您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天小編給大家分享一下C++對象的構造順序是什么的相關知識點,內容詳細,邏輯清晰,相信大部分人都還太了解這方面的知識,所以分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后有所收獲,下面我們一起來了解一下吧。
對于局部對象
當程序執行流到達對象的定義語句時進行構造
下面看一個局部對象的構造示例:
#include <stdio.h>
class Test
{
private:
int mi;
public:
Test(int i)
{
mi = i;
printf("Test(int i): %d\n", mi);
}
Test(const Test& obj)
{
mi = obj.mi;
printf("Test(const Test& obj): %d\n", mi);
}
};
int main()
{
int i = 0;
Test a1 = i;
while( i < 3 )
{
Test a2 = ++i;
}
if( i < 4 )
{
Test a = a1;
}
else
{
Test a(100);
}
return 0;
}輸出結果如下:
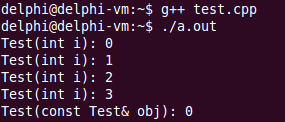
如果對象沒有被初始化會發生什么,下面看一個示例:
#include <stdio.h>
class Test
{
private:
int mi;
public:
Test(int i)
{
mi = i;
printf("Test(int i): %d\n", mi);
}
Test(const Test& obj)
{
mi = obj.mi;
printf("Test(const Test& obj): %d\n", mi);
}
int getMi()
{
return mi;
}
};
int main()
{
int i = 0;
Test a1 = i;
while( i < 3 )
{
Test a2 = ++i;
}
goto End;
Test a(100);
End:
printf("a.mi = %d\n", g.getMi());
return 0;
}在 g++ 編譯器下,就會報錯,讓不要使用 goto 語句,會跳過初始化
對于堆對象
當程序執行流到達 new 語句時創建對象
使用 new 創建對象將自動觸發構造函數的調用
下面看一個堆空間的構造順序示例:
#include <stdio.h>
class Test
{
private:
int mi;
public:
Test(int i)
{
mi = i;
printf("Test(int i): %d\n", mi);
}
Test(const Test& obj)
{
mi = obj.mi;
printf("Test(const Test& obj): %d\n", mi);
}
int getMi()
{
return mi;
}
};
int main()
{
int i = 0;
Test* a1 = new Test(i); // Test(int i): 0
while( ++i < 10 )
if( i % 2 )
new Test(i); // Test(int i): 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
if( i < 4 )
new Test(*a1);
else
new Test(100); // Test(int i): 100
return 0;
}輸出結果如下:
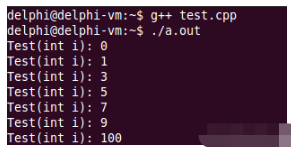
對于全局對象
