您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“C++數據結構關于棧迷宮示例分析”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“C++數據結構關于棧迷宮示例分析”吧!
理解棧的抽象數據類型定義及操作特點。掌握順序棧的存儲結構的描述。掌握順序棧的基本操作的實現方法。理解棧的廣泛應用。
閱讀課程教材P44~45頁內容,掌握棧的邏輯定義及“后進先出”的特點,理解抽象數據類型棧的定義。閱讀課程教材P45~47頁內容,理解順序棧的存儲特點及存儲表示,掌握順序棧各種基本操作(InitStack、StackEmpty、GetTop、Push、Pop等)的實現方法。閱讀課程教材P50~52頁內容,理解“迷宮求解”問題的含義,體會求解過程中棧的應用。仔細分析主要實現算法,理解求解步驟和方法。
按如下要求編寫程序,進行調試,寫出調試正確的源代碼,給出測試結果。
1.完成順序棧的存儲表示,實現順序棧的各種基本操作,包括InitStack、StackEmpty、GetTop、Push、Pop等操作。
2.利用順序棧求解迷宮中從入口到出口的一條路徑,并輸出結果。
說明:
(1)使用二維數組maze描述迷宮,迷宮的規模及初態自定。
(2)路徑的輸出形式可用文字描述,也可用圖形描述。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100
#define STACKINCREMENT 10
typedef struct {//棧元素類型
int x;//坐標
int y;//坐標
int di;//方向
}position;
using namespace std;
typedef struct {//棧
position *base;
position *top;
int stacksize;
}Stack;
/*************************迷宮**********************************/
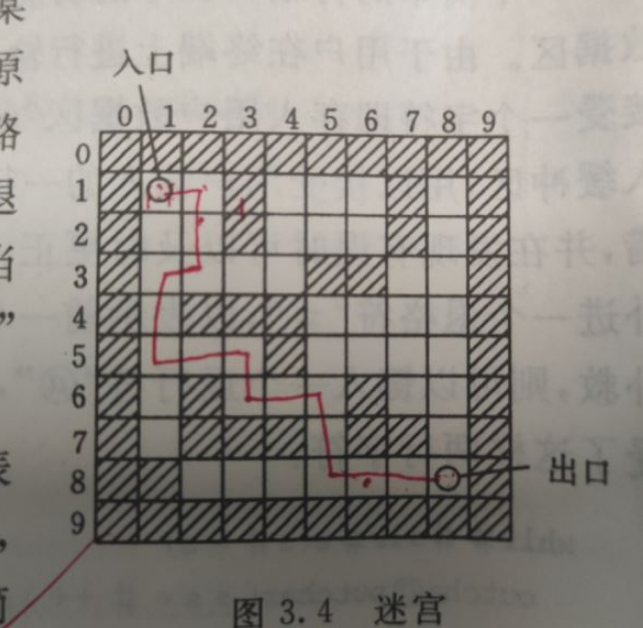
int Maze[10][10] = {//迷宮 Maze(妹子)原型如下圖:1表示路不通0表示可以通過。
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},//0
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},//1
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},//2
{1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1},//3
{1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1},//4
{1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},//5
{1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},//6
{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1},//7
{1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1},//8
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1} //9
};
class boos {//創建了一個角色類
private:
Stack sq_stack;//棧
position temp;
public:
/******************************棧的基本方法*******************/
void InitStack() {//創建棧
bool StackEmpty()//判斷是否空棧
bool GetTop(position &temp)//獲得棧頂
bool Push(position &temp)//入
bool Pop(position &temp)//出棧
void free_Stack()//釋放棧空間
/******************************走迷宮方法*******************/
bool findMaze(int star_x, int star_y, int endr_x, int end_y)
//迷宮的入口和出口坐標
};這是一些基礎方法 用于對棧的操作。
void InitStack() {//創建空的棧
sq_stack.base = (position *)malloc(sizeof(Stack)*STACK_INIT_SIZE);
if (!sq_stack.base) exit(-1);
sq_stack.top = sq_stack.base;/*FHL*/
sq_stack.stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;
cout << "棧創建成功" << endl;
}
bool StackEmpty() {判斷是否空棧
if (sq_stack.top == sq_stack.base)return 1;
else
return 0;
}
bool GetTop(position &temp) {//得到棧頂元素
if (StackEmpty())return false;
temp= *(sq_stack.top-1);
return true;
}
bool Push(position &temp){//入棧/*FHL*/
if (sq_stack.top - sq_stack.base >= sq_stack.stacksize) {
