您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“有哪些LFU實現方式”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“有哪些LFU實現方式”吧!
LFU實現
力扣原題描述如下:
請你為 最不經常使用(LFU)緩存算法設計并實現數據結構。它應該支持以下操作:get 和 put。 get(key) - 如果鍵存在于緩存中,則獲取鍵的值(總是正數),否則返回 -1。 put(key, value) - 如果鍵不存在,請設置或插入值。當緩存達到其容量時,則應該在插入新項之前,使最不經常使用的項無效。在此問題中,當存在平局(即兩個或更多個鍵具有相同使用頻率)時,應該去除 最近 最少使用的鍵。 「項的使用次數」就是自插入該項以來對其調用 get 和 put 函數的次數之和。使用次數會在對應項被移除后置為 0 。 示例: LFUCache cache = new LFUCache( 2 /* capacity (緩存容量) */ ); cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); cache.get(1); // 返回 1 cache.put(3, 3); // 去除 key 2 cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到key 2) cache.get(3); // 返回 3 cache.put(4, 4); // 去除 key 1 cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到 key 1) cache.get(3); // 返回 3 cache.get(4); // 返回 4 來源:力扣(LeetCode) 鏈接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lfu-cache
就是要求我們設計一個 LFU 算法,根據訪問次數(訪問頻次)大小來判斷應該刪除哪個元素,get和put操作都會增加訪問頻次。當訪問頻次相等時,就判斷哪個元素是最久未使用過的,把它刪除。
因此,這道題需要考慮兩個方面,一個是訪問頻次,一個是訪問時間的先后順序。
方案一:使用優先隊列思路:
我們可以使用JDK提供的優先隊列 PriorityQueue 來實現 。因為優先隊列內部維護了一個二叉堆,即可以保證每次 poll 元素的時候,都可以根據我們的要求,取出當前所有元素的最大值或是最小值。只需要我們的實體類實現 Comparable 接口就可以了。
因此,我們需要定義一個 Node 來保存當前元素的訪問頻次 freq,全局的自增的 index,用于比較大小。然后定義一個 Map
當 cache 容量不足時,根據訪問頻次 freq 的大小來刪除最小的 freq 。若相等,則刪除 index 最小的,因為index是自增的,越大說明越是最近訪問過的,越小說明越是很長時間沒訪問過的元素。
因本質是用二叉堆實現,故時間復雜度為O(logn)。
public class LFUCache4 { public static void main(String[] args) { LFUCache4 cache = new LFUCache4(2); cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); // 返回 1 System.out.println(cache.get(1)); cache.put(3, 3); // 去除 key 2 // 返回 -1 (未找到key 2) System.out.println(cache.get(2)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); cache.put(4, 4); // 去除 key 1 // 返回 -1 (未找到 key 1) System.out.println(cache.get(1)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); // 返回 4 System.out.println(cache.get(4)); } //緩存了所有元素的node Map<Integer,Node> cache; //優先隊列 Queue<Node> queue; //緩存cache 的容量 int capacity; //當前緩存的元素個數 int size; //全局自增 int index = 0; //初始化 public LFUCache4(int capacity){ this.capacity = capacity; if(capacity > 0){ queue = new PriorityQueue<>(capacity); } cache = new HashMap<>(); } public int get(int key){ Node node = cache.get(key); // node不存在,則返回 -1 if(node == null) return -1; //每訪問一次,頻次和全局index都自增 1 node.freq++; node.index = index++; // 每次都重新remove,再offer是為了讓優先隊列能夠對當前Node重排序 //不然的話,比較的 freq 和 index 就是不準確的 queue.remove(node); queue.offer(node); return node.value; } public void put(int key, int value){ //容量0,則直接返回 if(capacity == 0) return; Node node = cache.get(key); //如果node存在,則更新它的value值 if(node != null){ node.value = value; node.freq++; node.index = index++; queue.remove(node); queue.offer(node); }else { //如果cache滿了,則從優先隊列中取出一個元素,這個元素一定是頻次最小,最久未訪問過的元素 if(size == capacity){ cache.remove(queue.poll().key); //取出元素后,size減 1 