您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要為大家展示了“Java字符串拼接的方法有哪些”,內容簡而易懂,條理清晰,希望能夠幫助大家解決疑惑,下面讓小編帶領大家一起研究并學習一下“Java字符串拼接的方法有哪些”這篇文章吧。
> 字符串拼接一般使用“+”,但是“+”不能滿足大批量數據的處理,Java中有以下五種方法處理字符串拼接,各有優缺點,程序開發應選擇合適的方法實現。
1. 加號 “+”
2. String contact() 方法
3. StringUtils.join() 方法
4. StringBuffer append() 方法
5. StringBuilder append() 方法
> 經過簡單的程序測試,從執行100次到90萬次的時間開銷如下表:
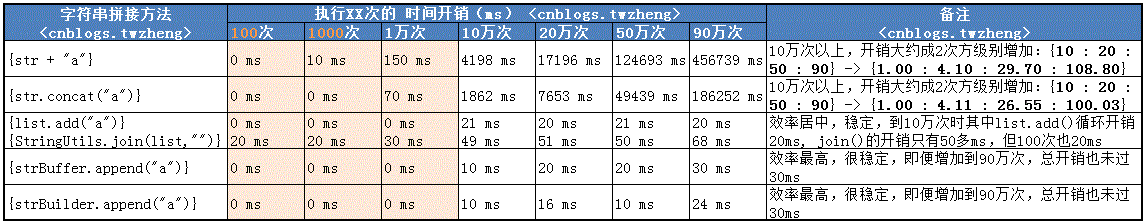
由此可以看出:
1. 方法1 加號 “+” 拼接 和 方法2 String contact() 方法 適用于小數據量的操作,代碼簡潔方便,加號“+” 更符合我們的編碼和閱讀習慣;
2. 方法3 StringUtils.join() 方法 適用于將ArrayList轉換成字符串,就算90萬條數據也只需68ms,可以省掉循環讀取ArrayList的代碼;
3. 方法4 StringBuffer append() 方法 和 方法5 StringBuilder append() 方法 其實他們的本質是一樣的,都是繼承自AbstractStringBuilder,效率最高,大批量的數據處理最好選擇這兩種方法。
4. 方法1 加號 “+” 拼接 和 方法2 String contact() 方法 的時間和空間成本都很高(分析在本文末尾),不能用來做批量數據的處理。
package cnblogs.twzheng.lab2;
/**
* @author Tan Wenzheng
*
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
public class TestString {
private static final int max = 100;
public void testPlus() {
System.out.println(">>> testPlus() <<<");
String str = "";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
str = str + "a";
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long cost = end - start;
System.out.println(" {str + \"a\"} cost=" + cost + " ms");
}
public void testConcat() {
System.out.println(">>> testConcat() <<<");
String str = "";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
str = str.concat("a");
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long cost = end - start;
System.out.println(" {str.concat(\"a\")} cost=" + cost + " ms");
}
public void testJoin() {
System.out.println(">>> testJoin() <<<");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
list.add("a");
}
long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long cost1 = end1 - start;
StringUtils.join(list, "");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long cost = end - end1;
System.out.println(" {list.add(\"a\")} cost1=" + cost1 + " ms");
System.out.println(" {StringUtils.join(list, \"\")} cost=" + cost
+ " ms");
}
public void testStringBuffer() {
System.out.println(">>> testStringBuffer() <<<");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
StringBuffer strBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
strBuffer.append("a");
}
strBuffer.toString();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long cost = end - start;
System.out.println(" {strBuffer.append(\"a\")} cost=" + cost + " ms");
}
public void testStringBuilder() {
System.out.println(">>> testStringBuilder() <<<");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
strBuilder.append("a");
}
strBuilder.toString();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long cost = end - start;
System.out
.println(" {strBuilder.append(\"a\")} cost=" + cost + " ms");
}
}1. 執行100次, private static final int max = 100;
>>> testPlus() <<<
{str + "a"} cost=0 ms
>>> testConcat() <<<
{str.concat("a")} cost=0 ms
>>> testJoin() <<<
{list.add("a")} cost1=0 ms
{StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=20 ms
>>> testStringBuffer() <<<
{strBuffer.append("a")} cost=0 ms
>>> testStringBuilder() <<<
{strBuilder.append("a")} cost=0 ms2. 執行1000次, private static final int max = 1000;
>>> testPlus() <<<
{str + "a"} cost=10 ms
>>> testConcat() <<<
{str.concat("a")} cost=0 ms
>>> testJoin() <<<
{list.add("a")} cost1=0 ms
{StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=20 ms
>>> testStringBuffer() <<<
{strBuffer.append("a")} cost=0 ms
>>> testStringBuilder() <<<
{strBuilder.append("a")} cost=0 ms3. 執行1萬次, private static final int max = 10000;
>>> testPlus() <<<
{str + "a"} cost=150 ms
>>> testConcat() <<<
{str.concat("a")} cost=70 ms
>>> testJoin() <<<
{list.add("a")} cost1=0 ms
{StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=30 ms
>>> testStringBuffer() <<<
{strBuffer.append("a")} cost=0 ms
>>> testStringBuilder() <<<
{strBuilder.append("a")} cost=0 ms4. 執行10萬次, private static final int max = 100000;
