您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“如何使用GraphQL”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
Int:有符號 32 位整數。
Float:有符號雙精度浮點值。
String:UTF‐8 字符序列。
Boolean:true 或者 false。
ID:ID 標量類型表示一個唯一標識符,通常用以重新獲取對象或者作為緩存中的鍵。ID 類型使用和 String 一樣的方式序列化;然而將其定義為 ID 意味著并不需要人類可讀型。
 代碼見gitee倉庫example
代碼見gitee倉庫example
query 查詢
mutation 突變(理解為修改即可)
subscription 腳本
實現接口Coercing
添加注解@DgsScalar 示例
@DgsScalar(name = "Date")
public class DateCoercing implements Coercing<date, string> {
private static final String PATTERN = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
@Override
public String serialize(Object o) throws CoercingSerializeException {
if (o instanceof Date && Objects.nonNull(o)) {
Date date = (Date)o;
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(PATTERN);
return sdf.format(date);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Date parseValue(Object o) throws CoercingParseValueException {
if (o instanceof Date && Objects.nonNull(o)) {
return (Date)o;
} else {
throw new CoercingParseValueException("type is not date ");
}
}
@Override
public Date parseLiteral(Object o) throws CoercingParseLiteralException {
if (o instanceof String && Objects.nonNull(o)) {
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(PATTERN);
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(o.toString(), formatter);
return Date.from(localDateTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
}
return null;
}
}
.graphql配置
type Show {
title: String
releaseYear: Int
now: Date
}
scalar Date
postman訪問 
當兩個查詢名相同時會引發沖突,這時可以使用別名獲取不同的結果
{
zhangsan: hello(name: "張三"),
lisi: hello(name: "李四")
}
輸出:
{
"data": {
"zhangsan": "hello:張三!",
"lisi": "hello:李四!"
}
}片段主要用于將多個相同的字段進行封裝,我們在實際開發中會遇到返回結果中很多字段名名相同,使用==fragment==在.graphql文件中定義
{
golang: shows (title: "golang"){
...showFields
},
java: shows (title: "java"){
...showFields
}
}
# 定義片段
fragment showFields on Show {
title
releaseYear
now
}
輸出
{
"data": {
"golang": [
{
"title": "golang",
"releaseYear": 2009,
"now": "2021-03-08 13:46:43"
}
],
"java": [
{
"title": "java",
"releaseYear": 1995,
"now": "2021-03-08 13:46:43"
}
]
}
}上面的on后面的類型必須在.graphql文件中有定義
自定義address.graphqls
# 多個.graphqls定義需要使用這種方式
extend type Query {
listAddress(id: Int): Address
}
extend type Mutation {
addAddress(input: AddressInput): Int
