您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
前言
相信大家應該都有所體會,在以前我們要實現流動性布局,比較繁瑣,Google開源了一個項目叫FlexboxLayout,相信大家都不陌生。下面我們來學習一下FlexboxLayout基礎知識,并通過一個案例來加深理解。如果你對FlexboxLayout很熟悉,請忽略本文。
一、什么是 Flexbox
簡單來說 Flexbox 是屬于web前端領域CSS的一種布局方案,是2009年W3C提出了一種新的布局方案,可以響應式地實現各種頁面布局,并且 React Native 也是使用的 Flex 布局。
我們可以簡單的理解為 Flexbox 是CSS領域類似 Linearlayout 的一種布局,但比 Linearlayout 要強大的多。
二、 什么是 FlexboxLayout?
我們在 Android 開發中使用 Linearlayout + RelativeLayout 基本可以實現大部分復雜的布局,但是Google就想了,有沒有類似 Flexbox 的一個布局呢?這使用起來一個布局就可以搞定各種復雜的情況了,于是 FlexboxLayout 就應運而生了。
所以 FlexboxLayout 是針對 Android 平臺的,實現類似 Flexbox 布局方案的一個開源項目
我們先看看官方Demo的效果圖
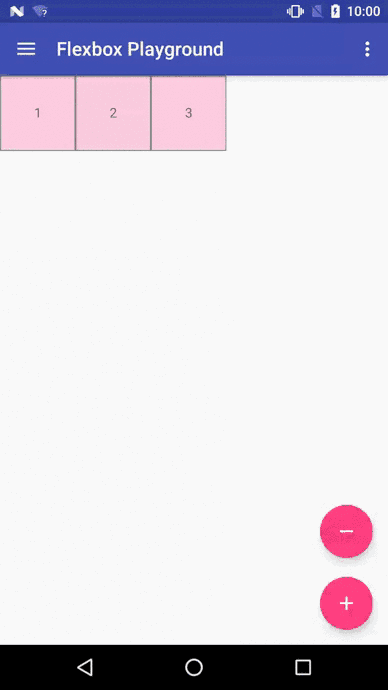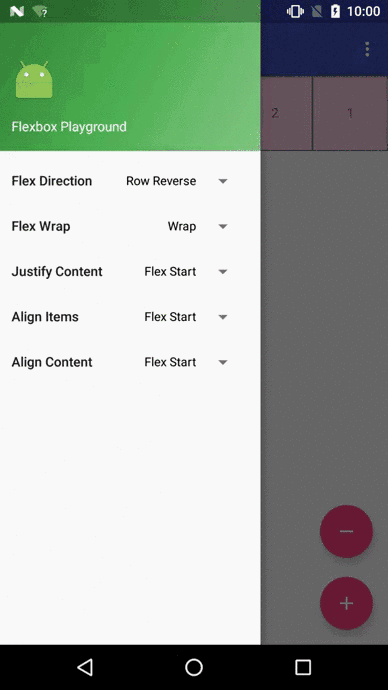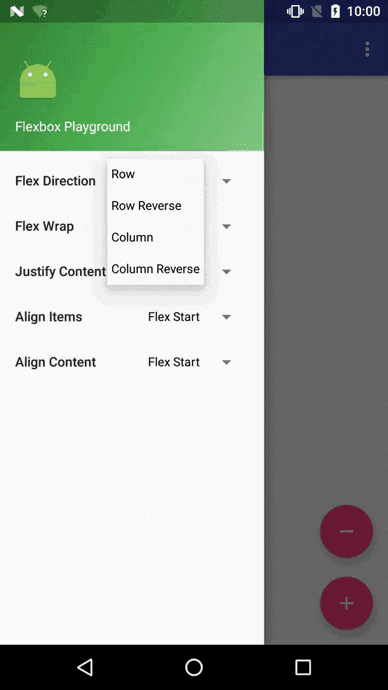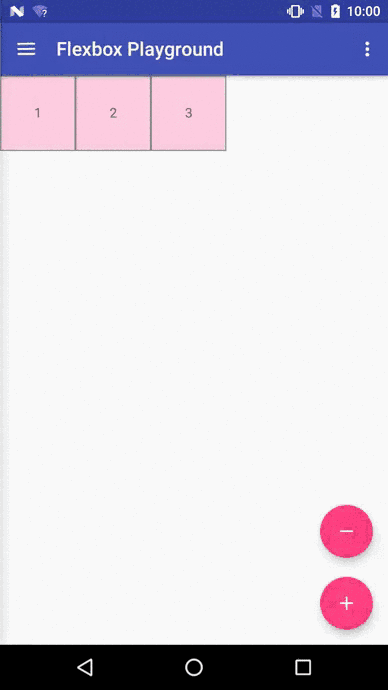
開源地址:https://github.com/google/flexbox-layout
本地下載:點擊這里
三、使用方式
使用方式很簡單,只需要添加以下依賴:
compile 'com.google.android:flexbox:0.2.2'
在xml布局中我們可以這樣使用
<com.google.android.flexbox.FlexboxLayout android:id="@+id/flexbox_layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" app:flexWrap="wrap"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv1" android:layout_width="120dp" android:layout_height="80dp" app:layout_flexBasisPercent="50%" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv2" android:layout_width="80dp" android:layout_height="80dp" app:layout_alignSelf="center"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv3" android:layout_width="160dp" android:layout_height="80dp" app:layout_alignSelf="flex_end"/> </com.google.android.flexbox.FlexboxLayout>
代碼中可以這樣使用
