您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章將為大家詳細講解有關springboot中@Value的示例分析,小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲。
springboot版本: springboot-2.0.6.RELEASE
springboot啟動過程中,有兩個比較重要的過程,如下:
1 掃描,解析容器中的bean注冊到beanFactory上去,就像是信息登記一樣。
2 實例化、初始化這些掃描到的bean。
@Value的解析就是在第二個階段。BeanPostProcessor定義了bean初始化前后用戶可以對bean進行操作的接口方法,它的一個重要實現類AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor正如javadoc所說的那樣,為bean中的@Autowired和@Value注解的注入功能提供支持。
@Value解析過程中的主要調用鏈,我用以下時序圖來表示:
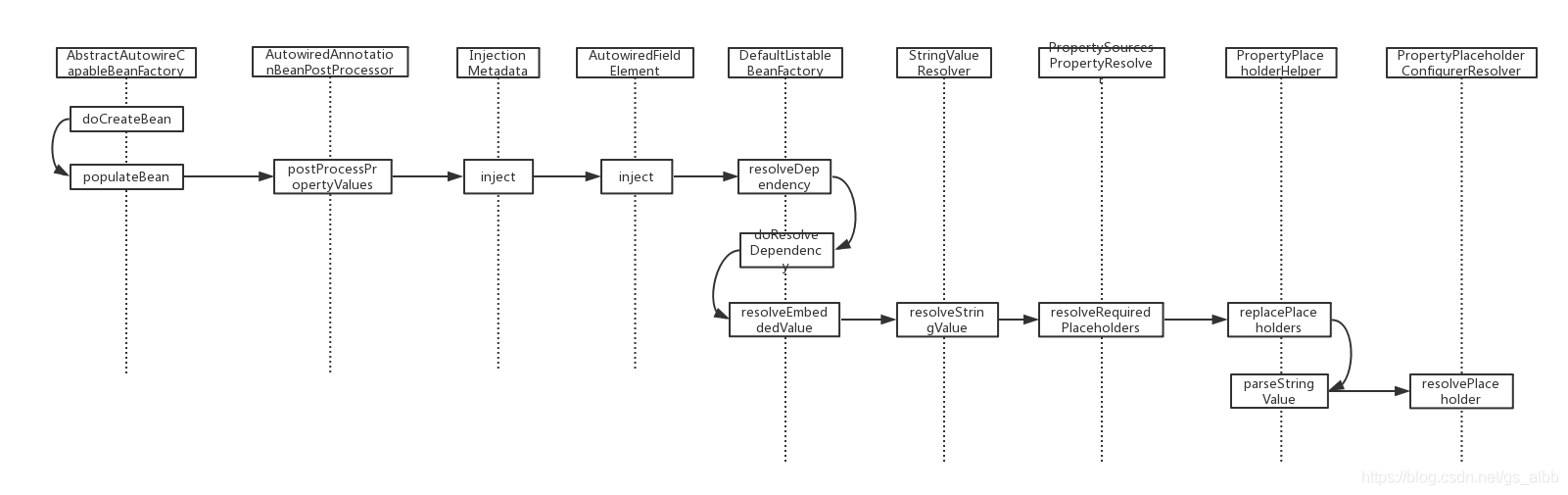
這里先簡單介紹一下圖上的幾個類的作用。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory: 提供了bean創建,屬性填充,自動裝配,初始胡。支持自動裝配構造函數,屬性按名稱和類型裝配。實現了AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口定義的createBean方法。
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 裝配bean中使用注解標注的成員變量,setter方法, 任意的配置方法。比較典型的是@Autowired注解和@Value注解。
InjectionMetadata: 類的注入元數據,可能是類的方法或屬性等,在AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor類中被使用。
AutowiredFieldElement: 是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的一個私有內部類,繼承InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement,描述注解的字段。
StringValueResolver: 一個定義了處置字符串值的接口,只有一個接口方法resolveStringValue,可以用來解決占位符字符串。本文中的主要實現類在PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer#processProperties方法中通過lamda表達式定義的。供ConfigurableBeanFactory類使用。
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver: 屬性資源處理器,主要功能是獲取PropertySources屬性資源中的配置鍵值對。
PropertyPlaceholderHelper: 一個工具類,用來處理帶有占位符的字符串。形如${name}的字符串在該工具類的幫助下,可以被用戶提供的值所替代。替代途經可能通過Properties實例或者PlaceholderResolver(內部定義的接口)。
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurerResolver: 上一行所說的PlaceholderResolver接口的一個實現類,是PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer類的一個私有內部類。實現方法resolvePlaceholder中調用了外部類的resolvePlaceholder方法。
這里主要介紹一下調用鏈中的比較重要的方法。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean方法用于填充bean屬性,執行完后可獲取屬性裝配后的bean。
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
...
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
// 遍歷所有InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor實例設置屬性字段值。
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor會進入此分支
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
//上行代碼執行后,bw.getWrappedInstance()就得到了@Value注解裝配屬性后的bean了
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
...
}InjectionMetadata#inject逐個裝配bean的配置屬性。
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
// 依次注入屬性
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}PropertyPlaceholderHelper#parseStringValue解析屬性值
/**
* 一個參數示例 value = "${company.ceo}"
*
*/
protected String parseStringValue(
String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(value);
// this.placeholderPrefix = "${"
int startIndex = value.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
while (startIndex != -1) {
// 占位符的結束位置,以value = "${company.ceo}"為例,endIndex=13
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {
// 獲取{}里的真正屬性名稱,此例為"company.ceo"
String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
String originalPlaceholder = placeholder;
if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions");
}
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key.
// 遞歸調用本方法,因為屬性鍵中可能仍然有占位符
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key...
// 獲取屬性鍵placeholder對應的屬性值
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
// 此處邏輯是當company.ceo=${bi:li}時,company.ceo最終被li所替代的原因
// 所以配置文件中,最好不要出現類似${}的東西,因為它本身就會被spring框架所解析
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
if (propVal == null) {
propVal = defaultValue;
}
}
}
if (propVal != null) {
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the
// previously resolved placeholder value.
propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// 將${company.ceo}替換為li
result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" +
placeholder + "'" + " in value \"" + value + "\"");
}
visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;
}
}
return result.toString();
}關于“springboot中@Value的示例分析”這篇文章就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,使各位可以學到更多知識,如果覺得文章不錯,請把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。