溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
C 結構體的定義
#include <stdio.h>
struct student
{
int ID;
char name[10];
int age;
}; //注意這里的分號
int main()
{
// 初始化
struct student student1 = {1111,"Redhat",20};
struct student student2 = {.ID = 1111,.name = "Debian",.age = 20};//C99才有
struct student student3 = {1111,"BSD",.ID = 20,.age = 30}; //ID = 20
//使用
printf("%d,%s,%d \n",student1.ID,student1.name,student1.age);
printf("%d,%s,%d \n",student2.ID,student2.name,student2.age);
printf("%d,%s,%d \n",student3.ID,student3.name,student3.age);
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
1111,Redhat,20
1111,Debian,20
20,BSD,30結構體內存分配情況
小的遵循大的數據類型,存在浪費內存的情況
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct student
{
unsigned char c1;
unsigned char c2;
unsigned int i1;
unsigned char c3;
unsigned char c4;
unsigned char c5;
unsigned char c6;
unsigned int i2;
};
int main()
{
printf("%ld \n",sizeof(struct student));
struct student student1;
memset(&student1,0x55,sizeof(struct student));
student1.i1 = 0x12345678;
student1.i2 = 0x23456789;
student1.c1 = 0x21;
student1.c2 = 0x22;
student1.c3 = 0x23;
student1.c4 = 0x24;
student1.c5 = 0x25;
student1.c6 = 0x26;
int *p = (int*) &student1;
for(int i = 0;i< sizeof(struct student)/4;i++)
{
printf("%p %x \n",p,*p);
p++;
}
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
16
0x7ffc7913b1c0 55552221
0x7ffc7913b1c4 12345678
0x7ffc7913b1c8 26252423
0x7ffc7913b1cc 23456789
可以看到內存初始化就是0X55,第一個的4個字節存在了浪費結構體,自定義數據類型:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct student
{
unsigned char c1:1;
unsigned char c2:3;
unsigned char c3:4;
};
int main()
{
printf("%ld \n",sizeof(struct student));
struct student student1;
student1.c1 = 1;
student1.c2 = 6;
student1.c3 = 14;
char *p = (char *)& student1;
printf("%x,%d,%d,%d \n",*p,student1.c1,student1.c2,student1.c3);
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
1
ffffffed,1,6,14結構體嵌套:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct man
{
unsigned char age;
};
struct student
{
unsigned char name[20];
struct man a_man;
};
int main()
{
printf("%ld \n",sizeof(struct student));
struct student student1;
student1.a_man.age = 10;
printf("student age = %d \n",student1.a_man.age);
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
21
student age = 10結構體數組,結構體嵌套
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct man
{
char name[20];
unsigned char age;
unsigned char heiget;
};
struct human
{
struct man son;
int money;
};
int main()
{
printf("%ld \n",sizeof(struct human));
/* 結構體數組 */
struct man people[3]={
{"奧巴馬",50,170},
{"金正恩",44,166},
{"樸槿惠",33,155},
};
/* 結構體嵌套 */
struct human a_human;
a_human.son.age = 10;
printf("son age = %d \n",a_human.son.age);
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
28
son age = 10結構體賦值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct man
{
char name[20];
unsigned char age;
unsigned char height;
};
int main()
{
struct man people1={"奧巴馬",50,170};
struct man people2;
people2 = people1; //結構體的賦值,people1的內存賦值到了people2,二者相互獨立!
