您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
C++ OpenCV如何進行圖像全景拼接,相信很多沒有經驗的人對此束手無策,為此本文總結了問題出現的原因和解決方法,通過這篇文章希望你能解決這個問題。
下面將使用OpenCV C++ 進行圖像全景拼接。目前使用OpenCV對兩幅圖像進行拼接大致可以分為兩類。
一、使用OpenCV內置API Stitcher 進行拼接。
二、使用特征檢測算法匹配兩幅圖中相似的點、計算變換矩陣、最后對其進行透視變換就可以了。
imageA

imageB

原圖如圖所示。本案例的需求是將上述兩幅圖片拼接成一幅圖像。首先使用OpenCV提供的Stitcher進行拼接。關于Stitcher的具體原理請大家自行查找相關資料。
bool OpenCV_Stitching(Mat imageA, Mat imageB)
{
vector<Mat>images;
images.push_back(imageA);
images.push_back(imageB);
Ptr<Stitcher>stitcher = Stitcher::create();
Mat result;
Stitcher::Status status = stitcher->stitch(images, result);// 使用stitch函數進行拼接
if (status != Stitcher::OK) return false;
imshow("OpenCV圖像全景拼接", result);
return true;
}
這就是使用OpenCV 內置Stitcher拼接出來的效果。
使用方法二進行圖像全景拼接。目前網上教程大致流程歸為:
1、使用特征檢測算子提取兩幅圖像的關鍵點,然后進行特征描述子匹配。我這里使用的是SURF算子。當然SIFT等其他特征檢測算子也可以。
//創建SURF特征檢測器 int Hessian = 800; Ptr<SURF>detector = SURF::create(Hessian); //進行圖像特征檢測、特征描述 vector<KeyPoint>keypointA, keypointB; Mat descriptorA, descriptorB; detector->detectAndCompute(imageA, Mat(), keypointA, descriptorA); detector->detectAndCompute(imageB, Mat(), keypointB, descriptorB); //使用FLANN算法進行特征描述子的匹配 FlannBasedMatcher matcher; vector<DMatch>matches; matcher.match(descriptorA, descriptorB, matches);

如圖為使用FLANN算法進行特征描述子匹配的結果。我們需要把那些匹配程度高的關鍵點篩選出來用以下面計算兩幅圖像的單應性矩陣。
2、篩選出匹配程度高的關鍵點
double Max = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
//float distance –>代表這一對匹配的特征點描述符(本質是向量)的歐氏距離,數值越小也就說明兩個特征點越相像。
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis > Max)
{
Max = dis;
}
}
//篩選出匹配程度高的關鍵點
vector<DMatch>goodmatches;
vector<Point2f>goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis < 0.15*Max)
{
//int queryIdx –>是測試圖像的特征點描述符(descriptor)的下標,同時也是描述符對應特征點(keypoint)的下標。
goodkeypointA.push_back(keypointA[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
//int trainIdx –> 是樣本圖像的特征點描述符的下標,同樣也是相應的特征點的下標。
goodkeypointB.push_back(keypointB[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
goodmatches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}如圖為imageA篩選出來的關鍵點。
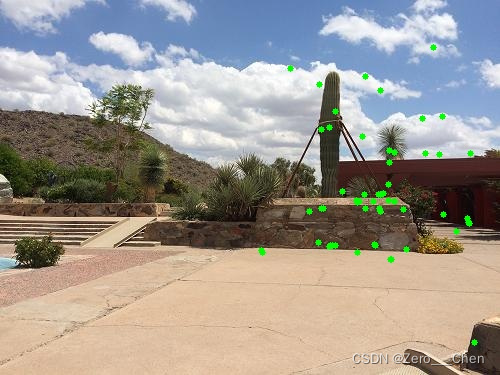
如圖為imageB篩選出來的關鍵點。

從上圖可以看出,我們已經篩選出imageA,imageB共有的關鍵點部分。接下來,我們需要使用這兩個點集計算兩幅圖的單應性矩陣。
計算單應性變換矩陣
//獲取圖像A到圖像B的投影映射矩陣,尺寸為3*3 Mat H = findHomography(goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB, RANSAC); Mat M = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0, 0, imageA.cols, 0, 1.0, 0, 0, 0, 1.0); Mat Homo = M * H;
根據計算出來的單應性矩陣對imageA進行透視變換
//進行透視變換
Mat DstImg;
warpPerspective(imageA, DstImg, Homo, Size(imageB.cols + imageA.cols, imageB.rows));
imshow("透視變換", DstImg);
如圖所示為imageA進行透視變換得到的結果。
根據上述操作,我們已經得到了經透視變換的imageA,接下來只需將imageA與imageB拼接起來就可以了。
imageB.copyTo(DstImg(Rect(imageA.cols, 0, imageB.cols, imageB.rows)));
imshow("圖像全景拼接", DstImg);bool Image_Stitching(Mat imageA, Mat imageB, bool draw)
{
//創建SURF特征檢測器
int Hessian = 800;
Ptr<SURF>detector = SURF::create(Hessian);
//進行圖像特征檢測、特征描述
vector<KeyPoint>keypointA, keypointB;
Mat descriptorA, descriptorB;