size--; } //否則,說明可以添加元素,于是創建一個新的node,添加到優先隊列中 Node newNode = new Node(key, value, index++); queue.offer(newNode); cache.put(key,newNode); //同時,size加 1 size++; } } //必須實現 Comparable 接口才可用于排序 private class Node implements Comparable<Node>{ int key; int value; int freq = 1; int index; public Node(){ } public Node(int key, int value, int index){ this.key = key; this.value = value; this.index = index; } @Override public int compareTo(Node o) { //優先比較頻次 freq,頻次相同再比較index int minus = this.freq - o.freq; return minus == 0? this.index - o.index : minus; } } }方案二:使用一條雙向鏈表
思路:
只用一條雙向鏈表,來維護頻次和時間先后順序。那么,可以這樣想。把頻次 freq 小的放前面,頻次大的放后面。如果頻次相等,就從當前節點往后遍歷,直到找到第一個頻次比它大的元素,并插入到它前面。(當然,如果遍歷到了tail,則插入到tail前面)這樣可以保證同頻次的元素,最近訪問的總是在最后邊。
因此,總的來說,最低頻次,并且最久未訪問的元素肯定就是鏈表中最前面的那一個了。這樣的話,當 cache容量滿的時候,直接把頭結點刪除掉就可以了。但是,我們這里為了方便鏈表的插入和刪除操作,用了兩個哨兵節點,來表示頭節點 head和尾結點tail。因此,刪除頭結點就相當于刪除 head.next。
PS:哨兵節點只是為了占位,實際并不存儲有效數據,只是為了鏈表插入和刪除時,不用再判斷當前節點的位置。不然的話,若當前節點占據了頭結點或尾結點的位置,還需要重新賦值頭尾節點元素,較麻煩。
為了便于理解新節點如何插入到鏈表中合適的位置,作圖如下:
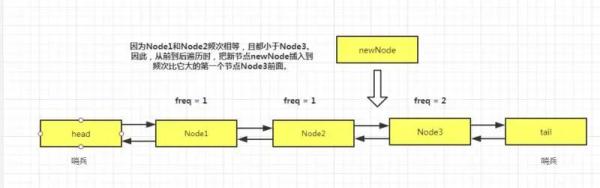
代碼如下:
public class LFUCache { public static void main(String[] args) { LFUCache cache = new LFUCache(2); cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); // 返回 1 System.out.println(cache.get(1)); cache.put(3, 3); // 去除 key 2 // 返回 -1 (未找到key 2) System.out.println(cache.get(2)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); cache.put(4, 4); // 去除 key 1 // 返回 -1 (未找到 key 1) System.out.println(cache.get(1)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); // 返回 4 System.out.println(cache.get(4)); } private Map<Integer,Node> cache; private Node head; private Node tail; private int capacity; private int size; public LFUCache(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; this.cache = new HashMap<>(); /** * 初始化頭結點和尾結點,并作為哨兵節點 */ head = new Node(); tail = new Node(); head.next = tail; tail.pre = head; } public int get(int key) { Node node = cache.get(key); if(node == null) return -1; node.freq++; moveToPostion(node); return node.value; } public void put(int key, int value) { if(capacity == 0) return; Node node = cache.get(key); if(node != null){ node.value = value; node.freq++; moveToPostion(node); }else{ //如果元素滿了 if(size == capacity){ //直接移除最前面的元素,因為這個節點就是頻次最小,且最久未訪問的節點 cache.remove(head.next.key); removeNode(head.next); size--; } Node newNode = new Node(key, value); //把新元素添加進來 addNode(newNode); cache.put(key,newNode); size++; } } //只要當前 node 的頻次大于等于它后邊的節點,就一直向后找, // 直到找到第一個比當前node頻次大的節點,或者tail節點,然后插入到它前面 private void moveToPostion(Node node){ Node nextNode = node.next; //先把當前元素刪除 removeNode(node); //遍歷到符合要求的節點 while (node.freq >= nextNode.freq && nextNode != tail){ nextNode = nextNode.next; } //把當前元素插入到nextNode前面 node.pre = nextNode.pre; node.next = nextNode; nextNode.pre.next = node; nextNode.pre = node; } //添加元素(頭插法),并移動到合適的位置 private void addNode(Node node){ node.pre = head; node.next = head.next; head.next.pre = node; head.next = node; moveToPostion(node); } //移除元素 private void removeNode(Node node){ node.pre.next = node.next; node.next.pre = node.pre; } class Node { int key; int value; int freq = 1; //當前節點的前一個節點 Node pre; //當前節點的后一個節點 Node next; public Node(){ } public Node(int key ,int value){ this.key = key; this.value = value; } } }可以看到不管是插入元素還是刪除元素時,都不需要額外的判斷,這就是設置哨兵節點的好處。
