您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇“Vue keep-alive的實現原理是什么”文章的知識點大部分人都不太理解,所以小編給大家總結了以下內容,內容詳細,步驟清晰,具有一定的借鑒價值,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章能有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看這篇“Vue keep-alive的實現原理是什么”文章吧。
使用vue的時候,想必大家都是用過keep-alive,其作用就是緩存頁面以及其狀態。使用了這么久vue只知道如何使用但不明白其中原理,昨天翻看實現代碼,這里做個筆記。
整個組件的源碼為:
const KeepAliveImpl = {
name: `KeepAlive`,
// Marker for special handling inside the renderer. We are not using a ===
// check directly on KeepAlive in the renderer, because importing it directly
// would prevent it from being tree-shaken.
__isKeepAlive: true,
props: {
include: [String, RegExp, Array],
exclude: [String, RegExp, Array],
max: [String, Number]
},
setup(props: KeepAliveProps, { slots }: SetupContext) {
const cache: Cache = new Map()
const keys: Keys = new Set()
let current: VNode | null = null
const instance = getCurrentInstance()!
// console.log('instance',instance)
// KeepAlive communicates with the instantiated renderer via the "sink"
// where the renderer passes in platform-specific functions, and the
// KeepAlive instance exposes activate/deactivate implementations.
// The whole point of this is to avoid importing KeepAlive directly in the
// renderer to facilitate tree-shaking.
const sink = instance.sink as KeepAliveSink
const {
renderer: {
move,
unmount: _unmount,
options: { createElement }
},
parentSuspense
} = sink
const storageContainer = createElement('div')
// console.log('sink',sink)
sink.activate = (vnode, container, anchor) => {
move(vnode, container, anchor, MoveType.ENTER, parentSuspense)
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
const component = vnode.component!
component.isDeactivated = false
if (component.a !== null) {
invokeHooks(component.a)
}
}, parentSuspense)
}
sink.deactivate = (vnode: VNode) => {
move(vnode, storageContainer, null, MoveType.LEAVE, parentSuspense)
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
const component = vnode.component!
if (component.da !== null) {
invokeHooks(component.da)
}
component.isDeactivated = true
}, parentSuspense)
}
function unmount(vnode: VNode) {
// reset the shapeFlag so it can be properly unmounted
vnode.shapeFlag = ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT
_unmount(vnode, instance, parentSuspense)
}
function pruneCache(filter?: (name: string) => boolean) {
cache.forEach((vnode, key) => {
const name = getName(vnode.type as Component)
if (name && (!filter || !filter(name))) {
pruneCacheEntry(key)
}
})
}
function pruneCacheEntry(key: CacheKey) {
const cached = cache.get(key) as VNode
if (!current || cached.type !== current.type) {
unmount(cached)
} else if (current) {
// current active instance should no longer be kept-alive.
// we can't unmount it now but it might be later, so reset its flag now.
current.shapeFlag = ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT
}
cache.delete(key)
keys.delete(key)
}
watch(
() => [props.include, props.exclude],
([include, exclude]) => {
include && pruneCache(name => matches(include, name))
exclude && pruneCache(name => matches(exclude, name))
},
{ lazy: true }
)
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
cache.forEach(unmount)
})
return () => {
if (!slots.default) {
return null
}
const children = slots.default()
let vnode = children[0]
if (children.length > 1) {
if (__DEV__) {
warn(`KeepAlive should contain exactly one component child.`)
}
current = null
return children
} else if (
!isVNode(vnode) ||
!(vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT)
) {
current = null
return vnode
}
const comp = vnode.type as Component
const name = getName(comp)
const { include, exclude, max } = props
if (
(include && (!name || !matches(include, name))) ||
(exclude && name && matches(exclude, name))
) {
return vnode
}
const key = vnode.key == null ? comp : vnode.key
const cached = cache.get(key)
// clone vnode if it's reused because we are going to mutate it
if (vnode.el) {
vnode = cloneVNode(vnode)
}
cache.set(key, vnode)
if (cached) {
// copy over mounted state
vnode.el = cached.el
vnode.anchor = cached.anchor
vnode.component = cached.component
if (vnode.transition) {
// recursively update transition hooks on subTree
setTransitionHooks(vnode, vnode.transition!)
