您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有關怎么在C++中動態內存分配,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結了以下內容,希望大家根據這篇文章可以有所收獲。
按需分配,根據需要分配內存,不浪費。
內存拷貝函數void* memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t n);
從源src中拷貝n字節的內存到dest中。需要包含頭文件#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int* b;
b = new int[15];
//從a拷貝10 * 4字節的內存到b
memcpy_s(b, sizeof(int) * 10, a, sizeof(int) * 10);
//進行賦值
for(int i = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); i < 15; i++){
*(b + i) = 15;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
printf("%d ", b[i]);
}
return 0;
}輸出結果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 15 15 15 15 15
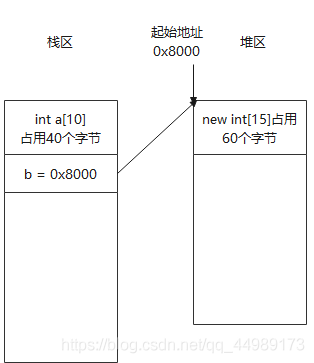
被調用函數之外需要使用被調用函數內部的指針對應的地址空間
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
//定義一個指針函數
void* test() {
void* a;
//分配100*4個字節給a指針
//mallocC語言的動態分配函數
a = malloc(sizeof(int) * 100);
if (!a) {
printf("內存分配失敗!");
return NULL;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
*((int*)a + i) = i;
}
return a;
}
int main() {
//test()返回void*的內存,需要強轉換
int* a = (int*)test();
//打印前20個
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
//C語言的釋放內存方法
free(a);
return 0;
}輸出結果:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
此處在main函數中使用了在test()函數中分配的動態內存重點地址。
也可以通過二級指針來保存,內存空間:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
//定義一個指針函數
void test(int **a) {
*a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 100);
if (!*a) {
printf("內存分配失敗!");
exit(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
*(*a + i) = i;
}
}
int main() {
//test()返回void*的內存,需要強轉換
int* a;
test(&a);
//打印前20個
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
free(a);
return 0;
}突破棧區的限制,可以給程序分配更多的空間。
棧區的大小有限,在Windows系統下,棧區的大小一般為1~2Mb
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
void test() {
//分配一個特別大的數組
int a[102400 * 3];// 100k * 3 * 4 = 1200K
a[0] = 0;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}點運行會出現Stack overflow的提示(棧區溢出!)。
修改:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
void test() {
//在堆中分配一個特別大的數組1G
//在Windows 10 系統限制的堆為2G
int* a = (int*)malloc(1024 * 1000 * 1000 * 1); //1G
a[0] = 0;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}成功運行!但是當分配兩個G的動態內存時,就會報錯,這個時候分配失敗,a = NULL;
1、按需分配,根據需要分配內存,不浪費。
2、被調用函數之外需要使用被調用函數內部的指針對應的地址空間。
3、突破棧區的限制,可以給程序分配更多的空間。
看完上述內容,你們對怎么在C++中動態內存分配有進一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識或者相關內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。