FlexboxLayout flexboxLayout = (FlexboxLayout) findViewById(R.id.flexbox_layout); flexboxLayout.setFlexDirection(FlexboxLayout.FLEX_DIRECTION_COLUMN); View view = flexboxLayout.getChildAt(0); FlexboxLayout.LayoutParams lp = (FlexboxLayout.LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams(); lp.order = -1; lp.flexGrow = 2; view.setLayoutParams(lp);
我們來看看要模仿的布局
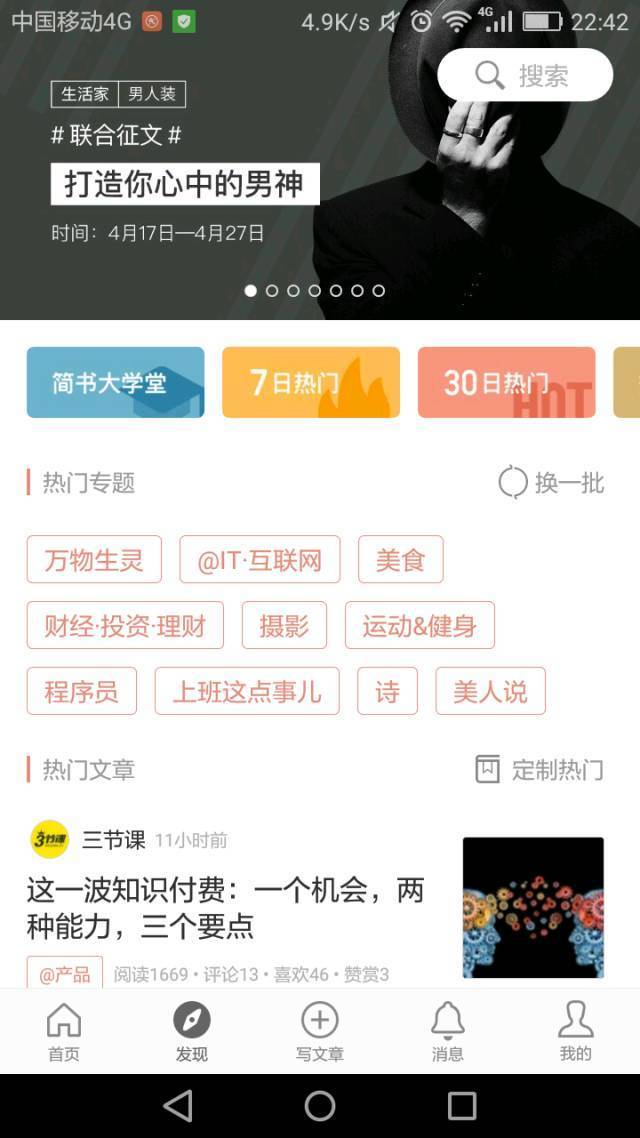
下面我們來實現它,先來看最終實現的效果:
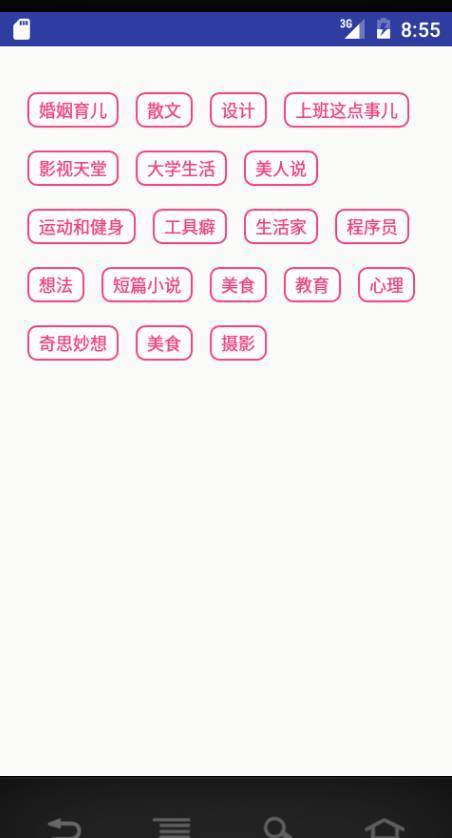
實現方法如下:
1. 新建activity_flow.xml布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <com.google.android.flexbox.FlexboxLayout android:id="@+id/flexbox_layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" app:flexWrap="wrap" /> </RelativeLayout>
布局很簡單,只有一個FlexboxLayout 因為我們需要動態創建它的item,所以就在這里固定寫TextView了
2. 新建ActivityFlow Activity,填充數據源
String[] tags = {"婚姻育兒", "散文", "設計", "上班這點事兒", "影視天堂", "大學生活", "美人說", "運動和健身", "工具癖", "生活家", "程序員", "想法", "短篇小說", "美食", "教育", "心理", "奇思妙想", "美食", "攝影"};
flexboxLayout = (FlexboxLayout) findViewById(R.id.flexbox_layout);
for (int i = 0; i < tags.length; i++) {
Book model = new Book();
model.setId(i);
model.setName(tags[i]);
flexboxLayout.addView(createNewFlexItemTextView(model));
}
其中Book為一個實體,這個不是關鍵,關鍵的是createNewFlexItemTextView方法
我們要動態加載FlexboxLayout其FlexItem 并且讓FlexboxLayout中的item支持點擊事件,因為我們需要知道用戶點擊了哪個專題跳轉。
我們來看一下createNewFlexItemTextView方法
/**
* 動態創建TextView
* @param book
* @return
*/
private TextView createNewFlexItemTextView(final Book book) {
TextView textView = new TextView(this);
textView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
textView.setText(book.getName());