sq_stack.base = (position*)realloc(sq_stack.base
sizeof(position)*(sq_stack.stacksize + STACKINCREMENT));
if(!sq_stack.base) exit(-1);/*FHL*/
sq_stack.top = sq_stack.base + sq_stack.stacksize;
sq_stack.stacksize += STACKINCREMENT;
}
*sq_stack.top = temp;
sq_stack.top++;
return true;
}
bool Pop(position &temp) {//出棧
if (StackEmpty()) return 0;
sq_stack.top--;
temp = *sq_stack.top;
return 1;
}
void free_Stack() {
free(sq_stack.base);
}bool findMaze(int star_x, int star_y, int endr_x, int end_y) {//迷宮的入口和出口坐標
int i, j, k = 0;//i j表示目前的坐標
int tep_di,next_x,tep_y;//下一步的坐標
bool flag;
position fan_maze[200];
InitStack();//先創建空棧
temp.x = star_x, temp.y = star_y, temp.di - 1;//開始位置
Push(temp);//入棧操作。/*FHL*/
Maze[star_x][star_y]=-1;//-1表示走過;
while (!StackEmpty()) {//棧不為空
GetTop(temp);/*FHL*/
i = temp.x, j = temp.y , tep_di=temp.di;
if (i == endr_x && j == end_y) {
cout << "找到走出迷宮的路" << endl;
k = 0;
while (!StackEmpty()) {
Pop(temp);
fan_maze[k] = temp;
k++;//k指向下一個被插入的位置;
}
cout <<"起點:"<< "(" << fan_maze[k-1].x << ',' << fan_maze[k-1].y << ")->" << endl;
int count = 1;
for(k-=2;k>0;k--) {
cout<<"(" << fan_maze[k].x <<','<< fan_maze[k].y<<")->";
if (count % 3 == 0) cout << endl;
count++;
}
cout << "(" << fan_maze[0].x << ',' << fan_maze[0].y << ")" << "終點" << endl;//出口的位置
free_Stack();//釋放申請的堆空間
return true;
}/*FHL*/
flag = 0;
while (tep_di < 4 && !flag) {
tep_di++;
if (tep_di == 0){ next_x = i; tep_y = j + 1;}
else if (tep_di == 1) { next_x = i + 1;tep_y = j; }
else if (tep_di == 2) { next_x = i;tep_y = j - 1; }
else { next_x = i - 1; tep_y = j; }
if( Maze[next_x][tep_y] == 0 ) flag = 1;
}
if(flag) {
(sq_stack.top-1)->di = tep_di;//記錄上次坐標走的方向。
temp.x = next_x, temp.y = tep_y,temp.di=-1;
Push(temp);//這次坐標入棧
Maze[next_x][tep_y] = -1;//當前坐標標記為走過。
}
else {
Pop(temp);
Maze[temp.x][temp.y] = 0;
}
}/*FHL*/
cout << "沒有找到對應的出口" << endl;
free_Stack();//釋放申請的堆空間
return false;
}
};int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,8,8);
system("pause");/*FHL*/
return 0;
}int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,1,1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
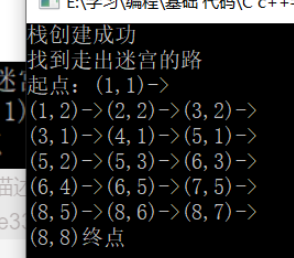
2.1(8,8)是終點
int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,8,8);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.2(8,2)是終點
int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,8,2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,9,9);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“C++數據結構關于棧迷宮示例分析”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對C++數據結構關于棧迷宮示例分析這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。