您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“C語言結構體強制轉換的方法”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“C語言結構體強制轉換的方法”吧!
在C語言中,結構體無法用以下方式強制轉換:
Struct_B b; Struct_A a = (Struct_A)b;
但可以使用指針間接轉換:
Struct_B *b; Struct_A *a = (Struct_A *)b;
很明顯,這樣強行給指針賦值,容易出現異常。讓我們來做一下測試。
先定義4個結構體
typedef struct {
int array[4];
}Struct_A;
typedef struct {
int *ptr_b;
} Struct_B;
typedef struct {
int int1;
int int_array1[2];
float float_array2[2];
}Struct_C;
typedef struct{
char char1;
char char_array[2];
}Struct_D;然后進行轉換測試
void main(){
//先對定義Struct_A變量a
Struct_A *a = malloc(sizeof(Struct_A));
if(a==NULL){return;};
int temp_a[4] = {0,1,2,3};
memcpy(a->array, &temp_a, 4*sizeof(int));
//將指針a賦值給b, c, d
Struct_B *b = (Struct_B *)a;
Struct_C *c = (Struct_C *)a;
Struct_D *d = (Struct_D *)a;
//打印一些重要的長度作為參考
printf("The system bits is %d\n", __WORDSIZE);
printf("The Size of int: %d Byte\nThe Size of int poniter: %d Byte\n", sizeof(int), sizeof(int*));
printf("The Size of float: %d Byte\n", sizeof(float));
printf("The Size of char: %d Byte\nThe Size of char pointer: %d Byte\n", sizeof(char), sizeof(char*));
//打印賦值結果
print_all_struct(a,b,c,d);
printf_a(a);
printf_b(b);
printf_c(c);
printf_d(d);
return;
}輸出(注釋為后期添加)為:
The system bits is 64 The Size of int: 4 Byte #64 位系統int占4個字節 The Size of int poniter: 8 Byte #64 位系統指針占8字節 The Size of float: 4 Byte #64 位系統float占4字節 The Size of char: 1 Byte #64 位系統char占1個字節 The Size of char pointer: 8 Byte #64 位系統指針占8字節 Show points #四個結構體的指針相等,說明指針賦值成功 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ |Pointer of a |Pointer of b |Pointer of