detector->detectAndCompute(imageA, Mat(), keypointA, descriptorA);
detector->detectAndCompute(imageB, Mat(), keypointB, descriptorB);
//使用FLANN算法進行特征描述子的匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector<DMatch>matches;
matcher.match(descriptorA, descriptorB, matches);
double Max = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
//float distance –>代表這一對匹配的特征點描述符(本質是向量)的歐氏距離,數值越小也就說明兩個特征點越相像。
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis > Max)
{
Max = dis;
}
}
//篩選出匹配程度高的關鍵點
vector<DMatch>goodmatches;
vector<Point2f>goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis < 0.15*Max)
{
//int queryIdx –>是測試圖像的特征點描述符(descriptor)的下標,同時也是描述符對應特征點(keypoint)的下標。
goodkeypointA.push_back(keypointA[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
//int trainIdx –> 是樣本圖像的特征點描述符的下標,同樣也是相應的特征點的下標。
goodkeypointB.push_back(keypointB[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
goodmatches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
if (draw)
{
Mat result;
drawMatches(imageA, keypointA, imageB, keypointB, goodmatches, result);
imshow("特征匹配", result);
Mat temp_A = imageA.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < goodkeypointA.size(); i++)
{
circle(temp_A, goodkeypointA[i], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
imshow("goodkeypointA", temp_A);
Mat temp_B = imageB.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < goodkeypointB.size(); i++)
{
circle(temp_B, goodkeypointB[i], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
imshow("goodkeypointB", temp_B);
}
//findHomography計算單應性矩陣至少需要4個點
/*
計算多個二維點對之間的最優單映射變換矩陣H(3x3),使用MSE或RANSAC方法,找到兩平面之間的變換矩陣
*/
if (goodkeypointA.size() < 4 || goodkeypointB.size() < 4) return false;
//獲取圖像A到圖像B的投影映射矩陣,尺寸為3*3
Mat H = findHomography(goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB, RANSAC);
Mat M = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0, 0, imageA.cols, 0, 1.0, 0, 0, 0, 1.0);
Mat Homo = M * H;
//進行透視變換
Mat DstImg;
warpPerspective(imageA, DstImg, Homo, Size(imageB.cols + imageA.cols, imageB.rows));
imshow("透視變換", DstImg);
imageB.copyTo(DstImg(Rect(imageA.cols, 0, imageB.cols, imageB.rows)));
imshow("圖像全景拼接", DstImg);
return true;
}
最終拼接效果如圖所示。
#include<iostream>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
#include<opencv2/stitching.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
//1、使用特征檢測算法找到兩張圖像中相似的點,計算變換矩陣
//2、將A透視變換后得到的圖片與B拼接
bool Image_Stitching(Mat imageA, Mat imageB, bool draw)
{
//創建SURF特征檢測器
int Hessian = 800;
Ptr<SURF>detector = SURF::create(Hessian);
//進行圖像特征檢測、特征描述
vector<KeyPoint>keypointA, keypointB;
Mat descriptorA, descriptorB;
detector->detectAndCompute(imageA, Mat(), keypointA, descriptorA);
detector->detectAndCompute(imageB, Mat(), keypointB, descriptorB);
//使用FLANN算法進行特征描述子的匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector<DMatch>matches;
matcher.match(descriptorA, descriptorB, matches);
double Max = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