>>> testPlus() <<<
{str + "a"} cost=4198 ms
>>> testConcat() <<<
{str.concat("a")} cost=1862 ms
>>> testJoin() <<<
{list.add("a")} cost1=21 ms
{StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=49 ms
>>> testStringBuffer() <<<
{strBuffer.append("a")} cost=10 ms
>>> testStringBuilder() <<<
{strBuilder.append("a")} cost=10 ms5. 執行20萬次, private static final int max = 200000;
>>> testPlus() <<<
{str + "a"} cost=17196 ms
>>> testConcat() <<<
{str.concat("a")} cost=7653 ms
>>> testJoin() <<<
{list.add("a")} cost1=20 ms
{StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=51 ms
>>> testStringBuffer() <<<
{strBuffer.append("a")} cost=20 ms
>>> testStringBuilder() <<<
{strBuilder.append("a")} cost=16 ms6. 執行50萬次, private static final int max = 500000;
>>> testPlus() <<<
{str + "a"} cost=124693 ms
>>> testConcat() <<<
{str.concat("a")} cost=49439 ms
>>> testJoin() <<<
{list.add("a")} cost1=21 ms
{StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=50 ms
>>> testStringBuffer() <<<
{strBuffer.append("a")} cost=20 ms
>>> testStringBuilder() <<<
{strBuilder.append("a")} cost=10 ms7. 執行90萬次, private static final int max = 900000;
>>> testPlus() <<<
{str + "a"} cost=456739 ms
>>> testConcat() <<<
{str.concat("a")} cost=186252 ms
>>> testJoin() <<<
{list.add("a")} cost1=20 ms
{StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=68 ms
>>> testStringBuffer() <<<
{strBuffer.append("a")} cost=30 ms
>>> testStringBuilder() <<<
{strBuilder.append("a")} cost=24 msString contact 和 StringBuffer,StringBuilder 的源代碼都可以在Java庫里找到,有空可以研究研究。
1. 其實每次調用contact()方法就是一次數組的拷貝,雖然在內存中是處理都是原子性操作,速度非常快,但是,最后的return語句會創建一個新String對象,限制了concat方法的速度。
public String concat(String str) {
int otherLen = str.length();
if (otherLen == 0) {
return this;
}
int len = value.length;
char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
str.getChars(buf, len);
return new String(buf, true);
}2. StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 的append方法都繼承自AbstractStringBuilder,整個邏輯都只做字符數組的加長,拷貝,到最后也不會創建新的String對象,所以速度很快,完成拼接處理后在程序中用strBuffer.toString()來得到最終的字符串。
/**
* Appends the specified string to this character sequence.
* <p>
* The characters of the {@code String} argument are appended, in
* order, increasing the length of this sequence by the length of the
* argument. If {@code str} is {@code null}, then the four
* characters {@code "null"} are appended.
* <p>
* Let <i>n</i> be the length of this character sequence just prior to
* execution of the {@code append} method. Then the character at
* index <i>k</i> in the new character sequence is equal to the character
* at index <i>k</i> in the old character sequence, if <i>k</i> is less
* than <i>n</i>; otherwise, it is equal to the character at index
* <i>k-n</i> in the argument {@code str}.
*
* @param str a string.
* @return a reference to this object.
*/
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null) str = "null";
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}/**
* This method has the same contract as ensureCapacity, but is
* never synchronized.
*/
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0)
expandCapacity(minimumCapacity);
}
/**
* This implements the expansion semantics of ensureCapacity with no
* size check or synchronization.
*/
void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2;
if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
if (newCapacity < 0) {
if (minimumCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
}3. 字符串的加號“+” 方法, 雖然編譯器對其做了優化,使用StringBuilder的append方法進行追加,但是每循環一次都會創建一個StringBuilder對象,且都會調用toString方法轉換成字符串,所以開銷很大。
注:執行一次字符串“+”,相當于 str = new StringBuilder(str).append("a").toString();
4. 本文開頭的地方統計了時間開銷,根據上述分析再想想空間的開銷。常說拿空間換時間,反過來是不是拿時間換到了空間呢,但是在這里,其實時間是消耗在了重復的不必要的工作上(生成新的對象,toString方法),所以對大批量數據做處理時,加號“+” 和 contact 方法絕對不能用,時間和空間成本都很高。
以上是“Java字符串拼接的方法有哪些”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內容對大家有所幫助,如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。