您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“Gin框架中bind怎么使用”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“Gin框架中bind怎么使用”吧!
Gin框架中,有bind函數可以非常方便的將url的查詢參數query parameter、http的Header,body中提交上來的數據格式,如form,json,xml等,綁定到go中的結構體中去,這期間Binding做了啥事情,這么多個Bindding函數,我們該如何選擇,一起通過源碼來解開其中神秘的面紗吧。
type Binding interface {
Name() string
Bind(*http.Request, interface{}) error
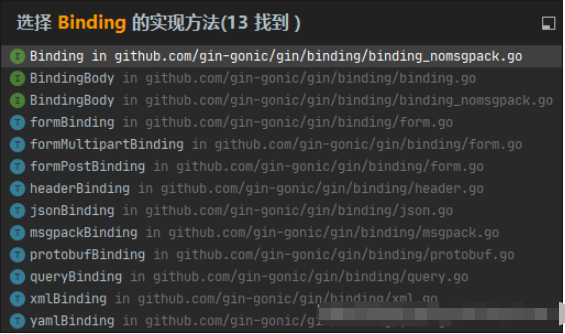
}Binding是一個接口,在源碼中,有10個實現了Binding的結構體,以及3個接口
// Bind checks the Content-Type to select a binding engine automatically,
// Depending the "Content-Type" header different bindings are used:
// "application/json" --> JSON binding
// "application/xml" --> XML binding
// otherwise --> returns an error.
// It parses the request's body as JSON if Content-Type == "application/json" using JSON or XML as a JSON input.
// It decodes the json payload into the struct specified as a pointer.
// It writes a 400 error and sets Content-Type header "text/plain" in the response if input is not valid.
func (c *Context) Bind(obj interface{}) error {
b := binding.Default(c.Request.Method, c.ContentType())
return c.MustBindWith(obj, b)
}// MustBindWith binds the passed struct pointer using the specified binding engine.
// It will abort the request with HTTP 400 if any error occurs.
// See the binding package.
func (c *Context) MustBindWith(obj interface{}, b binding.Binding) error {
if err := c.ShouldBindWith(obj, b); err != nil {
c.AbortWithError(http.StatusBadRequest, err).SetType(ErrorTypeBind) // nolint: errcheck
return err
}
return nil
}從注解和源碼可以看出,MustBindWith最終也是調用了SouldBindWith,并且對ShouldBindWith的結果進行了判斷,如果有錯誤,則以http 400的狀態碼進行退出。
// ShouldBindWith binds the passed struct pointer using the specified binding engine.
// See the binding package.
func (c *Context) ShouldBindWith(obj interface{}, b binding.Binding) error {
return b.Bind(c.Request, obj)
}這個方法是所有其他綁定方法的一個基礎,基本上所有的綁定方法都需要用到這個方法來對數據結構進行一個綁定
以上為主要的bingding的過程,其他派生出來的如BindJSON、ShouldBindJSON等,為具體的數據類型的快捷方式而已,只是幫我們把具體的bingding的數據類型提前給封裝了起來而已,如Json格式的bingding函數
// BindJSON is a shortcut for c.MustBindWith(obj, binding.JSON).
func (c *Context) BindJSON(obj interface{}) error {
return c.MustBindWith(obj, binding.JSON)
}context.BindJSON從源碼上分析,可以看到,僅僅比Bind方法少了一句
b := binding.Default(c.Request.Method, c.ContentType())
這一句是為了判斷當前的請求方法和contentType,來給context.MustBindWith傳的一個具體的bingding類型。
Json的實現的Binding接口如下
func (jsonBinding) Bind(req *http.Request, obj interface{}) error {
if req == nil || req.Body == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("invalid request")
}
return decodeJSON(req.Body, obj)
}jsonBinding結構體實現了Binding接口的Bind方法,將請求過來的Body數據進行解碼,綁定到obj里面去
// ShouldBindJSON is a shortcut for c.ShouldBindWith(obj, binding.JSON).
func (c *Context) ShouldBindJSON(obj interface{}) error {
return c.ShouldBindWith(obj, binding.JSON)
}從源碼的注解來看,ShouldBindJSON其實就是ShouldBindWith(obj, binding.JSON)的快捷方式,簡單來說,就是在ShouldBindWith(obj, binding.JSON)上面固定了參數,當我們明確規定,body提交的參數內容為json時,簡化了我們的調用和增強了代碼的可讀性。
// ShouldBindUri binds the passed struct pointer using the specified binding engine.
func (c *Context) ShouldBindUri(obj interface{}) error {
m := make(map[string][]string)
for _, v := range c.Params {
m[v.Key] = []string{v.Value}
}
return binding.Uri.BindUri(m, obj)
}從url綁定采用的方法跟header和body的方式不一樣,不需要傳入一個實現Binding接口的結構體類型
// BindUri binds the passed struct pointer using binding.Uri.
