您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“JuypterNotebook中最有幫助的項目設置有哪些”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在JuypterNotebook中最有幫助的項目設置有哪些問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”JuypterNotebook中最有幫助的項目設置有哪些”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
1. 確保Python版本
檢查JupyterNotebook中的Python解釋器版本:
import sys sys.version'3.7.6 (default, Jan 8 2020, 13:42:34) \n[Clang 4.0.1 (tags/RELEASE_401/final)]'
為確保項目由Python解釋器的最低及以上要求版本運行,可在項目設置中添加以下代碼:
# Python ≥3.7 is required import sys assert sys.version_info >= (3, 7)
Python需要為3.7及以上版本,否則會拋出AssertionError。
2. 確保程序包版本
檢查安裝的程序包版本,如TensorFlow。
import tensorflow as tf tf.__version__'2.0.0'
確保項目是由TensorFlow2.0及以上版本運行的,否則會拋出AssertionError。
# TensorFlow ≥2.0 is required import tensorflow as tf assert tf.__version__ >= "2.0"
3. 避免繪制模糊圖像
JuypterNotebook中的默認繪圖看起來有些模糊。例如,一張查找缺失值的簡單熱圖。
(https://towardsdatascience.com/using-pandas-pipe-function-to-improve-code-readability-96d66abfaf8)
import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline# Default figure format png sns.heatmap(df.isnull(), yticklabels=False, cbar=False, cmap='viridis')
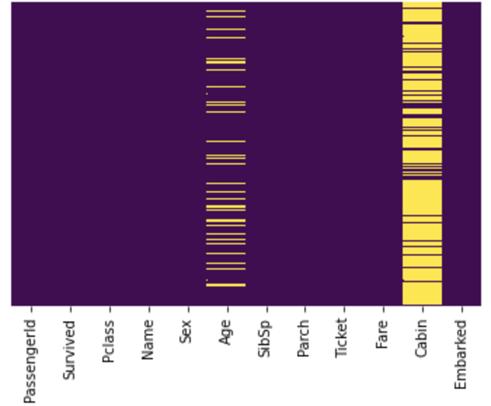
默認圖像看起來很模糊
由上圖可以看出,文本很模糊,Cabin欄中的缺失值過于擁擠,Embarked欄中的缺失值無法識別。
要解決這個問題,可在%matplotlib inline之后使用%config InlineBackend.figure_format='retina'或 %configInlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg',即:
%matplotlib inline %config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina' # or 'svg'sns.heatmap(df.isnull(), yticklabels=False, cbar=False, cmap='viridis')
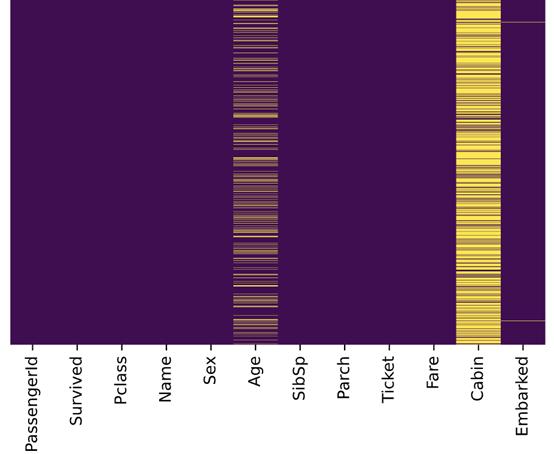
圖片格式設置為retina或svg
與先前的圖片比較,上圖更加清晰,Embarked欄中的缺失值也能成功識別。
4. 在不同運行中保持輸出穩定
數據科學項目中很多地方都在使用隨機數字。例如:
來自Scikit-Learn的 train_test_split()
用于初始化權重的np.random.rand()
若未重置隨機種子,則每次調用都會出現不同的數字:
>>> np.random.rand(4) array([0.83209492, 0.10917076, 0.15798519, 0.99356723]) >>> np.random.rand(4) array([0.46183001, 0.7523687 , 0.96599624, 0.32349079])
np.random.seed(0)使隨機數字可預測:
>>> np.random.seed(0) >>> np.random.rand(4) array([0.5488135 , 0.71518937, 0.60276338, 0.54488318]) >>> np.random.seed(0) >>> np.random.rand(4) array([0.5488135 , 0.71518937, 0.60276338, 0.54488318])
如果(每次)都重置隨機種子,那么每次都會出現相同的數據組。因此,項目能在不同運行中保持輸出穩定。
5. 多單元輸出
默認情況下,JupyterNotebook不能在同一單元中輸出多種結果。要輸出多種結果,可使用IPython重新配置shell。
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
6. 將圖片保存到文件
Matplotlib能通過savefig()方法保存圖片,但如果給定路徑不存在則會引發錯誤。