//memcpy(&people2,&people1,sizeof(people1));
//相當于memcpy(&people2,&people1,sizeof(people1));
printf("%s,%d,%d \n",people2.name,people2.age,people2.height);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/*區別于數組
char str1[10] = {"Hello!"};
char str2[20];
str2 = str1; //這是不允許的。數組的名僅是一個地址,不允許賦值。
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//這個不是賦值,這個只能是指向了那個地址
char str3[] = {"Hello !"};
char *p1 = str3;
char *p2 = p1;
*/
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
奧巴馬,50,170結構體賦值里面的指針變量
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct man
{
char *name;
unsigned char age;
unsigned char height;
};
int main()
{
struct man people1={"樸槿惠",40,170};
struct man people2;
people2 = people1;//結構體賦值
printf("%s,%d,%d \n",people2.name,people2.age,people2.height);
people2.name = "王麻子"; //指針指向常量"王麻子"
printf("%s,%d,%d \n",people2.name,people2.age,people2.height);
/*結構體指針*/
struct man people3;
people3.name = malloc(20);
strcpy(people3.name,"孫悟空");
printf("%s,%d,%d \n",people3.name,people3.age,people3.height);
//free(people3.name); //堆釋放會對下面的strcpy(people4.name,people3.name);有影響
/*如果結構體里面有指針,不能通過簡單賦值完成操作,因為指向的是一樣的*/
struct man people4;
people4.name = malloc(strlen(people3.name)+1);
strcpy(people4.name,people3.name);
people4.age = people3.age;
people4.height = people3.height;
printf("%s,%d,%d \n",people4.name,people4.age,people4.height);
free(people3.name); //堆釋放
free(people4.name); //堆釋放
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
樸槿惠,40,170
王麻子,40,170
孫悟空,0,0
孫悟空,0,0結構體指針 初步1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct man
{
char *name;
unsigned char age;
unsigned char height;
};
int main()
{
struct man people1;
struct man *people2 = &people1;
(*people2).name = malloc(10);
(*people2).age = 20;
(*people2).height = 170;
/* 上面的形式可以寫成一下:*/
people2 -> name = malloc(10);
people2 -> age = 20;
people2 -> height = 170;
}
編譯通過
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$結構體指針 初步2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct man
{
unsigned char id;
char name[20];
unsigned char height;
};
int main()
{
struct man people[3] = {
{1,"wang",181}, //wang屬于常量
{2,"li",182},
{3,"zhang",189},
};
/* 定義一個結構體指針 */
struct man *people2 = &people[0];
printf("%d,%s,%d \n",people2->id,people2->name,people2->height);
/* 訪問方式2,也可以方便for循環 */
printf("%d,%s,%d \n",people2[1].id,people2[1].name,people2[1].height);
people2++;//一次會移動一個結構體
printf("%d,%s,%d \n",people2->id,people2->name,people2->height);
/*
struct man people1 = {1,"wang",181};
struct man people2 = {2,"wang",181};
struct man people3 = {3,"wang",181};
不要嘗試用循環來遍歷這樣的數據,因為您不知道編譯器是怎么安排的
最好放在同一個數組里面
*/
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
1,wang,181
2,li,182
2,li,182結構體的指針,初步3
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct man
{
unsigned char id;
char *name;
unsigned char age;
};
int main()
{
struct man *sp = malloc(sizeof(struct man));
sp->id = 5;
sp->age = 10;
sp->name = malloc(10);
strcpy(sp->name,"zhang");
printf("%d,%s,%d \n",sp->id,sp->name,sp->age);
free(sp->name); // 一定先釋放這個
free(sp); //要不然sp-name永遠找不到了
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
5,zhang,10動態獲取用戶輸入,不會浪費內存空間
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct test