//float distance –>代表這一對匹配的特征點描述符(本質是向量)的歐氏距離,數值越小也就說明兩個特征點越相像。
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis > Max)
{
Max = dis;
}
}
//篩選出匹配程度高的關鍵點
vector<DMatch>goodmatches;
vector<Point2f>goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis < 0.15*Max)
{
//int queryIdx –>是測試圖像的特征點描述符(descriptor)的下標,同時也是描述符對應特征點(keypoint)的下標。
goodkeypointA.push_back(keypointA[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
//int trainIdx –> 是樣本圖像的特征點描述符的下標,同樣也是相應的特征點的下標。
goodkeypointB.push_back(keypointB[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
goodmatches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
if (draw)
{
Mat result;
drawMatches(imageA, keypointA, imageB, keypointB, goodmatches, result);
imshow("特征匹配", result);
Mat temp_A = imageA.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < goodkeypointA.size(); i++)
{
circle(temp_A, goodkeypointA[i], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
imshow("goodkeypointA", temp_A);
Mat temp_B = imageB.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < goodkeypointB.size(); i++)
{
circle(temp_B, goodkeypointB[i], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
imshow("goodkeypointB", temp_B);
}
//findHomography計算單應性矩陣至少需要4個點
/*
計算多個二維點對之間的最優單映射變換矩陣H(3x3),使用MSE或RANSAC方法,找到兩平面之間的變換矩陣
*/
if (goodkeypointA.size() < 4 || goodkeypointB.size() < 4) return false;
//獲取圖像A到圖像B的投影映射矩陣,尺寸為3*3
Mat H = findHomography(goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB, RANSAC);
Mat M = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0, 0, imageA.cols, 0, 1.0, 0, 0, 0, 1.0);
Mat Homo = M * H;
//進行透視變換
Mat DstImg;
warpPerspective(imageA, DstImg, Homo, Size(imageB.cols + imageA.cols, imageB.rows));
imshow("透視變換", DstImg);
imageB.copyTo(DstImg(Rect(imageA.cols, 0, imageB.cols, imageB.rows)));
imshow("圖像全景拼接", DstImg);
return true;
}
bool OpenCV_Stitching(Mat imageA, Mat imageB)
{
vector<Mat>images;
images.push_back(imageA);
images.push_back(imageB);
Ptr<Stitcher>stitcher = Stitcher::create();
Mat result;
Stitcher::Status status = stitcher->stitch(images, result);// 使用stitch函數進行拼接
if (status != Stitcher::OK) return false;
imshow("OpenCV圖像全景拼接", result);
return true;
}
int main()
{
Mat imageA = imread("image1.jpg");
Mat imageB = imread("image2.jpg");
if (imageA.empty() || imageB.empty())
{
cout << "No Image!" << endl;
system("pause");
return -1;
}
if (!Image_Stitching(imageA, imageB, true))
{
cout << "can not stitching the image!" << endl;
}
if (!OpenCV_Stitching(imageA, imageB))
{
cout << "can not stitching the image!" << endl;
}
waitKey(0);
system("pause");
return 0;
}小編使用OpenCV C++進行圖像全景拼接,關鍵步驟有以下幾點。
1、使用特征檢測算子提取兩幅圖像的關鍵點,然后進行特征描述子匹配。
2、篩選出匹配程度高的關鍵點計算兩幅圖的單應性矩陣。
3、利用計算出來的單應性矩陣對其中一張圖片進行透視變換。
4、將透視變換的圖片與另一張圖片進行拼接。
看完上述內容,你們掌握C++ OpenCV如何進行圖像全景拼接的方法了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或想了解更多相關內容,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝各位的閱讀!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。