您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“CSS中定位布局的細節有哪些”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“CSS中定位布局的細節有哪些”吧!

相對定位:盒子可以根據自己原來的位置進行位置調整(通過位置描述詞實現)。
位置描述詞:
left: 向右移動; right 向左移動;top 向下移動;bottom 向上移動
(當里面值為負數的時候,往相反方向移動)
舉個例子:
原來:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>相對定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
p {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid #000;
margin: 50px auto;
}
p {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
position: relative;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
</style></head><body>
<p>
<p></p>
</p></body></html>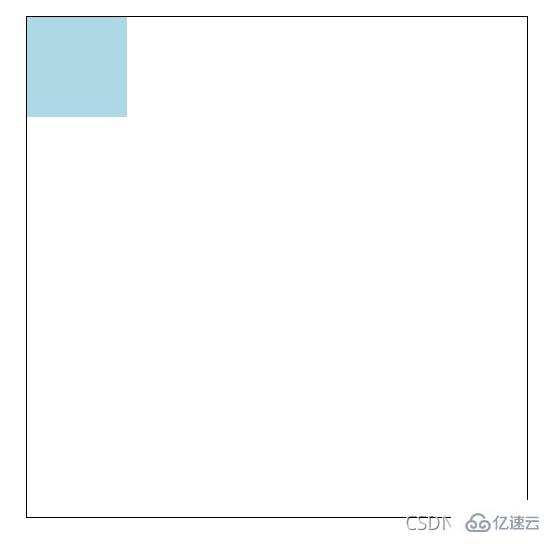
將 p 設置成相對定位:
p {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
position: relative;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;}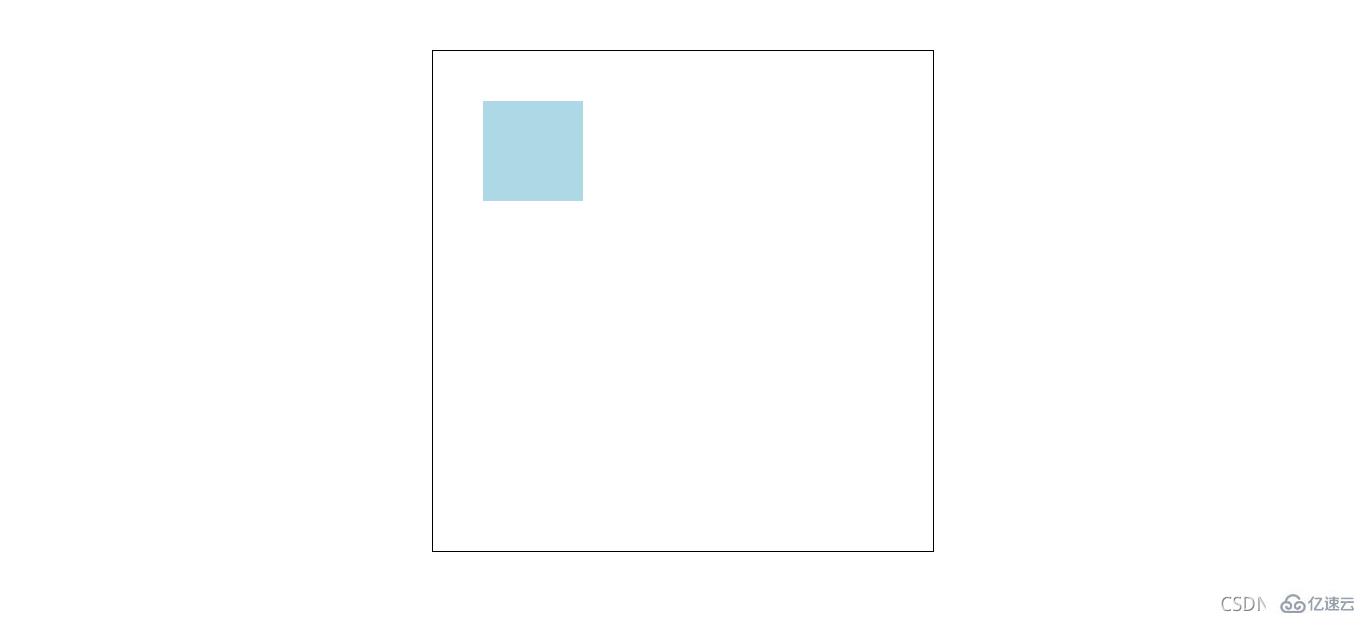
性質
相對定位的元素,本質上仍在原來的位置,只不過在新的地方渲染出現,不會對頁面其它元素產生影響。
用途
用來微調元素位置
相對定位的盒子可以用來做絕對定位的參考盒子
舉個例子:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>相對定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
nav {
width: 780px;
height: 50px;
margin: 40px auto;
}
nav ul {
list-style: none;
}
nav ul li {
float: left;
width: 156px;
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
text-align: center;
}
nav ul li a {
display: block;
width: 156px;
height: 50px;
background-color: lightcyan;
color: #000;
text-decoration: none;
}
nav ul li a:hover {
border-top: 3px solid red;
}
</style></head><body>
<nav>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="#">導航一</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">導航二</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">導航三</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">導航四</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#">導航五</a>
</li>
</ul>
</nav></body></html>這個時候效果是這樣:
會發現鼠標懸浮在上面的時候,導航那一塊區域都會下沉
我們給它設置了相對定位并微調之后:
nav ul li a:hover {
border-top: 3px solid red;
position: relative;
top: -3px;}
這樣就可以解決剛剛的問題了
絕對定位:盒子以坐標進行位置描述,擁有自己絕對位置。
絕對定位的參考盒子:
絕對定位的盒子會以自己的祖先元素中,離自己最近的擁有定位屬性的盒子,當做基準點。
這個盒子通常是相對定位的,所以也被稱作 “子絕父相”。
位置描述詞:
left:到左邊的距離;right:到右邊的距離;top:到上邊的距離;bottom:到下邊的距離