c |Pointer of d | ------------------------------------------------------------------------ |0x5555555592a0 |0x5555555592a0 |0x5555555592a0 |0x5555555592a0 | ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Struct_A: #包含一個數組array[4] 0x5555555592a0: a->array[0] = 0 #結構體中第1個元素(array)起始地址與結構體指針(a)相等 0x5555555592a4: a->array[1] = 1 #結構體指針(a)+int長度(4字節) 得array中第2個元素地址 0x5555555592a8: a->array[2] = 2 #結構體指針(a)+int長度(4字節)*2 得array中第3個元素地址 0x5555555592ac: a->array[3] = 3 Struct_B: #包含一個int指針ptr_b &(b->ptr_b): 0x5555555592a0 #結構體中第1個元素int指針ptr_b的 地址 等于結構體指針(b) b->ptr_b: 0x100000000 #是地址相等,而不是值相等,要注意區分。沒有為指針ptr_b分配內存,故地址為0x100000000 Struct_C: 0x5555555592a0: c->int1: 0 #第1個元素地址等于指針c,該地址有值,元素類型與內存的值中一致,"賦值"成功 0x5555555592a4: c->int_array1[0]: 1 #指針c+int長度(4字節)得到元素 c->int_array1[0]的地址,該地址有值,值類型與內存的值中一致,"賦值"成功 0x5555555592a8: c->int_array1[1]: 2 #指針c+int長度(4字節)*2剛好是 c->int_array1[1]的起始地址,該地址有值,值類型與內存的值中一致,"賦值"成功 0x5555555592ac: c->float_array2[0]: 0.000000 #地址有值,但類型不是float,”賦值“失敗 0x5555555592b0: c->float_array2[1]: 0.000000 #這個地址沒有值,float默認值為0.000000 Struct_D: 0x5555555592a0: d->char1: (null) #第1個元素地址等于指針d, 但值的類型與內存中不同,”賦值“失敗 0x5555555592a1: d->char_array[0]: (null) #值的類型不同,導致長度不同,得到的地址中無值 0x5555555592a2: d->char_array[1]: (null) #同上
我們先來看輸出結果的圖解: 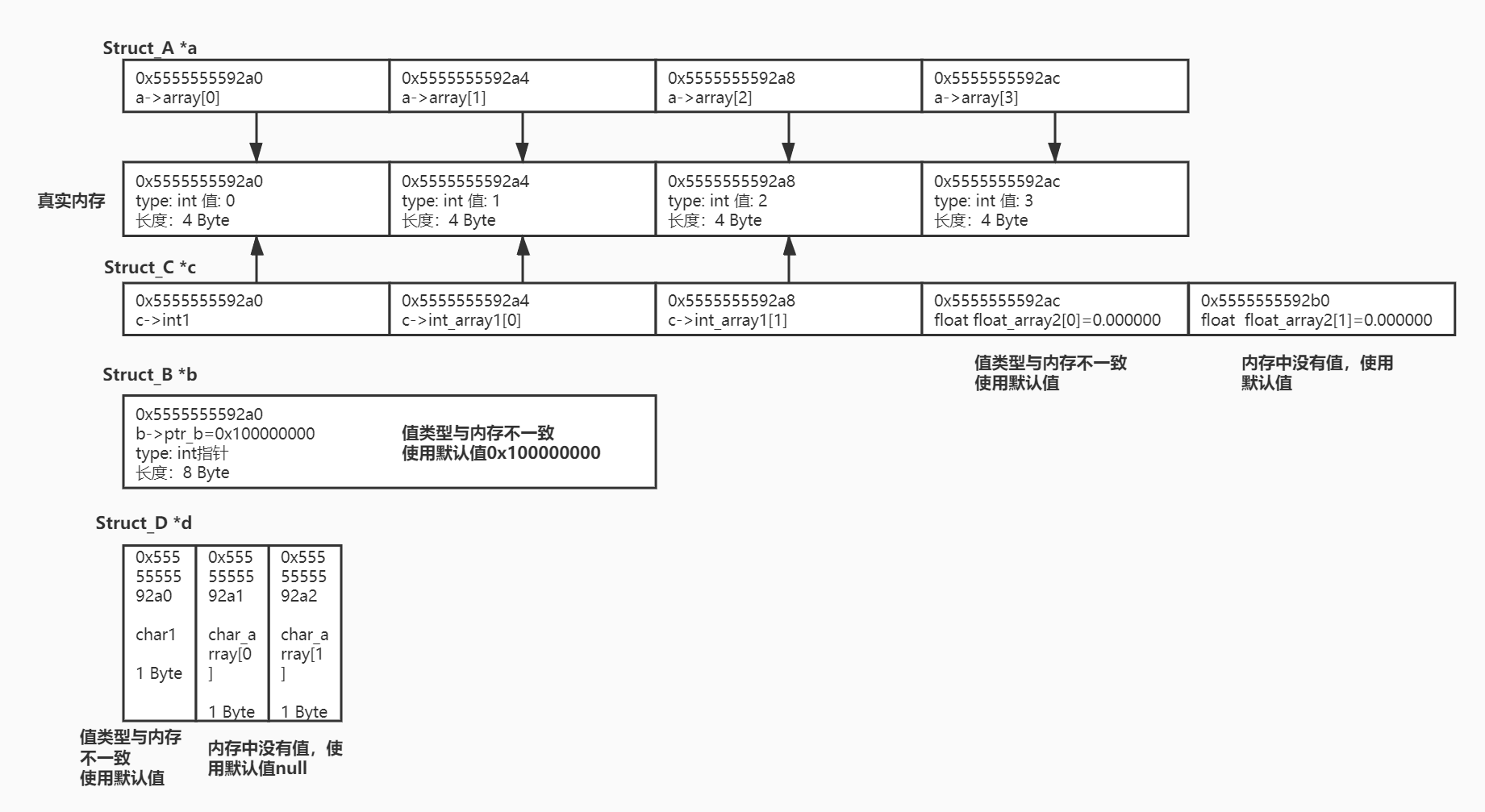
從上面的結果我們可以得出幾個結論:
結構體指針等于第一個元素的起始地址
如果第一個元素是指針p,請注意是指針變量的地址&p,而不是指針本身p
結構體內的元素在內存中順序排列,賦值時也是順序”賦值“。滿足兩個條件即可”賦值“成功:
元素起始地址上有值
元素類型與內存中的值類型一致
嚴格來說其實并不是賦值,而是指定了結構體的起始地址,根據元素的長度可以順序得到各個元素的地址,如果元素地址上有值,且元素類型與內存中的值一致,則可以直接使用,否則無法使用,自動轉為默認值。
補充: 到這里有的讀者可能會問,內存中并沒有存儲數據類型,為什么筆者一直在強調元素類型與內存中的值類型是否一致呢?