{
char *name; //指針哦
};
struct man
{
unsigned char id;
char *name;
unsigned char age;
//struct test *p; //有嵌套了一層,這是很難搞的
};
int main()
{
struct man *sp = malloc(sizeof(struct man) * 10);
memset(sp,0,sizeof(struct man) * 10);// 內存清零
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++)
{
sp[i].id = i;
sp[i].age = i;
char buf[999]={0};
scanf("%s",buf);
int len = strlen(buf);
sp[i].name =malloc(len+1) ;
sprintf(sp[i].name,"%s",buf);
}
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("%d,%s,%d \n",sp[i].id,sp[i].name,sp[i].age);
}
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++)//循環釋放
{
free(sp[i].name);
}
free(sp); //全部釋放
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
12
1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
a
s
wsswdwdwdwdwedfwefefvdvgdf,kvdfvdfvdvmdvm
mcsfdmcdsmc'nv vnvpmvpwvm[sdv
fsdv dvdf e fdf f
0,12,0
1,1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111,1
2,2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222,2
3,a,3
4,s,4
5,wsswdwdwdwdwedfwefefvdvgdf,kvdfvdfvdvmdvm,5
6,mcsfdmcdsmc'nv,6
7,vnvpmvpwvm[sdv,7
8,fsdv,8
9,dvdf,9形參是結構體的函數
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct man
{
unsigned char id;
char *name;
unsigned char age;
};
void fun1(struct man a_man)
{
printf("id = %d,age = %d,name = %s \n",a_man.id,a_man.age,a_man.name);
strcpy(a_man.name,"haha"); //會影響傳過來的數據,因為指向的是同一塊內存
a_man.id = 99; //而id就不會發生變化
}
int main()
{
//struct man people1 = {0,"wang",100};
struct man people1;
people1.id = 0;
people1.age = 10;
people1.name = malloc(10);
strcpy(people1.name,"wang");
fun1(people1);
printf("id = %d,age = %d,name = %s \n",people1.id,people1.age,people1.name);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
id = 0,age = 10,name = wang
id = 0,age = 10,name = haha結構體參數,地址與傳值
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ cat main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct man
{
unsigned char id;
char name[100];
unsigned char age;
};
void fun1(struct man a_man)//傳值過來
{
printf("id = %d,age = %d,name = %s \n",a_man.id,a_man.age,a_man.name);
strcpy(a_man.name,"haha"); //無法修改
a_man.id = 99; //無法修改
}
void fun2(struct man *sp) //地址傳過來
//void fun2(const struct man *sp) //保護起來,防止修改
{
printf("id = %d,age = %d,name = %s \n",sp->id,sp->age,sp->name);
strcpy(sp->name,"魯智深"); //可以修改
sp->id = 66; //可以修改
}
int main()
{
struct man people1;
people1.id = 0;
people1.age = 10;
strcpy(people1.name,"wang");
fun1(people1);//fun1無法修改參數值
printf("id = %d,age = %d,name = %s \n",people1.id,people1.age,people1.name);
fun2(&people1);
printf("id = %d,age = %d,name = %s \n",people1.id,people1.age,people1.name);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
id = 0,age = 10,name = wang
id = 0,age = 10,name = wang
id = 0,age = 10,name = wang
id = 66,age = 10,name = 魯智深如何修改機構體內部的數組
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct str
{
char buf[100];
};
void fun1(struct str s)
{
strcpy(s.buf,"hello ");
}
void fun2(char s[])
{
strcpy(s,"hello");
}
int main()
{
struct str s={"world!"}; ;
fun1(s);//傳結構體,相當于賦值過去了,不會改變變量 (會很消耗內存的性能)
printf("%s \n",s.buf);
char s1[100]="world!";
fun2(s1);//數組會把地址傳過去,會修改變量
printf("%s \n",s1);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
world!
