您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“怎么使用Rust內置trait:PartialEq和Eq”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“怎么使用Rust內置trait:PartialEq和Eq”吧!
Rust 在很多地方使用了 traits, 從非常淺顯的操作符重載, 到 Send, Sync 這種非常微妙的特性。一些 traits 是可以被自動派生的(你只需要寫#[derive(Copy, Clone, PartialEq, Eq, Debug, Default, Hash, ...)] 就能得到一個神奇的實現, 它通常是對的。
PartialEq 和 Eq這兩個 Traits 的名稱實際上來自于抽象代數中的等價關系和局部等價關系,實際上兩者的區別僅有一點,即是否在相等比較中是否滿足反身性(Reflexivity)。
/// [`eq`]: PartialEq::eq
/// [`ne`]: PartialEq::ne
#[lang = "eq"]
#[stable(feature = "rust1", since = "1.0.0")]
#[doc(alias = "==")]
#[doc(alias = "!=")]
#[rustc_on_unimplemented(
message = "can't compare `{Self}` with `{Rhs}`",
label = "no implementation for `{Self} == {Rhs}`"
)]
pub trait PartialEq<Rhs: ?Sized = Self> {
/// This method tests for `self` and `other` values to be equal, and is used
/// by `==`.
#[must_use]
#[stable(feature = "rust1", since = "1.0.0")]
fn eq(&self, other: &Rhs) -> bool;
/// This method tests for `!=`.
#[inline]
#[must_use]
#[stable(feature = "rust1", since = "1.0.0")]
fn ne(&self, other: &Rhs) -> bool {
!self.eq(other)
}
}如果我們想比較某個類型的兩個值 x 和 y 是否相等(不等),例如:x == y (x != y),那么我們就必須為類型實現 PartialEq Trait。
PartialEq 可使用 #[derive] 來交由編譯器實現,當一個 struct 在進行相等比較時,會對其中每一個字段進行比較;如果遇到枚舉時,還會對枚舉所擁有的數據進行比較。
我們也可以自己實現 PartialEq,實現時只需要實現判斷是否相等的函數 fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool ,Rust 會自動提供 fn ne(&self, other: &Self) -> bool。例子如下:
enum BookFormat {
Paperback,
Hardback,
Ebook,
}
struct Book {
isbn: i32,
format: BookFormat,
}
impl PartialEq for Book {
fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {
self.isbn == other.isbn
}
}pub trait Eq: PartialEq<Self> {
// this method is used solely by #[deriving] to assert
// that every component of a type implements #[deriving]
// itself, the current deriving infrastructure means doing this
// assertion without using a method on this trait is nearly
// impossible.
//
// This should never be implemented by hand.
#[doc(hidden)]
#[inline]
#[stable(feature = "rust1", since = "1.0.0")]
fn assert_receiver_is_total_eq(&self) {}
}實現 Eq 的前提是已經實現了 PartialEq,因為實現 Eq 不需要額外的代碼,只需要在實現了PartialEq 的基礎上告訴編譯器它的比較滿足自反性就可以了。對于上面的例子只需要:#[derive(Eq)] 或 impl Eq for Book {}。
enum BookFormat {
Paperback,
Hardback,
Ebook,
}
struct Book {
isbn: i32,
format: BookFormat,
}
impl PartialEq for Book {
fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {
self.isbn == other.isbn
}
}
impl Eq for Book {}這兩個 Traits 的名稱實際上來自于抽象代數中的等價關系和局部等價關系。
等價關系(equivalence relation)即設 \displaystyle RR 是某個集合 \displaystyle AA 上的一個二元關系。若 \displaystyle RR 滿足以下條件:
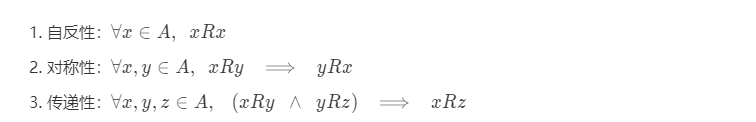
則稱 \displaystyle RR 是一個定義在 \displaystyle AA 上的等價關系。
并非所有的二元關系都是等價關系, Eq 和 PartialEq 的區別在于是否在相等比較中是否滿足自反性,即 x == x。
例如對于浮點類型,Rust 只實現了 PartialEq 而沒有實現 Eq,原因在于 NaN != Nan,不滿足自反性。
Eq 相比 PartialEq 需要額外滿足反身性,即 a == a,對于浮點類型,Rust 只實現了 PartialEq 而不是 Eq,原因就是 NaN != NaN。
當一個類型同時實現了 Eq 和 Hash 時,該類型滿足下列特性:
k1 == k2 -> hash(k1) == hash(k2)
即,當兩個 key 相等時,它們的哈希值必然相等。Rust 里的 HashMap 和 HashSet 都依賴該特性。
到此,相信大家對“怎么使用Rust內置trait:PartialEq和Eq”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。