}
type Address {
id: Int
street: String
city: String
country: String
customerId: Int
}
input AddressInput {
street: String
city: String
country: String
customerId: Int
}自定義的其他的schema文件查詢需要使用type extend 具體類型方式
mutation用于修改對象,dgs使用注意事項
@DgsData中的parentType="Mutation",field需要與schema中的保持一致
對象類型在java中定義的同時,需要在對應的.graphqls文件中定義,類型是input
input AddressInput {
street: String
city: String
country: String
customerId: Int
}graphiql查詢頁面中的對象要放在變量中定義
查詢輸入框的示例
添加以對象格式傳參
mutation AddAddress($addAddress: AddressInput) {
addAddress(input: $addAddress)
}
修改的請求參數直接以參數形式傳遞
mutation UpdateAddress {
updateAddress(id: 1, street: "鳳陽街道", city: "廣州") {
id
street
city
customerId
}
}
query variables中的變量值
{
"addAddress": {
"street": "江海街道", "city": "廣州", "country": "中國", "customerId": 1
}
} 變更中的多個字段(Multiple fields in mutations) 一個變更也能包含多個字段,一如查詢。查詢和變更之間名稱之外的一個重要區別是:
變更中的多個字段(Multiple fields in mutations) 一個變更也能包含多個字段,一如查詢。查詢和變更之間名稱之外的一個重要區別是:
非變量定義方式
mutation AddAddress1 {
addAddress(input: {
street: "昌崗街道",
city: "廣州",
country: "中國",
customerId: 1
})
}
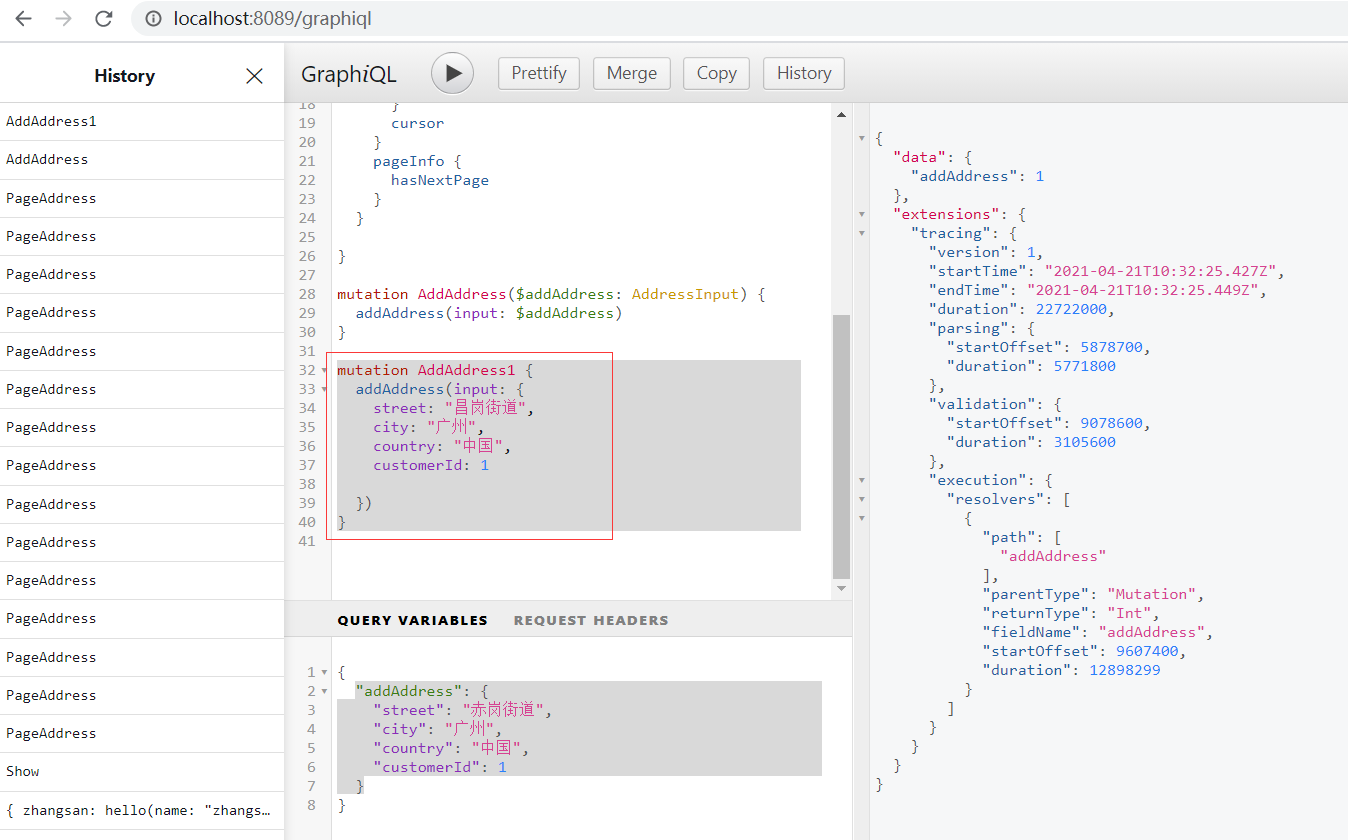查詢字段時,是并行執行,而變更字段時,是線性執行,一個接著一個。
上面我們主要是查詢,省略了query關鍵字和查詢名稱,生產中加上這些可以減少代碼歧義
query Abc {
hello(name: "zhangsan")
}
mutation AddAddress($addAddress: AddressInput) {
addAddress(input: $addAddress)
}
mutation UpdateAddress {
updateAddress(id: 1, street: "鳳陽街道", city: "廣州") {
id
street
city
customerId
}
}操作類型可以是 query、mutation 或 subscription,描述你打算做什么類型的操作。操作類型是必需的,除非你使用查詢簡寫語法,在這種情況下,你無法為操作提供名稱或變量定義。
操作名稱是你的操作的有意義和明確的名稱。它僅在有多個操作的文檔中是必需的,但我們鼓勵使用它,因為它對于調試和服務器端日志記錄非常有用。 當在你的網絡或是 GraphQL 服務器的日志中出現問題時,通過名稱來從你的代碼庫中找到一個查詢比嘗試去破譯內容更加容易。 就把它想成你喜歡的程序語言中的函數名
前面都是基于多個參數查詢,為了擴展減少修改代碼,我們通常將多個參數封裝成對象。GraphQL 擁有一級方法將動態值提取到查詢之外,然后作為分離的字典傳進去。這些動態值即稱為變量
使用變量之前,我們得做三件事:
使用 $variableName 替代查詢中的靜態值。
聲明 $variableName 為查詢接受的變量之一。
將 variableName: value 通過傳輸專用(通常是 JSON)的分離的變量字典中。
示例:
添加地址的變量
mutation AddAddress($addAddress: AddressInput) {
addAddress(input: $addAddress)
}
輸入框中的實際變量值
{
"addAddress": {
"street": "江海街道", "city": "廣州", "country": "中國", "customerId": 1
}
}變量定義看上去像是上述查詢中的 ($addAddress: AddressInput)。其工作方式跟類型語言中函數的參數定義一樣。它以列出所有變量,<font color="red">變量前綴必須為 $</font>,后跟其類型,本例中為 AddressInput。
所有聲明的變量都必須是標量、枚舉型或者輸入對象類型。所以如果想要傳遞一個復雜對象到一個字段上,你必須知道服務器上其匹配的類型。可以從Schema頁面了解更多關于輸入對象類型的信息。