hello結構體函數 初始化結構體
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct str
{
char buf[100];
};
struct str getstr()
{
struct str s;
strcpy(s.buf,"Hello World!");
return s;
}
char *getstr1()
{
char buf[100];//在棧區
strcpy(buf,"Hello World!");
//return buf;//無法返回有效數據
}
int main()
{
//char *tmp = getstr1(); 非法執行
struct str tmp = getstr();
printf("%s \n",tmp.buf);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
Hello World!【指向結構體的指針】
返回結構體,消耗很大
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct str
{
char buf[100];
};
struct str getstr()
{
struct str s;
strcpy(s.buf,"Hello World!");
return s;
}
char *getstr1()
{
char buf[100];//在棧區
strcpy(buf,"Hello World!");
//return buf;//無法返回有效數據
}
int main()
{
//char *tmp = getstr1(); 非法執行
struct str tmp = getstr(); //內存拷貝,消耗很大
printf("%s \n",tmp.buf);
return 0;
}返回結構體指針,消耗很小
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct str
{
char buf[100];
};
struct str *getstr()
{
struct str *s = malloc(sizeof(struct str));
printf("%p \n",s);
strcpy(s->buf,"Hello World!");
return s;//把指針返回去
}
int main()
{
struct str *tmp = getstr(); //內存拷貝,消耗很大
printf("%p \n",tmp);
printf("%s \n",tmp->buf);
free(tmp);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
0x8cc010
0x8cc010
Hello World!聯合體初步1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
union var
{
char c;
int i;
short d;
char *s;//很危險
};
struct str
{
char c;
int i;
short d;
};
int main()
{
/* 結構體與聯合體元素地址區別 */
union var v;//聯合體元素公用用一個地址
printf("%p \n" ,&(v.c));
printf("%p \n" ,&(v.i));
printf("%p \n" ,&(v.d));//小端對齊,高位放高位,低位放低位
struct str s;//結構體,元素分別獨立
printf("%p \n" ,&(s.c));
printf("%p \n" ,&(s.i));
printf("%p \n" ,&(s.d));
/* 修改聯合體元素 */
printf("%ld \n",sizeof(v));
v.c = 100;
printf("%d \n",v.c);
v.i = 1;
printf("%d \n",v.c);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
0x7ffc3f56e5d0
0x7ffc3f56e5d0
0x7ffc3f56e5d0
0x7ffc3f56e5e0
0x7ffc3f56e5e4
0x7ffc3f56e5e8
8
100
1枚舉
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
enum spectrum {red,yellow,green,blue,white,black};//申明一個枚舉
enum number {zero=10,one=9,two,three};//申明一個枚舉
void test(int i) {printf("test \n");}
void test1(int a,int b) {printf("test1\n");}
void test2(int a,int b,int c) {printf("test2\n");}
void *function_factory(enum number n)
{
if(n == zero) return test;
if(n == one) return test1;
if(n == two) return test2;
}
void getcolor(enum spectrum color)
{
if(color == red) printf("red \n");
if(color == yellow) printf("yellow \n");
if(color == green) printf("green \n");
if(color == blue) printf("blue \n");
}
int main()
{
enum number b = one;
void *p = function_factory(b);
printf("%p ,%p \n",p,test1);
enum spectrum color = red;
getcolor(color);
printf("%d,%d,%d \n",red,yellow,green);
printf("%d,%d,%d \n",zero,one,two);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
0x400594 ,0x400594
red
0,1,2
10,9,10typedef 初步
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef unsigned char BYTE;
#define mybyte unsigned char
typedef unsigned int UINT;//嚴格檢查變量類型
#define MAX 100 //簡單替換,不做變量類型檢查,沒有分號
struct student
{
int id;
char name[100];
};
int main()
{
BYTE b1 = 0xff;
printf("%x \n",b1);
UINT u1 = 0xFF00FF00;
printf("%x \n",u1);
//正常使用
struct student student1;
//typedef 來定義
typedef struct student STUDENT; //自定義 數據類型
STUDENT student2;
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
ff
ff00ff00沒有用typedef之前的代碼,看著很暈
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
const char *func1(const char *str1,const char *str2)
{
char *p = malloc(strlen(str1) + strlen(str2) +1);
strcpy(p,str1);
strcat(p,str2);
return p;
}
const char *func2(const char *(*p)(const char *str1,const char *str2),const char *s1,const char *s2)
{
return p(s1,s2);
}
int main()
{
const char *tmp1 = "Hello";
