 如果指針重合,隨著 b 后續的增加
// 就不會有滿足 a+b+c=0 并且 b<c 的 c 了,可以退出循環
if (second == third) {
break;
}
if (nums[second] + nums[third] == target) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(nums[first]);
list.add(nums[second]);
list.add(nums[third]);
ans.add(list);
}
}
}
return ans;
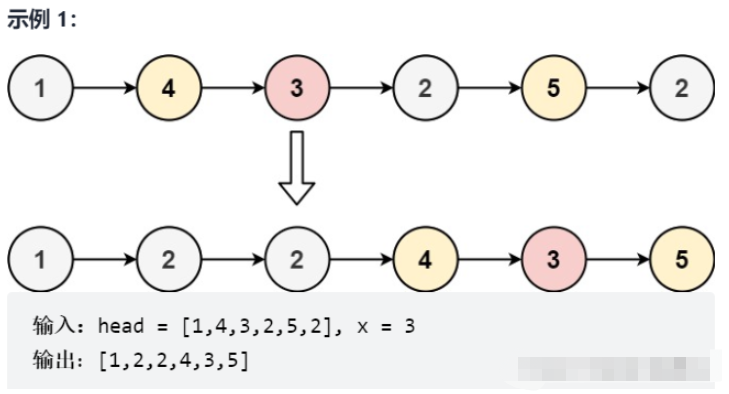
}力扣面試題02.04
給你一個鏈表的頭節點 head 和一個特定值 x ,請你對鏈表進行分隔,使得所有 小于 x 的節點都出現在 大于或等于 x 的節點之前。
你不需要 保留 每個分區中各節點的初始相對位置。
代碼實現
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
// 創建small和big兩個小鏈表的頭節點
ListNode smallHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode bigHead = new ListNode(-1);
// 按照升序插入,因此需要尾插
// 分別指向兩個子鏈表的尾部
ListNode smallTail = smallHead;
ListNode bigTail = bigHead;
//遍歷原鏈表,根據值放入small和big鏈表中
while(head != null){
if(head.val < x){
smallTail.next = head;
smallTail = head;
}else{
bigTail.next = head;
bigTail = head;
}
head = head.next;
}
bigTail.next = null;
//拼接小鏈表和大鏈表
smallTail.next = bigHead.next;
return smallHead.next;
}力扣88題
給你兩個按 非遞減順序 排列的整數數組 nums1 和 nums2,另有兩個整數 m 和 n ,分別表示 nums1 和 nums2 中的元素數目。請你 合并 nums2 到 nums1 中,使合并后的數組同樣按 非遞減順序 排列。
注意:最終,合并后數組不應由函數返回,而是存儲在數組 nums1 中。為了應對這種情況,nums1 的初始長度為 m + n,其中前 m 個元素表示應合并的元素,后 n 個元素為 0 ,應忽略。nums2 的長度為 n 。

代碼實現
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int p1 = 0, p2 = 0;
int[] sorted = new int[m + n];
int cur;
while (p1 < m || p2 < n) {
if (p1 == m) {
cur = nums2[p2++];
} else if (p2 == n) {
cur = nums1[p1++];
} else if (nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]) {
cur = nums1[p1++];
} else {
cur = nums2[p2++];
}
sorted[p1 + p2 - 1] = cur;
}
for (int i = 0; i != m + n; ++i) {
nums1[i] = sorted[i];
}
}力扣167題
給你一個下標從 1 開始的整數數組 numbers ,該數組已按 非遞減順序排列 ,請你從數組中找出滿足相加之和等于目標數 target 的兩個數。如果設這兩個數分別是 numbers[index1] 和 numbers[index2] ,則 1 <= index1 < index2 <= numbers.length 。
以長度為 2 的整數數組 [index1, index2] 的形式返回這兩個整數的下標 index1 和 index2。

代碼實現
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int low = 0, high = numbers.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int sum = numbers[low] + numbers[high];
if (sum == target) {
return new int[]{low + 1, high + 1};
} else if (sum < target) {
++low;
} else {
--high;
}
}
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}(力扣209)給定一個含有 n 個正整數的數組和一個正整數 target 。
找出該數組中滿足其和 ≥ target 的長度最小的 連續子數組 [numsl, numsl+1, …, numsr-1, numsr] ,并返回其長度。如果不存在符合條件的子數組,返回 0

代碼實現
//滑動窗口法
public int minSubArrayLen(int s, int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int start = 0, end = 0;
int sum = 0;
while (end < n) {
sum += nums[end];
while (sum >= s) {
ans = Math.min(ans, end - start + 1);
sum -= nums[start];
start++;
}
end++;
}
return ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : ans;
}給你鏈表的頭結點 head ,請將其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的鏈表 。
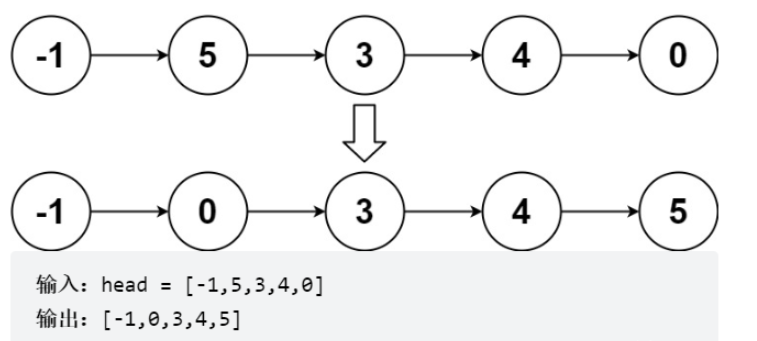
解題思路
通過遞歸實現鏈表歸并排序,有以下兩個環節:
1,分割 cut 環節: 找到當前鏈表中點,并從中點將鏈表斷開(以便在下次遞歸 cut 時,鏈表片段擁有正確邊界); 我們使用 fast,slow 快慢雙指針法,奇數個節點找到中點,偶數個節點找到中心左邊的節點。 找到中點 slow 后,執行 slow.next = None 將鏈表切斷。 遞歸分割時,輸入當前鏈表左端點 head 和中心節點 slow 的下一個節點 tmp(因為鏈表是從 slow 切斷的)。 cut 遞歸終止條件: 當head.next == None時,說明只有一個節點了,直接返回此節點。
2,合并 merge 環節: 將兩個排序鏈表合并,轉化為一個排序鏈表。 雙指針法合并,建立輔助ListNode h 作為頭部。 設置兩指針 left, right 分別指向兩鏈表頭部,比較兩指針處節點值大小,由小到大加入合并鏈表頭部,指針交替前進,直至添加完兩個鏈表。 返回輔助ListNode h 作為頭部的下個節點 h.next。
代碼實現
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode fast = head.next, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode tmp = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(tmp);
ListNode h = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res = h;
while (left != null && right != null) {
if (left.val < right.val) {
h.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
h.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
h = h.next;
}
h.next = left != null ? left : right;
return res.next;
}讀到這里,這篇“Java雙指針法怎么使用”文章已經介紹完畢,想要掌握這篇文章的知識點還需要大家自己動手實踐使用過才能領會,如果想了解更多相關內容的文章,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。