變量定義可以是可選的或者必要的。上例中,AddressInput 后并沒有 <font color="red">!</font>,因此其是可選的。但是如果你傳遞變量的字段要求非空參數,那變量一定是必要的。
可以通過在查詢中的類型定義后面附帶默認值的方式,將默認值賦給變量。
query HeroNameAndFriends($episode: Episode = "JEDI") {
hero(episode: $episode) {
name
friends {
name
}
}
}當所有變量都有默認值的時候,你可以不傳變量直接調用查詢。如果任何變量作為變量字典的部分傳遞了,它將覆蓋其默認值。
指令可以用來動態控制是否顯示某個字段,有些場景下我們可能需要使用對象的A屬性,一些場景不需要A屬性,可以使用指令控制
query movies($withDirector: Boolean!) {
movies {
title
director @skip(if: $withDirector)
actor @include (if: $withDirector) {
name
}
actor {
home
}
}
}
變量
{
"withDirector": false
}變量值為true  變量值為false
變量值為false  對于字段操作可以使用
對于字段操作可以使用@skip,如果對對象中的某些屬性操作可以使用@include
我們用了 GraphQL 中一種稱作指令的新特性。一個指令可以附著在字段或者片段包含的字段上,然后以任何服務端期待的方式來改變查詢的執行。GraphQL 的核心規范包含兩個指令,其必須被任何規范兼容的 GraphQL 服務器實現所支持:
@include(if: Boolean) 僅在參數為 true 時,包含此字段。
@skip(if: Boolean) 如果參數為 true,跳過此字段。 指令在你不得不通過字符串操作來增減查詢的字段時解救你。服務端實現也可以定義新的指令來添加新的特性。
如果你查詢的字段返回的是接口或者聯合類型,那么你可能需要使用內聯片段來取出下層具體類型的數據:
/**
* 根據枚舉類型不同獲取不同類型的結果,graphql中使用的是內聯片段
* @param filter
* @return
*/
@DgsData(parentType = "Query", field = "movieFilter")
public List<movie> movieFilter(@InputArgument("filter")MovieType filter) {
return initMovie(filter);
}
private List<movie> initMovie(MovieType movieType) {
List<movie> movies = new ArrayList<>();
Actor actor1 = new Actor();
actor1.setHome("廣州");
actor1.setName("張三");
Actor actor2 = new Actor();
actor2.setHome("上海");
actor2.setName("李四");
if (movieType.equals(MovieType.Action) || movieType.equals(MovieType.All)) {
movies.add(new ActionMovie("Crouching Tiger", null, 0, actor1));
movies.add(new ActionMovie("Black hawk down", null, 10, actor1));
}
if (movieType.equals(MovieType.Scary) || movieType.equals(MovieType.All)) {
movies.add(new ScaryMovie("American Horror Story", null, true, 10, actor2));
movies.add(new ScaryMovie("Love Death + Robots", null, false, 4, actor2));
}
return movies;
}schema
# 定義枚舉
enum MovieType {
Scary
Action
All
}
type Query {
movieFilter(filter: MovieType): [Movie]
}
graphiql查詢
某些情況下,你并不知道你將從 GraphQL 服務獲得什么類型,這時候你就需要一些方法在客戶端來決定如何處理這些數據。GraphQL 允許你在查詢的任何位置請求 __typename,一個元字段,以獲得那個位置的對象類型名稱 
枚舉類型是一種特殊的標量,它限制在一個特殊的可選值集合內。
驗證這個類型的任何參數是可選值的的某一個
與類型系統溝通,一個字段總是一個有限值集合的其中一個值。
enum Episode {
NEWHOPE
EMPIRE
JEDI
}跟許多類型系統一樣,GraphQL 支持接口。一個接口是一個抽象類型,它包含某些字段,而對象類型必須包含這些字段,才能算實現了這個接口。
interface Movie {
title: String
director: String