由于每次訪問元素的時候,都需要按一定的規則把元素放置到合適的位置,因此,元素需要從前往后一直遍歷。所以,時間復雜度 O(n)。
方案三:用 LinkedHashSet維護頻次鏈表
思路:
我們不再使用一條鏈表,同時維護頻次和訪問時間了。此處,換為用 map 鍵值對來維護,用頻次作為鍵,用當前頻次對應的一條具有先后訪問順序的鏈表來作為值。它的結構如下:
Map<Integer, LinkedHashSet<Node>> freqMap
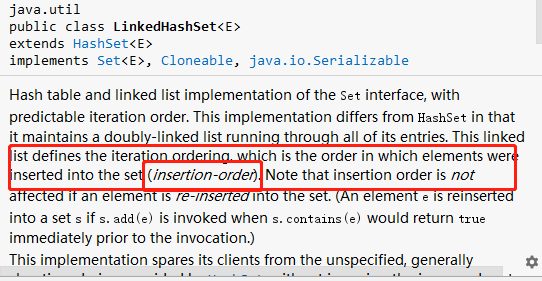
由于LinkedHashSet 的 iterator迭代方法是按插入順序的,因此迭代到的第一個元素肯定是當前頻次下,最久未訪問的元素。這樣的話,當緩存 cache滿的時候,直接刪除迭代到的第一個元素就可以了。
另外 freqMap,也需要在每次訪問元素的時候,重新維護關系。從當前元素的頻次對應的雙向鏈表中移除當前元素,并加入到高頻次的鏈表中。
public class LFUCache1 { public static void main(String[] args) { LFUCache1 cache = new LFUCache1(2); cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); // 返回 1 System.out.println(cache.get(1)); cache.put(3, 3); // 去除 key 2 // 返回 -1 (未找到key 2) System.out.println(cache.get(2)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); cache.put(4, 4); // 去除 key 1 // 返回 -1 (未找到 key 1) System.out.println(cache.get(1)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); // 返回 4 System.out.println(cache.get(4)); } //緩存 cache private Map<Integer,Node> cache; //存儲頻次和對應雙向鏈表關系的map private Map<Integer, LinkedHashSet<Node>> freqMap; private int capacity; private int size; //存儲最小頻次值 private int min; public LFUCache1(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; cache = new HashMap<>(); freqMap = new HashMap<>(); } public int get(int key) { Node node = cache.get(key); if(node == null) return -1; //若找到當前元素,則頻次加1 freqInc(node); return node.value; } public void put(int key, int value) { if(capacity == 0) return; Node node = cache.get(key); if(node != null){ node.value = value; freqInc(node); }else{ if(size == capacity){ Node deadNode = removeNode(); cache.remove(deadNode.key); size --; } Node newNode = new Node(key,value); cache.put(key,newNode); addNode(newNode); size++; } } //處理頻次map private void freqInc(Node node){ //從原來的頻次對應的鏈表中刪除當前node LinkedHashSet<Node> set = freqMap.get(node.freq); if(set != null) set.remove(node); //如果當前頻次是最小頻次,并且移除元素后,鏈表為空,則更新min值 if(node.freq == min && set.size() == 0){ min = node.freq + 1; } //添加到新的頻次對應的鏈表 node.freq ++; LinkedHashSet<Node> newSet = freqMap.get(node.freq); //如果高頻次鏈表還未存在,則初始化一條 if(newSet == null){ newSet = new LinkedHashSet<Node>(); freqMap.put(node.freq,newSet); } newSet.add(node); } //添加元素,更新頻次 private void addNode(Node node){ //添加新元素,肯定是需要加入到頻次為1的鏈表中的 LinkedHashSet<Node> set = freqMap.get(1); if(set == null){ set = new LinkedHashSet<>(); freqMap.put(1,set); } set.add(node); //更新最小頻次為1 min = 1; } //刪除頻次最小,最久未訪問的元素 