}
// avoid vnode being mounted as fresh
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE
// make this key the freshest
keys.delete(key)
keys.add(key)
} else {
keys.add(key)
// prune oldest entry
if (max && keys.size > parseInt(max as string, 10)) {
pruneCacheEntry(Array.from(keys)[0])
}
}
// avoid vnode being unmounted
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE
current = vnode
return vnode
}
}
}很容易看出keep-alive其實就是vue自己封裝的一個組件,和普通組件一樣。
再講keep-alive組件前先了解下vue組件的整個渲染
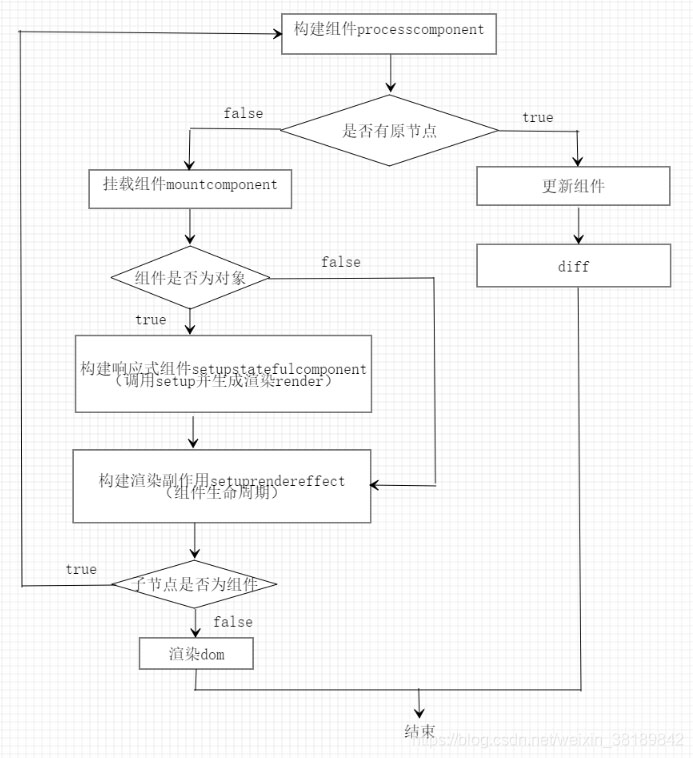
組件掛載:
調用setupStatefulComponent函數觸發組件setup方法,其中組件的setup方法核心代碼其實就幾行:
return () => {
const children = slots.default()
let vnode = children[0]
cache.set(key, vnode)
if (cached) {
vnode.el = cached.el
vnode.anchor = cached.anchor
vnode.component = cached.component
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE
keys.delete(key)
keys.add(key)
} else {
keys.add(key)
}
return vnode
}主要邏輯為三:
1.確認需要渲染的slot、
2.將其狀態置入緩存或讀取已存在的緩存、
3.返回slot對應的vnode,緊接著調用setupRenderEffect,渲染出dom。
組件更新(slot變化):
當slot變化后,首先會調用keep-alive組件的render即setup的返回函數,邏輯見上面setup方法。緊接著當某個slot卸載時,會調用deactivate函數,當某個slot重新掛載時,則會調用activate函數,核心代碼如下:
const storageContainer = createElement('div')
sink.activate = (vnode, container, anchor) => {
move(vnode, container, anchor, MoveType.ENTER, parentSuspense)
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
const component = vnode.component!
component.isDeactivated = false
if (component.a !== null) {
invokeHooks(component.a)
}
}, parentSuspense)
}
sink.deactivate = (vnode: VNode) => {
move(vnode, storageContainer, null, MoveType.LEAVE, parentSuspense)
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
const component = vnode.component!
if (component.da !== null) {
invokeHooks(component.da)
}
component.isDeactivated = true
}, parentSuspense)
}邏輯也很簡單,當組件卸載時,將其移入緩存的dom節點中,調用slot的deactivate生命周期,當組件重新掛載時候,將其移入至掛載的dom節點中。
總結來說,keep-alive實現原理就是將對應的狀態放入一個cache對象中,對應的dom節點放入緩存dom中,當下次再次需要渲染時,從對象中獲取狀態,從緩存dom中移出至掛載dom節點中。
在平常開發中,有些組件只需要加載一次,后面的數據將不存在變化,亦或者是組件需要緩存狀態,滾動條位置等,這個時候,keep-alive的用處就立刻凸顯出來了。
include表示需要緩存的頁面,exclude表示不需要緩存的頁面,你可以只設置其中一個即可,但兩個同時設置的時候,切記exclude優先級高于include,例如a組件在exclude中和include中都存在,那么,a組件是不會被緩存的
<template> <div id="app"> <keep-alive :include="whiteList" :exclude="blackList"> <router-view v-if="isRouterAlive" ></router-view> </keep-alive> </div> </template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
isRouterAlive:true,
whiteList:['styleLibrary','OrderList','SalesData'],
blackList:['Footer'],
personShow:false,
}
},
}
</script><template> <div id="app"> <keep-alive> <router-view v-if="$route.meta.keepAlive"></router-view> <!--緩存組件--> </keep-alive> <router-view v-if="!$route.meta.keepAlive"></router-view> <!--非緩存組件--> </div> </template>
將需要緩存的組件的$route.meta中的keepAlive設置為true,反之為false
{
path:'/login',
name:'login',
component:resolve=>require(['@/pages/login'],resolve),
meta:{
keepAlive:true,
title:'登錄',
savedPosition:true,
}
},以上就是關于“Vue keep-alive的實現原理是什么”這篇文章的內容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小編分享的內容對大家有幫助,若想了解更多相關的知識內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。