對象的構造順序是不確定的
不同的編譯器使用不同的規則確定構造順序
下面看一個全局對象的構造順序示例:
test.h:
#ifndef _TEST_H_
#define _TEST_H_
#include <stdio.h>
class Test
{
public:
Test(const char* s)
{
printf("%s\n", s);
}
};
#endiftest.cpp:
#include "test.h"
Test t4("t4");
int main()
{
Test t5("t5");
}t1.cpp:
#include "test.h"
Test t1("t1");t2.cpp:
#include "test.h"
Test t2("t2");t3.cpp:
#include "test.h"
Test t3("t3");在 gcc 編譯器中,輸出結果如下:
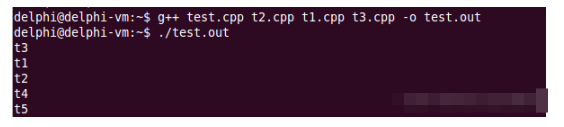
下面看一下使用 VS2012 編譯這些代碼:
(不知道 VS2012怎么使用命令行窗口編譯程序的可以看《命令行》不需要可以跳過)
這足以說明全局變量的構造順序是不確定的。
以下面的代碼為例
test.h:
#ifndef _TEST_H_
#define _TEST_H_
#include <stdio.h>
class Test
{
public:
Test(const char* s)
{
printf("%s\n", s);
}
};
#endiftest.cpp:
#include "test.h"
Test t4("t4");
int main()
{
Test t5("t5");
}t1.cpp:
#include "test.h"
Test t1("t1");t2.cpp:
#include "test.h"
Test t2("t2");t3.cpp:
#include "test.h"
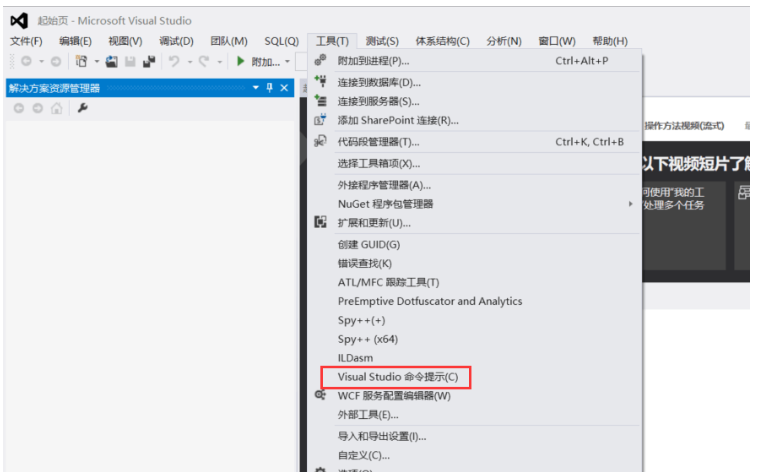
Test t3("t3");第一步,打開 VS2012,選擇 工具 -> Visual Studio 命令提示
第二步,實用 cd/d 進入需要編譯的文件夾。(注意換盤符需要輸入/d)
我想要編譯的文件在C:\Users\HuZeQiu\Desktop\demo 文件夾里。
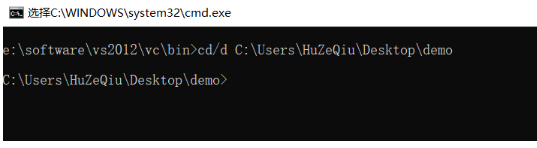
輸入cd/d C:\Users\HuZeQiu\Desktop\demo,按下回車鍵,如下,就轉到了目的文件夾
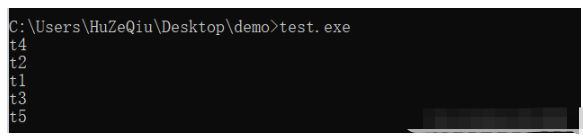
第三步,輸入 cltest.cpp t2.cpp t1.cpp t3.cpp -otest.exe 編譯程序。(cl 命令是用來編譯程序)按下回車鍵后開始編譯,生成 test.exe 可執行文件,如下:
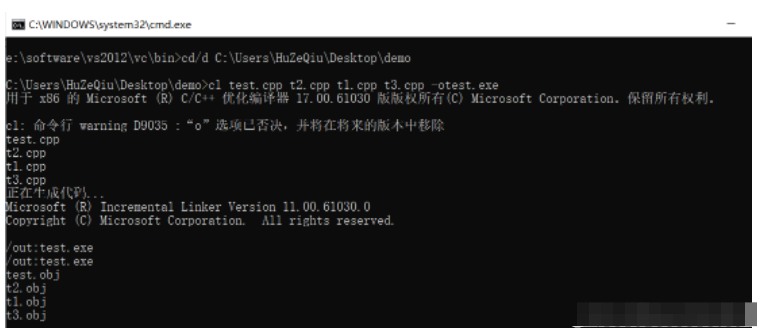
第四步,運行 test.exe,直接輸入 test.exe 即可,就可以看到運行結果
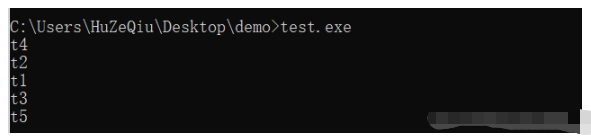
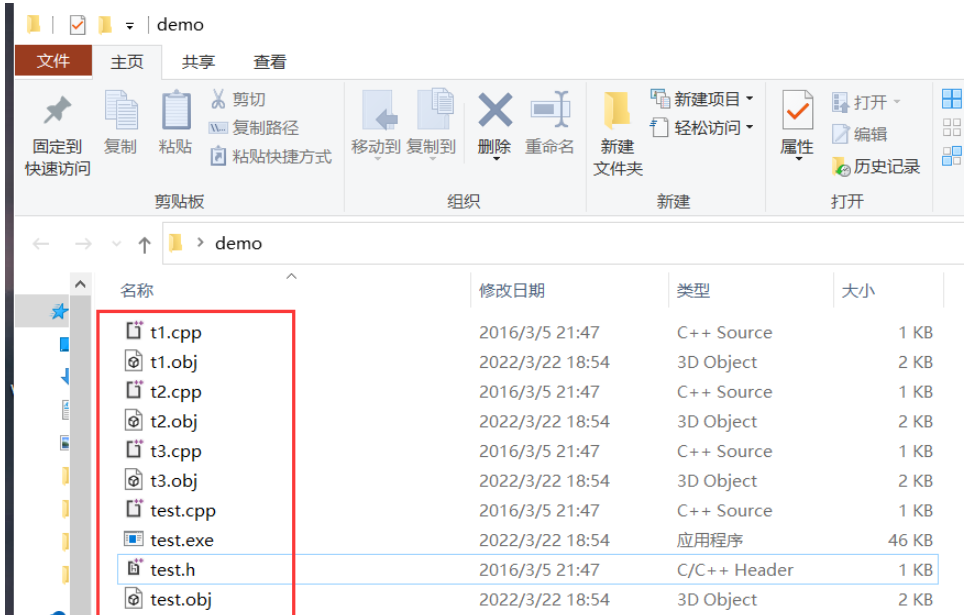
編譯后的文件夾如下:
以上就是“C++對象的構造順序是什么”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家閱讀完這篇文章都有很大的收獲,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識,如果還想學習更多的知識,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。