private Node removeNode(){ //找到最小頻次對應的 LinkedHashSet LinkedHashSet<Node> set = freqMap.get(min); //迭代到的第一個元素就是最久未訪問的元素,移除之 Node node = set.iterator().next(); set.remove(node); //如果當前node的頻次等于最小頻次,并且移除元素之后,set為空,則 min 加1 if(node.freq == min && set.size() == 0){ min ++; } return node; } private class Node { int key; int value; int freq = 1; public Node(int key, int value){ this.key = key; this.value = value; } public Node(){ } } }方案四:手動實現一個頻次鏈表
思路:
由于方案三用的是JDK自帶的 LinkedHashSet ,其是實現了哈希表和雙向鏈表的一個類,因此為了減少哈希相關的計算,提高效率,我們自己實現一條雙向鏈表來替代它。
那么,這條雙向鏈表,就需要維護當前頻次下的所有元素的先后訪問順序。我們采用頭插法,把新加入的元素添加到鏈表頭部,這樣的話,最久未訪問的元素就在鏈表的尾部。
同樣的,我們也用兩個哨兵節點來代表頭尾節點,以方便鏈表的操作。
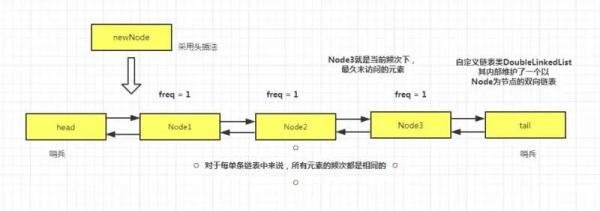
代碼如下:
public class LFUCache2 { public static void main(String[] args) { LFUCache2 cache = new LFUCache2(2); cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); // 返回 1 System.out.println(cache.get(1)); cache.put(3, 3); // 去除 key 2 // 返回 -1 (未找到key 2) System.out.println(cache.get(2)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); cache.put(4, 4); // 去除 key 1 // 返回 -1 (未找到 key 1) System.out.println(cache.get(1)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); // 返回 4 System.out.println(cache.get(4)); } private Map<Integer,Node> cache; private Map<Integer,DoubleLinkedList> freqMap; private int capacity; private int size; private int min; public LFUCache2(int capacity){ this.capacity = capacity; cache = new HashMap<>(); freqMap = new HashMap<>(); } public int get(int key){ Node node = cache.get(key); if(node == null) return -1; freqInc(node); return node.value; } public void put(int key, int value){ if(capacity == 0) return; Node node = cache.get(key); if(node != null){ node.value = value; //更新value值 freqInc(node); }else{ //若size達到最大值,則移除頻次最小,最久未訪問的元素 if(size == capacity){ //因鏈表是頭插法,所以尾結點的前一個節點就是最久未訪問的元素 DoubleLinkedList list = freqMap.get(min); //需要移除的節點 Node deadNode = list.tail.pre; cache.remove(deadNode.key); list.removeNode(deadNode); size--; } //新建一個node,并把node放到頻次為 1 的 list 里面 Node newNode = new Node(key,value); DoubleLinkedList newList = freqMap.get(1); if(newList == null){ newList = new DoubleLinkedList(); freqMap.put(1,newList); } newList.addNode(newNode); cache.put(key,newNode); size++; min = 1;//此時需要把min值重新設置為1 } } //修改頻次 private void freqInc(Node node){ //先刪除node對應的頻次list DoubleLinkedList list = freqMap.get(node.freq); if(list != null){ list.removeNode(node); } //判斷min是否等于當前node的頻次,且當前頻次的list為空,是的話更新min值 if(min == node.freq && list.isEmpty()){ min ++; } //然后把node頻次加 1,并把它放到高頻次list node.freq ++; DoubleLinkedList newList = freqMap.get(node.freq); if(newList == null){ newList = new DoubleLinkedList(); freqMap.put(node.freq, newList); } newList.addNode(node); } private class Node { int key; int value; int freq = 1; Node pre; Node next; public Node(){ } public Node(int key, int value){ this.key = key; this.value = value; } } //自實現的一個雙向鏈表 private class DoubleLinkedList { Node head; Node tail; // 設置兩個哨兵節點,作為頭、尾節點便于插入和刪除操作 public DoubleLinkedList(){ head = new Node(); tail = new Node(); head.next = tail; tail.pre = head; } //采用頭插法,每次都插入到鏈表的最前面,即 head 節點后邊 public void addNode(Node node){ node.pre = head; node.next = head.next; //注意先把head的后節點的前節點設置為node head.next.pre = node; head.next = node; } //刪除元素 public void removeNode(Node node){ node.pre.next = node.next; node.next.pre = node.pre; } //判斷是否為空,即是否存在除了哨兵節點外的有效節點 public boolean isEmpty(){ //判斷頭結點的下一個節點是否是尾結點,是的話即為空 return head.next == tail; } } }方案五:用雙向鏈表嵌套
思路:
可以發現方案三和方案四,都是用 freqmap 來存儲頻次和它對應的鏈表之間的關系,它本身也是一個哈希表。這次,我們完全用自己實現的雙向鏈表來代替 freqMap,進一步提高效率。
但是,結構有些復雜,它是一個雙向鏈表中,每個元素又是雙向鏈表。為了便于理解,我把它的結構作圖如下:(為了方便,分別叫做外層鏈表,內層鏈表)
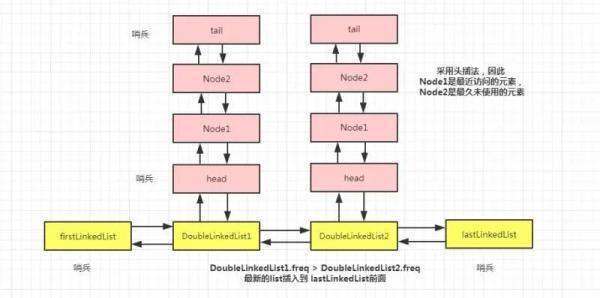
我們把整體看成一個由 DoubleLinkedList組成的雙向鏈表,然后,每一個 DoubleLinkedList 對象中又是一個由 Node 組成的雙向鏈表。像極了 HashMap 數組加鏈表的形式。
但是,我們這里沒有數組,也就不存在哈希碰撞的問題。并且都是雙向鏈表,都有哨兵存在,便于靈活的從鏈表頭部或者尾部開始操作元素。
這里,firstLinkedList 和 lastLinkedList 分別代表外層鏈表的頭尾結點。鏈表中的元素 DoubleLinkedList 有一個字段 freq 記錄了頻次,并且按照前大后小的順序組成外層鏈表,即圖中的 DoubleLinkedList1.freq 大于它后面的 DoubleLinkedList2.freq。
每當有新頻次的 DoubleLinkedList 需要添加進來的時候,直接插入到 lastLinkedList 這個哨兵前面,因此 lastLinkedList.pre 就是一個最小頻次的內部鏈表。
內部鏈表中是由 Node組成的雙向鏈表,也有兩個哨兵代表頭尾節點,并采用頭插法。其實,可以看到內部鏈表和方案四,圖中所示的雙向鏈表結構是一樣的,不用多說了。
這樣的話,我們就可以找到頻次最小,并且最久未訪問的元素,即
//頻次最小,最久未訪問的元素,cache滿時需要刪除 lastLinkedList.pre.tail.pre
于是,代碼就好理解了:
public class LFUCache3 { public static void main(String[] args) { LFUCache3 cache = new LFUCache3(2); cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); // 返回 1 System.out.println(cache.get(1)); cache.put(3, 3); // 去除 key 2 // 返回 -1 (未找到key 2) System.out.println(cache.get(2)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); cache.put(4, 4); // 去除 key 1 // 返回 -1 (未找到 key 1) System.out.println(cache.get(1)); // 返回 3 System.out.println(cache.get(3)); // 返回 4 System.out.println(cache.get(4)); } Map<Integer,Node> cache; /** * 這兩個代表的是以 DoubleLinkedList 連接成的雙向鏈表的頭尾節點, * 且為哨兵節點。每個list中,又包含一個由 node 組成的一個雙向鏈表。 * 最外層雙向鏈表中,freq 頻次較大的 list 在前面,較小的 list 在后面 */ DoubleLinkedList firstLinkedList, lastLinkedList; int capacity; int size; public LFUCache3(int capacity){ this.capacity = capacity; cache = new HashMap<>(); //初始化外層鏈表的頭尾節點,作為哨兵節點 firstLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList(); lastLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList(); firstLinkedList.next = lastLinkedList; lastLinkedList.pre = firstLinkedList; } //存儲具體鍵值對信息的node private class Node { int key; int value; int freq = 1; Node pre; Node next; DoubleLinkedList doubleLinkedList; public Node(){ } public Node(int key, int value){ this.key = key; this.value = value; } } public int get(int key){ Node node = cache.get(key); if(node == null) return -1; freqInc(node); return