// It will abort the request with HTTP 400 if any error occurs.
func (c *Context) BindUri(obj interface{}) error {
if err := c.ShouldBindUri(obj); err != nil {
c.AbortWithError(http.StatusBadRequest, err).SetType(ErrorTypeBind) // nolint: errcheck
return err
}
return nil
}BindUri也是對ShouldBindUri的一個封裝,多了一個對ShouldBindUri結果的一個判斷 代碼實例
代碼如下
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
type queryHeader struct {
Myheader string `header:"myheader"`
Mydemo string `header:"mydemo"`
}
type queryBody struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
Sex int `json:"sex"`
}
type queryParameter struct {
Year int `form:"year"`
Month int `form:"month"`
}
type queryUri struct {
Id int `uri:"id"`
Name string `uri:"name"`
}
func bindUri(context *gin.Context){
var q queryUri
err:= context.ShouldBindUri(&q)
if err != nil {
context.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest,gin.H{
"result":err.Error(),
})
return
}
context.JSON(http.StatusOK,gin.H{
"result":"綁定成功",
"uri": q,
})
}
func bindQuery(context *gin.Context){
var q queryParameter
err:= context.ShouldBindQuery(&q)
if err != nil {
context.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest,gin.H{
"result":err.Error(),
})
return
}
context.JSON(http.StatusOK,gin.H{
"result":"綁定成功",
"query": q,
})
}
func bindBody(context *gin.Context){
var q queryBody
err:= context.ShouldBindJSON(&q)
if err != nil {
context.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest,gin.H{
"result":err.Error(),
})
return
}
context.JSON(http.StatusOK,gin.H{
"result":"綁定成功",
"body": q,
})
}
func bindhead(context *gin.Context){
var q queryHeader
err := context.ShouldBindHeader(&q)
if err != nil {
context.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest,gin.H{
"result":err.Error(),
})
return
}
context.JSON(http.StatusOK,gin.H{
"result":"綁定成功",
"header": q,
})
}
func main(){
srv := gin.Default()
srv.GET("/binding/header",bindhead)
srv.GET("/binding/body",bindBody)
srv.GET("/binding/query",bindQuery)
srv.GET("/binding/:id/:name",bindUri)
srv.Run(":9999")
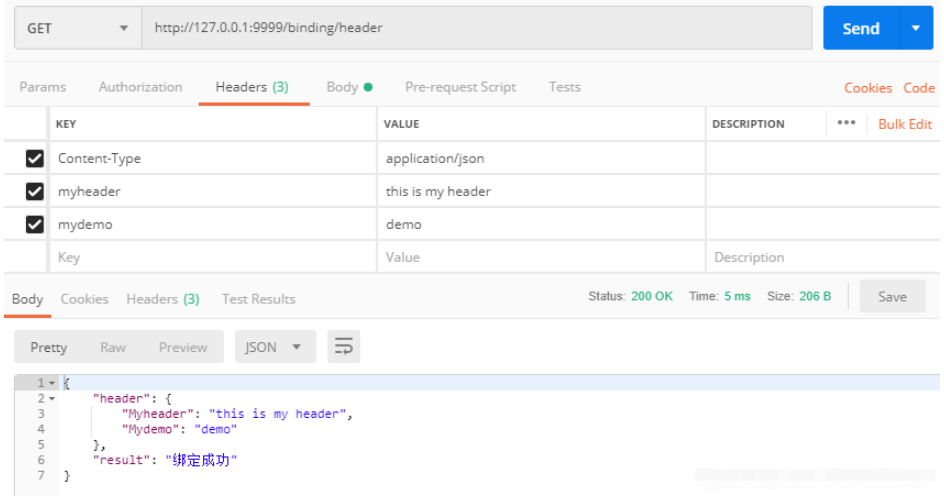
}綁定Header數據
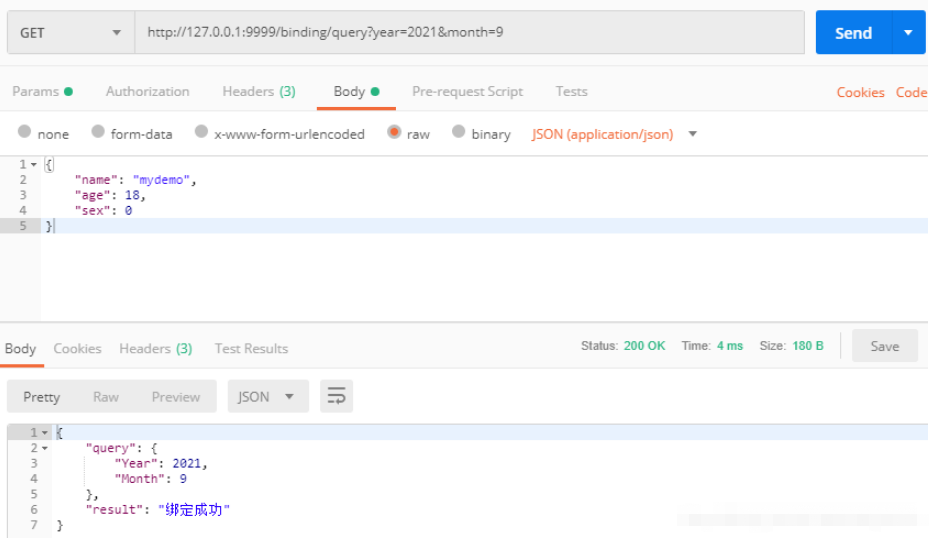
綁定QueryParameter數據
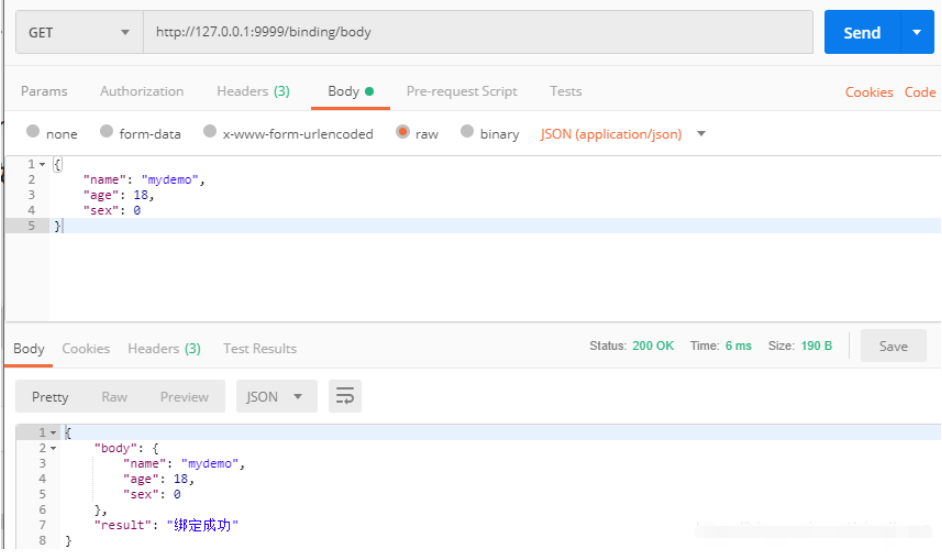
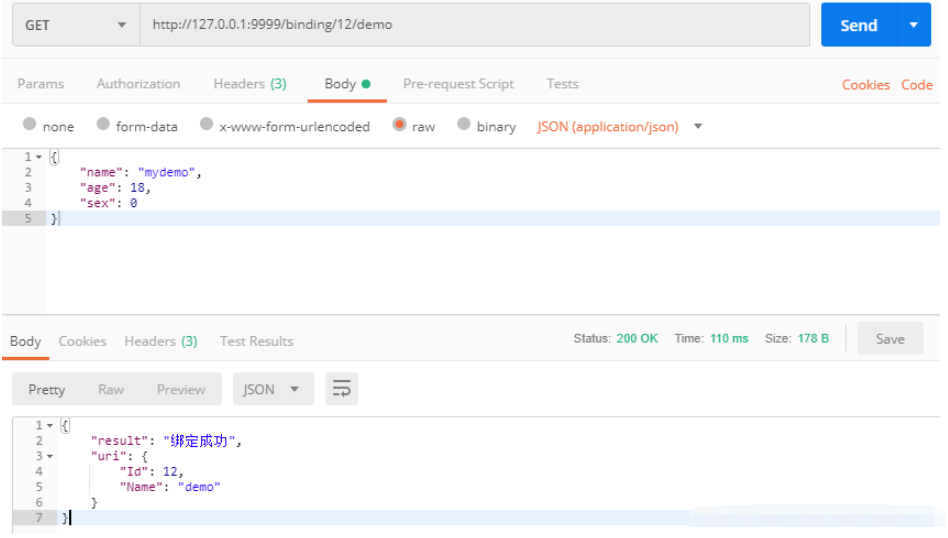
綁定Body Json數據
綁定Uri數據
到此,相信大家對“Gin框架中bind怎么使用”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。