您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了android studio如何綁定服務和線程實現計時器,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
實驗目的:
熟悉和掌握Android線程的使用
實驗要求:
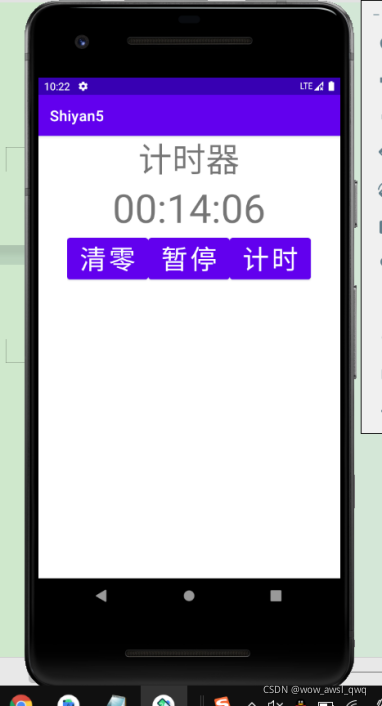
1.完成一個秒表,具備啟停功能
2.通過綁定服務實現功能,通過Thread+handler更新界面
這章節沒花什么時間去學,其他事情又很多,所以只是簡單實現了一下,在生命周期那里還是有些沒處理的地方,因此
主要思路是:在服務中啟動一個線程實現計數的功能,并且每隔10ms調用一下更新界面的函數,這需要用到Thread+handler,當然還需要一些控制啟停的公有函數供activity調用,同過綁定的服務的方式,activity中可以獲得服務的實例,所以以activity作為控制器,對不同的按鈕事件調用service的控制啟停的函數或者計數清零的函數,以此來實現計時器的功能。完成實驗后發現這樣實現的計時器精度比較粗糙,不過功能正常,更好的思路是使用時間函數,不過在本次實驗的目的是練習線程和綁定服務的使用,因此沒有繼續改動。
實驗代碼:
MyService .java
package com.example.shiyan5;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class MyService extends Service {
private final IBinder binder = new MyBinder();
private Thread workThread;
private int count=0;
private boolean c_stop=true;
public MyService() {
}
public void clearcount()
{
count=0;
}
public void countstop(){
c_stop=true;
}
public void countstart(){
c_stop=false;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
workThread=new Thread(null,backgroundWork);
workThread.start();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder {
MyService getService() {
return MyService.this;
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
return binder;
//throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
private Runnable backgroundWork =new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true)
{
if(c_stop==false)
{
count++;
}
MainActivity.UpdateGUI(count);
Thread.sleep(10);//10毫秒計數一次Z
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
}MainActivity.java
package com.example.shiyan5;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
static TextView textView1,textView2;
Button bt_clear,bt_stop,bt_start;
MyService mService;
boolean mBound;
static int count;
static Handler handler=new Handler();
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
MyService.MyBinder binder = (MyService.MyBinder) service;
mService = binder.getService();//通過這個來獲取服務的實例
mBound = true;
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName arg0) {
mBound = false;
}
};
public static void UpdateGUI(int s_count)
{
count=s_count;
handler.post(RefreshText);
}
private static Runnable RefreshText=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String sa,sb,sc;
int a=count%100;
if(a<10)sa="0"+a;else sa=String.valueOf(a);
int b=(count/100)%60;
if(b<10)sb="0"+b;else sb=String.valueOf(b);
int c=(count/100/60)%60;
if(c<10)sc="0"+c;else sc=String.valueOf(c);
textView2.setText(sc+":"+sb+":"+sa);
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mBound=false;
textView1=(TextView) findViewById(R.id.textview);
textView2=(TextView) findViewById(R.id.textview_2);
bt_clear=(Button) findViewById(R.id.bt_clear);
bt_stop=(Button) findViewById(R.id.bt_stop);
bt_start=(Button) findViewById(R.id.bt_start);
bt_clear.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if(mBound==true){
mService.clearcount();
mService.countstop();
}
}
});
bt_start.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if(mBound==true)
{
mService.countstart();
}
}
});
bt_stop.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if(mBound==true)
{
mService.countstop();
}
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
Intent intent=new Intent(this,MyService.class);
bindService(intent,connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
unbindService(connection);
mBound=false;
}
}activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:id="@+id/textview" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:text="計時器" android:textSize="46sp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview_2" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="54sp" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <LinearLayout android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <Button android:id="@+id/bt_clear" android:text="清零" android:textSize="36sp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <Button android:id="@+id/bt_stop" android:text="暫停" android:textSize="36sp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <Button android:id="@+id/bt_start" android:text="計時" android:textSize="36sp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“android studio如何綁定服務和線程實現計時器”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持億速云,關注億速云行業資訊頻道,更多相關知識等著你來學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。