node.value; } public void put(int key, int value){ if(capacity == 0) return; Node node = cache.get(key); if(node != null){ node.value = value; freqInc(node); }else{ if(size == capacity){ /** * 如果滿了,則需要把頻次最小的,且最久未訪問的節點刪除 * 由于list組成的鏈表頻次從前往后依次減小,故最小的頻次list是 lastLinkedList.pre * list中的雙向node鏈表采用的是頭插法,因此最久未訪問的元素是 lastLinkedList.pre.tail.pre */ //最小頻次list DoubleLinkedList list = lastLinkedList.pre; //最久未訪問的元素,需要刪除 Node deadNode = list.tail.pre; cache.remove(deadNode.key); list.removeNode(deadNode); size--; //如果刪除deadNode之后,此list中的雙向鏈表空了,則刪除此list if(list.isEmpty()){ removeDoubleLinkedList(list); } } //沒有滿,則新建一個node Node newNode = new Node(key, value); cache.put(key,newNode); //判斷頻次為1的list是否存在,不存在則新建 DoubleLinkedList list = lastLinkedList.pre; if(list.freq != 1){ DoubleLinkedList newList = new DoubleLinkedList(1); addDoubleLinkedList(newList,list); newList.addNode(newNode); }else{ list.addNode(newNode); } size++; } } //修改頻次 private void freqInc(Node node){ //從當前頻次的list中移除當前 node DoubleLinkedList list = node.doubleLinkedList; if(list != null){ list.removeNode(node); } //如果當前list中的雙向node鏈表空,則刪除此list if(list.isEmpty()){ removeDoubleLinkedList(list); } //當前node頻次加1 node.freq++; //找到當前list前面的list,并把當前node加入進去 DoubleLinkedList preList = list.pre; //如果前面的list不存在,則新建一個,并插入到由list組成的雙向鏈表中 //前list的頻次不等于當前node頻次,則說明不存在 if(preList.freq != node.freq){ DoubleLinkedList newList = new DoubleLinkedList(node.freq); addDoubleLinkedList(newList,preList); newList.addNode(node); }else{ preList.addNode(node); } } //從外層雙向鏈表中刪除當前list節點 public void removeDoubleLinkedList(DoubleLinkedList list){ list.pre.next = list.next; list.next.pre = list.pre; } //知道了它的前節點,即可把新的list節點插入到其后面 public void addDoubleLinkedList(DoubleLinkedList newList, DoubleLinkedList preList){ newList.pre = preList; newList.next = preList.next; preList.next.pre = newList; preList.next = newList; } //維護一個雙向DoubleLinkedList鏈表 + 雙向Node鏈表的結構 private class DoubleLinkedList { //當前list中的雙向Node鏈表所有頻次都相同 int freq; //當前list中的雙向Node鏈表的頭結點 Node head; //當前list中的雙向Node鏈表的尾結點 Node tail; //當前list的前一個list DoubleLinkedList pre; //當前list的后一個list DoubleLinkedList next; public DoubleLinkedList(){ //初始化內部鏈表的頭尾節點,并作為哨兵節點 head = new Node(); tail = new Node(); head.next = tail; tail.pre = head; } public DoubleLinkedList(int freq){ head = new Node(); tail = new Node(); head.next = tail; tail.pre = head; this.freq = freq; } //刪除當前list中的某個node節點 public void removeNode(Node node){ node.pre.next = node.next; node.next.pre = node.pre; } //頭插法將新的node插入到當前list,并在新node中記錄當前list的引用 public void addNode(Node node){ node.pre = head; node.next = head.next; head.next.pre = node; head.next = node; node.doubleLinkedList = this; } //當前list中的雙向node鏈表是否存在有效節點 public boolean isEmpty(){ //只有頭尾哨兵節點,則說明為空 return head.next == tail; } } }到此,相信大家對“有哪些LFU實現方式”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。