textView.setTextSize(12);
textView.setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.colorAccent));
textView.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.tag_states);
textView.setTag(book.getId());
textView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Log.e(TAG, book.getName());
}
});
int padding = Util.dpToPixel(this, 4);
int paddingLeftAndRight = Util.dpToPixel(this, 8);
ViewCompat.setPaddingRelative(textView, paddingLeftAndRight, padding, paddingLeftAndRight, padding);
FlexboxLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = new FlexboxLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
int margin = Util.dpToPixel(this, 6);
int marginTop = Util.dpToPixel(this, 16);
layoutParams.setMargins(margin, marginTop, margin, 0);
textView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
return textView;
}
其他有關Book實體和Util類,也貼出來一下
Book實體
public class Book {
private int id;
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Book() {
}
}
Util工具類
public class Util {
public static int pixelToDp(Context context, int pixel) {
DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
return pixel < 0 ? pixel : Math.round(pixel / displayMetrics.density);
}
public static int dpToPixel(Context context, int dp) {
DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
return dp < 0 ? dp : Math.round(dp * displayMetrics.density);
}
}
這樣關于流動布局[FlexboxLayout],我們就實現完成了,是不是很簡單。
總結
以上就是關于Android輕松搞定流動布局(FlexboxLayout)的全部內容了,希望本文的內容對各位Android開發者們能帶來一定的幫助,如果有疑問大家可以留言交流,謝謝大家對億速云的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。