const char *tmp2 = "world!";
const char *s = func2(func1,tmp1,tmp2);
printf("%s \n",s);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
Helloworld!typedef優化 對比
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//定義一個指向這種函數類型的指針
typedef const char *(*FUNC1)(const char *str1,const char *str2);
const char *func1(const char *str1,const char *str2)
{
char *p = malloc(strlen(str1) + strlen(str2) +1);
strcpy(p,str1);
strcat(p,str2);
return p;
}
const char *func2(FUNC1 p,const char *s1,const char *s2)
{
return p(s1,s2);
}
int main()
{
const char *tmp1 = "Hello";
const char *tmp2 = "world!";
const char *s = func2(func1,tmp1,tmp2);
printf("%s \n",s);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
Helloworld!typedef深入1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//定義一個指向這種函數類型的指針 的數據類型
typedef const char *(*FUNC1)(const char *str1,const char *str2);
//這是函數的原始申明
const char *func1(const char *str1,const char *str2)
{
char *p = malloc(strlen(str1) + strlen(str2) +1);
strcpy(p,str1);
strcat(p,str2);
return p;
}
const char *func2(FUNC1 p,const char *s1,const char *s2)
{
return p(s1,s2);
}
FUNC1 test()
{
FUNC1 tmp = func1;
return tmp;
}
int main()
{
//定義10個FUNC1數據類型
FUNC1 f[10];
//定義一個數組10個元素,參數是const char *str1,const char *str2,返回值是 const char *
const char *(*p[10])(const char *str1,const char *str2);
const char *tmp1 = "Hello ";
const char *tmp2 = "world!";
const char *s = func2(func1,tmp1,tmp2);
printf("%s \n",s);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
Hello world!超級復雜的typedef
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ cat main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef unsigned char BYTE;
typedef unsigned int UINT;
#define MYBYTE unsigned char
#define MAX 100
//typedef 100 MYMAX;
struct student
{
int ID;
char name[MAX];
};
typedef struct student STUDENT;
typedef const char *(*FUNC1)(const char *str1, const char *str2);
const char *func1(const char *str1, const char *str2)
{
char *p = malloc(strlen(str1) + strlen(str2) + 1);
strcpy(p, str1);
strcat(p, str2);
return p;
}
/*
const char *(*)(const char *str1, const char *str2) test()
{
FUNC1 tmp = func1;
return tmp;
}
*/
const char *func2(const char *(*p[])(const char *str1, const char *str2), const char *s1, const char *s2)
{
return (p[0])(s1, s2);
}
int main()
{
FUNC1 f[10];//
const char *tmp1 = "hello ";
const char *tmp2 = "world";
f[0] = func1;
const char *s = func2(f, tmp1, tmp2);
printf("s = %s\n", s);
BYTE b;
b = 0x12;
UINT i;
i = 0xffff;
STUDENT st;
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
s = hello world
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$【復習================================】
聯合體的指針,很危險
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
union var
{
char c;
int i;
short d;
char *s;//很危險
};
int main()
{
union var v;
v.s = (char *)malloc(100);
v.c = 1;
free(v.s);//致命錯誤!
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
Segmentation fault (core dumped)typedef 特別高級的用法
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ cat main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct student ST;
struct student
{
char name[200];
int id;
};
typedef const char *(*FUNC1)(const char *str1,const char *str2) ;
const char *funcl(const char *str1,const char *str2)
{
printf("%s,%s \n",str1,str2);
return NULL;
}
const char *func2(FUNC1 p, const char *str1,const char *str2)
{
return p(str1,str2);
}
int main()
{
ST student1;
strcpy(student1.name,"奧巴馬");
student1.id = 1;
printf("%d,%s \n",student1.id,student1.name);
return 0;
}
chunli@ubuntu:~/pointer$ gcc -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
1,奧巴馬不使用typedef
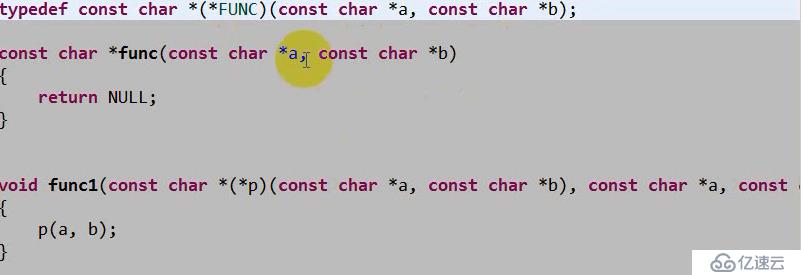
使用typedef

免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。