原因是不同類型的值在內存中的編碼存儲方式不一樣,一個按int編碼值是無法按float方式直接讀取的。詳細原理此處不再贅述。
最后附上完整代碼
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <bits/wordsize.h>
typedef struct {
int array[4];
}Struct_A;
typedef struct {
int *ptr_b;
} Struct_B;
typedef struct {
int int1;
int int_array1[2];
float float_array2[2];
}Struct_C;
typedef struct{
char char1;
char char_array[2];
}Struct_D;
void printf_a(Struct_A *a){
printf("Struct_A:\n");
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
printf("%p: a->array[%d] = %d\n", &((a->array)[i]), i, (a->array)[i]);
}
}
void printf_b(Struct_B *b){
printf("Struct_B:\n");
printf("&(b->ptr_b): %p\n",&(b->ptr_b));
printf("b->ptr_b: %p\n", b->ptr_b);
}
void printf_c(Struct_C *c){
printf("Struct_C:\n");
printf("%p: c->int1: %d\n", &(c->int1), c->int1);
printf("%p: c->int_array1[0]: %d\n", &(c->int_array1[0]), c->int_array1[0]);
printf("%p: c->int_array1[1]: %d\n", &(c->int_array1[1]), c->int_array1[1]);
printf("%p: c->float_array2[0]: %f\n", &(c->float_array2[0]), c->float_array2[0]);
printf("%p: c->float_array2[1]: %f\n", &(c->float_array2[1]), c->float_array2[1]);
}
void printf_d(Struct_D *d){
printf("Struct_D:\n");
printf("%p: d->char1: %s\n", &(d->char1), d->char1);
printf("%p: d->char_array[0]: %s\n", &(d->char_array[0]), d->char_array[0]);
printf("%p: d->char_array[1]: %s\n", &(d->char_array[1]), d->char_array[1]);
}
void print_all_struct(Struct_A *a, Struct_B *b, Struct_C *c, Struct_D *d){
printf("Show points\n");
printf(" -----------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("|Pointer of a |Pointer of b |Pointer of c |Pointer of d |\n");
printf(" -----------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("|%p |%p |%p |%p |\n", a, b, c, d);
printf(" -----------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
}
void main(){
Struct_A *a = malloc(sizeof(Struct_A));
if(a==NULL){return;};
int temp_a[4] = {0,1,2,3};
memcpy(a->array, &temp_a, 4*sizeof(int));
Struct_B *b = (Struct_B *)a;
Struct_C *c = (Struct_C *)a;
Struct_D *d = (Struct_D *)a;
printf("The system bits is %d\n", __WORDSIZE);
printf("The Size of int: %d Byte\nThe Size of int poniter: %d Byte\n", sizeof(int), sizeof(int*));
printf("The Size of float:%d\n",sizeof(float));
printf("The Size of char: %d Byte\nThe Size of char pointer: %d Byte\n", sizeof(char), sizeof(char*));
print_all_struct(a,b,c,d);
printf_a(a);
printf_b(b);
printf_c(c);
printf_d(d);
return;
}感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“C語言結構體強制轉換的方法”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對C語言結構體強制轉換的方法這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。