actor: Actor
}
type ScaryMovie implements Movie {
title: String
director: String
gory: Boolean
scareFactor: Int
actor: Actor
}
type ActionMovie implements Movie {
title: String
director: String
nrOfExplosions: Int
actor: Actor
}聯合類型和接口十分相似,但是它并不指定類型之間的任何共同字段。
union MovieResult = ScaryMovie | ActionMovie
在我們的schema中,任何返回一個 MovieResult 類型的地方,都可能得到一個 ScaryMovie、ActionMovie p。注意,聯合類型的成員需要是具體對象類型;你不能使用接口或者其他聯合類型來創造一個聯合類型。
這時候,如果你需要查詢一個返回 SearchResult 聯合類型的字段,那么你得使用條件片段才能查詢任意字段。
schema
# union 聯合類型
movieFilter(filter: MovieType): [MovieResult]
查詢
query Movie($filter: MovieType!) {
movieFilter(filter: $filter) {
__typename
... on ScaryMovie {
scareFactor
title
director
actor {
name
home
}
}
... on ActionMovie {
nrOfExplosions
title
director
actor {
name
home
}
}
}
}聯合類型可以理解為根據不同的參數返回不同類型數據的組合,與接口稍有不同,可以對比schema和查詢結果
實現instrumentation接口或者繼承SimpleInstrumentation可以進行日志、權限處理,類似spring中的aop
@Configuration
public class GraphQLConfig {
@Bean
@Primary
public Instrumentation instrumentation() {
Instrumentation instrumentation = new ChainedInstrumentation(new TracingInstrumentation(), new CustomInstrumentation());
return instrumentation;
}
}加@Primary是由于DgsAutoConfiguration.kt中有對應的bean注入了 
graphql中的分頁只能知道是否還有下一頁數據,不能獲取總量和當前頁,這種結果可以結合dataLoader緩存根據條件查詢滾動翻頁 schema.graphqls
### 分頁相關
type AddressConnection {
edges: [AddressEdge]
pageInfo: PageInfo
}
type AddressEdge {
cursor: String
node: Address
}
type PageInfo {
hasPreviousPage: Boolean!
hasNextPage: Boolean!
} /**
* 分頁查詢
* @param environment
* @param customerId 查詢條件
* @param first 后面的的多少條結果
* @param after 每條數據都有游標,當前游標后的幾條數據 與first配合使用,null則從第一條開始
* @param last 前面多少條數據
* @param before 當前游標前的幾條數據 與last配合使用,null則從最后一條開始
* @return
*/
@DgsData(parentType = "Query", field = "pageAddress")
public Connection<address> pageAddress(DataFetchingEnvironment environment, @InputArgument("customerId")Integer customerId, @InputArgument("first")Integer first,
@InputArgument("after")String after, @InputArgument("last")Integer last, @InputArgument("before")String before) {
List<address> addressList = addressMapper.selectList(Wrappers.<address>lambdaQuery().eq(Address::getCustomerId, customerId));
return new SimpleListConnection(addressList).get(environment);
}

“如何使用GraphQL”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。