plt.savefig('./figures/my_plot.png')FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] Nosuch file or directory: './figures/my_plot.png'最好的做法是將所有圖片都放到一個地方,如工作區的figures文件夾。可使用OS GUI(操作系統界面)或是在JupyterNotebook中運行logic指令,來手動創建一個figures文件夾,但是最好創建一個小函數來實現該操作。
當需要一些自定義圖形設置或附加子文件夾來分組圖形時,這種方法尤其適用。以下是將圖片保存到文件的函數:
import os %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# Where to save the figures PROJECT_ROOT_DIR = "." SUB_FOLDER = "sub_folder" #a sub-folder IMAGES_PATH = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, "images", SUB_FOLDER)defsave_fig(name, images_path=IMAGES_PATH, tight_layout=True,extension="png", resolution=300): if not os.path.isdir(images_path): os.makedirs(images_path) path = os.path.join(images_path, name+ "." + extension) print("Saving figure:",name) if tight_layout: plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig(path, format=extension,dpi=resolution)現在調用save_fig('figure_name'),會在工作區中創建一個images/sub_folder目錄,圖片以“figure_name.png”名稱被保存到目錄中。此外,還提供了三個最常用的設置:
tight_layout 能自動調整子圖填充
extension 能以多種格式保存圖片
resolution 可設置圖片分辨率
7. 下載數據(并解壓)
處理網絡數據對于數據科學工作者是常事。可以使用瀏覽器下載數據,并運行指令來解壓文件,但最好的是創建一個小函數來執行該操作。當數據需要定期更改時,這一點尤其重要。
編寫一個小腳本,在獲取最新數據時運行(也可以設置一個定期自動執行的計劃工作)即可。如果需要在多臺機器上安裝數據集,自動化抓取數據流程也十分有用。
以下是下載并解壓數據的函數:
import os import tarfile import zipfile import urllib # Where to save the data PROJECT_ROOT_DIR = "." SUB_FOLDER = "group_name" LOCAL_PATH = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, "datasets", SUB_FOLDER)defdownload(file_url, local_path = LOCAL_PATH): if not os.path.isdir(local_path): os.makedirs(local_path) # Download file print(">>>downloading") filename = os.path.basename(file_url) file_local_path =os.path.join(local_path, filename) urllib.request.urlretrieve(file_url,file_local_path) # untar/unzip file if filename.endswith("tgz")or filename.endswith("tar.gz"): print(">>>unpacking file:", filename) tar =tarfile.open(file_local_path, "r:gz") tar.extractall(path = local_path) tar.close() eliffilename.endswith("tar"): print(">>> unpackingfile:", filename) tar =tarfile.open(file_local_path, "r:") tar.extractall(path = local_path) tar.close() eliffilename.endwith("zip"): print(">>>unpacking file:", filename) zip_file = zipfile.ZipFile(file_local_path) zip_file.extractall(path =local_path) zip_file.close() print("Done")現在調用download("http://a_valid_url/housing.tgz"),會在工作區創建一個datasets/group_name目錄,下載housing.tgz,并從該目錄中提取出housing.csv ,這個小函數也能用于CSV和文本文件。
到此,關于“JuypterNotebook中最有幫助的項目設置有哪些”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。