舉個例子:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>絕對定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box {
position: absolute;
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
left: 200px;
top: 100px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
}
</style></head><body>
<p class="box">
</p></body></html>絕對定位的盒子垂直居中:
.box {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -自己高度一半;}絕對定位的盒子水平居中:
.box {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -自己寬度一半;}堆疊順序 z-index 屬性
設置絕對定位元素的壓疊順序.
是一個沒有單位的正整數,數值大的能夠壓住數值小的(即數值大的顯示在上層)
舉個例子:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>絕對定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box1 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
}
.box2 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
</style></head><body>
<p class="box1"></p>
<p class="box2"></p></body></html>此時效果如下:
這個時候我們想讓box1顯示在上層,就設置一個z-index 屬性。
.box1 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
z-index: 100;}.box2 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
background-color: lightblue;
z-index: 1;}看看效果: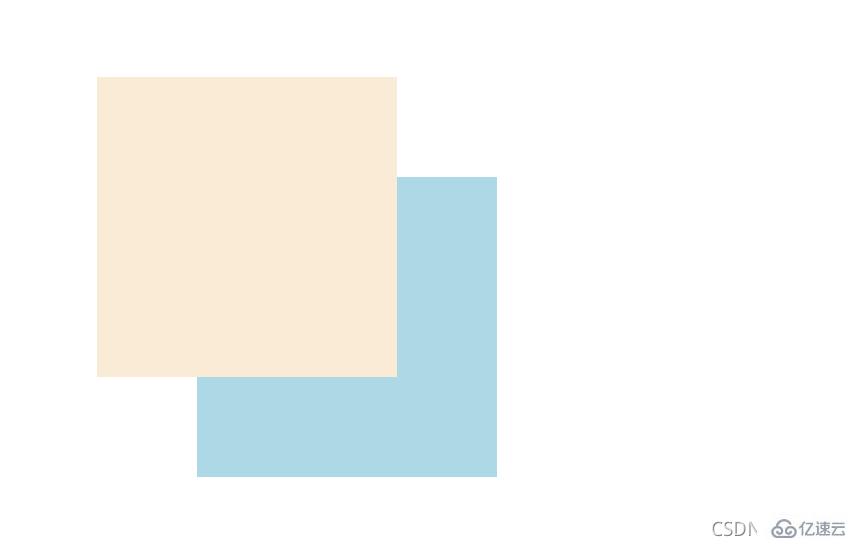
用途
絕對定位用來“壓蓋”,“遮罩”的效果
可以結合 CSS 精靈使用
可以結合 JS 實現一些動畫
固定定位:不管頁面如何滾動,它永遠以頁面為參考點,固定在那里。
位置描述詞:
left:到左邊的距離;right:到右邊的距離;top:到上邊的距離;bottom:到下邊的距離
.box {
position: fixed;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;}可以用來實現一些元素要一直浮現在當前窗口前,比如瀏覽一個頁面時的返回頂部按鈕,會一直出現在當前頁面的某個位置
舉個例子:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>固定定位</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box {
position: fixed;
bottom: 20px;
right: 20px;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: rgba(78, 209, 226, 0.5);
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 24px;
}
</style></head><body>
<a class="box">^</a>
<p>
<img src="https://dummyimage.com/600x400/00bcd4/fff" alt="">
</p>
<p>
<img src="https://dummyimage.com/600x400/00bcd4/fff" alt="">
</p>
<p>
<img src="https://dummyimage.com/600x400/00bcd4/fff" alt="">
</p></body></html>效果如下:
當頁面到下方時,右下角返回頂部的按鈕位置不變。
感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“CSS中定位布局的細節有哪些”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對CSS中定位布局的細節有哪些這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。