您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了Android如何模仿實現微博詳情頁滑動固定頂部欄的效果,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
先來看下我們今天要實現的效果:
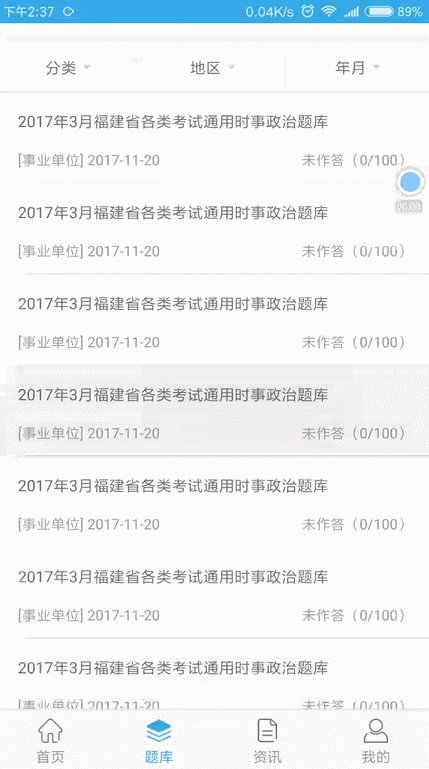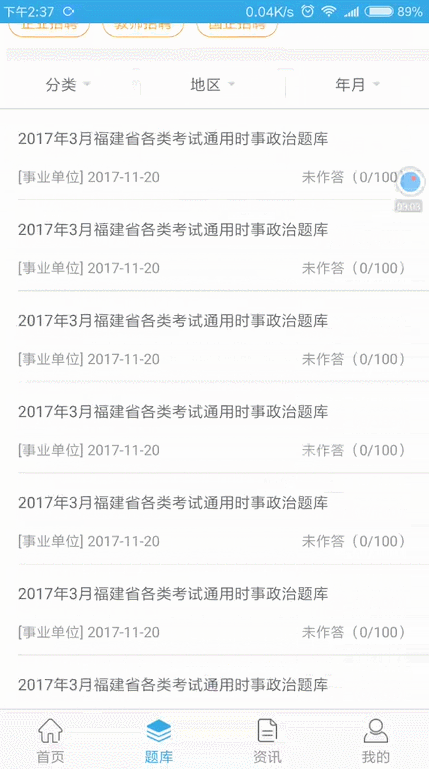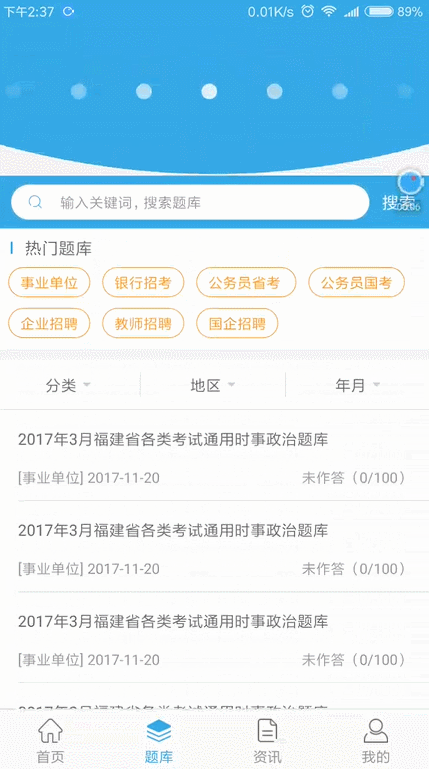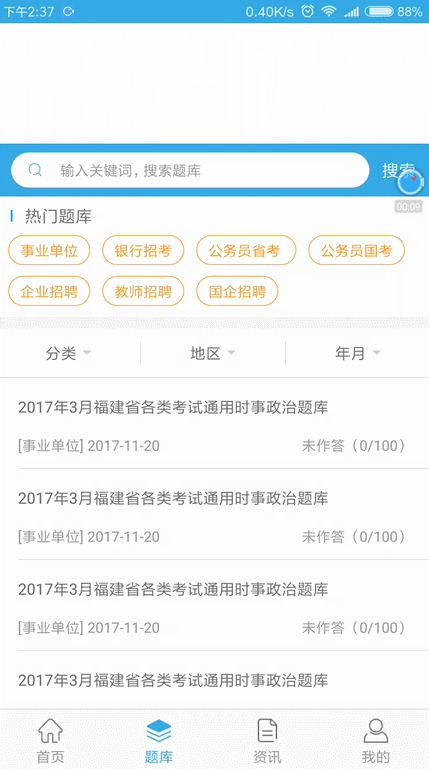
滑動固定頂部欄效果圖
這段時間公司準備重構一個項目,剛好用到這個效果,我就順帶寫了篇文章,關于這個效果網上可以找到一些相關資料的,昨晚看了一些,感覺都不是很好,有點模棱兩可的樣子,也沒提到需要注意的一些關鍵點,這里來做下整理,由于涉及到公司的代碼,這里我就寫個簡單的Demo來講解。

簡單Demo
傳統套路:
寫兩個一模一樣的固定欄,外層用幀布局(FrameLayout)包裹,然后把外層的固定欄先隱藏,當內層的固定欄滑動到外層固定欄位置的時候,把內層固定欄隱藏,外層的固定欄顯示,反之滑回來的時候把外層固定欄隱藏,內存固定欄顯示。
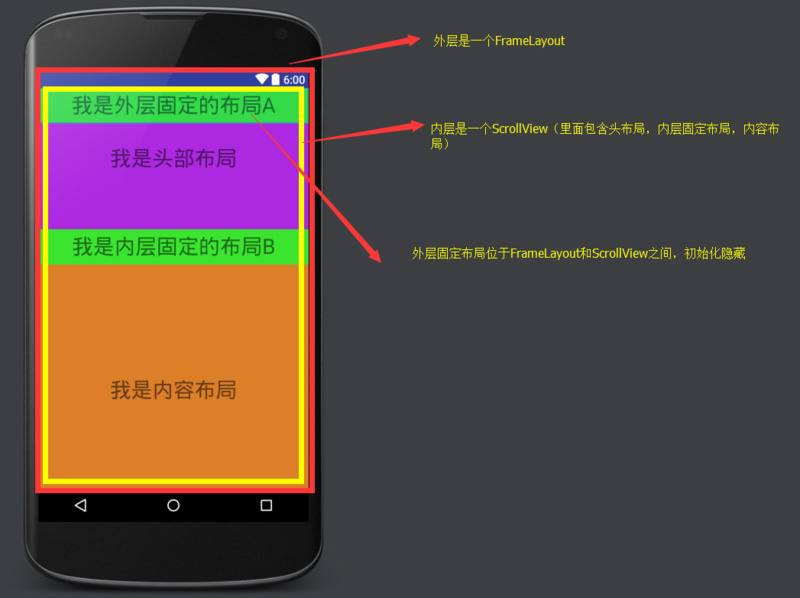
傳統套路圖
這樣做的有幾個不好的地方:
1、重復寫了一樣的布局,在XML渲染的時候耗費了性能(比如更多次的測量,布局等)
2、當頁面快速滾動的時候可能出現一系列的問題(布局重復,閃爍)
3、當這個固定布局帶有狀態的時候,邏輯會變得很復雜,比如上面那張GIF動圖,固定欄中帶有篩選分類,地區,年月信息,如果按照傳統套路來寫,那么在內層固定欄隱藏的時候需要把狀態記錄并且帶給外層固定欄,而且相對應很多動作監聽事件也需要寫多次。
新套路:
這里我換了一種思路,大體布局還是不變的,只是把兩個固定欄簡化成了一個,只是利用removeView和addView根據坐標點在頁面滑動的時候動態的把固定欄在內外部切換,這樣做的好處很好的解決了上面提到的1、2點問題,當然在快速的removeView和addView還是會出現頁面閃爍不自然的問題,后面會提到解決的小竅門。
先來看下XML布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <com.lcw.view.FixedHeaderScrollView.ObservableScrollView android:id="@+id/sv_contentView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:scrollbars="none" > <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/ll_contentView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_headerView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="200dp" android:text="我是頭部布局" android:textSize="30sp" android:background="#ad29e1" android:gravity="center"/> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/ll_topView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="50dp" android:gravity="center" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_topView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="50dp" android:text="我是內層固定的布局" android:background="#3be42f" android:textSize="30sp" android:gravity="center"/> </LinearLayout> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_contentView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="1000dp" android:text="我是內容布局" android:textSize="30sp" android:background="#dc7f28" android:paddingTop="160dp" android:gravity="top|center_horizontal"/> </LinearLayout> </com.lcw.view.FixedHeaderScrollView.ObservableScrollView> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/ll_fixedView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="50dp" android:orientation="vertical"/> </FrameLayout>
這里和上面提到的一樣,最外層用了FrameLayout(RelativeLayout也可以)包裹著一個ScrollView和一個LinearLayout,當我們頁面滑動到指定點的時候,需要把內層的“我是內層固定布局”移除,同時添加到外層的ViewGroup(LinearLayout)中。
自定義ScrollView,利用回調接口的方式使滑動數據對外暴露:
雖然谷歌官方給ScrollView提供了一個設置滑動監聽方法setOnScrollChangeListener,不過這個方法需要基于API23之上(Android6.0系統),在日常開發中,我們需要對老系統用戶進行兼容(當前兼容版本為Android4.1系統以上),所以這里我們需要去繼承ScrollView并把這個監聽事件通過接口的方式對外暴露,這里把這個View取名為ObservableScrollView。
package com.lcw.view.FixedHeaderScrollView;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
/**
* 監聽ScrollView的滑動數據
* Create by: chenwei.li
* Date: 2017/8/21
* time: 11:36
* Email: lichenwei.me@foxmail.com
*/
public class ObservableScrollView extends ScrollView{
public ObservableScrollView(Context context) {
this(context,null);
}
public ObservableScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs,0);
}
public ObservableScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
private OnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged mOnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged;
public void setOnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged(OnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged mOnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged) {
this.mOnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged = mOnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged;
}
public interface OnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged{
void onObservableScrollViewScrollChanged(int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt);
}
/**
* @param l Current horizontal scroll origin. 當前滑動的x軸距離
* @param t Current vertical scroll origin. 當前滑動的y軸距離
* @param oldl Previous horizontal scroll origin. 上一次滑動的x軸距離
* @param oldt Previous vertical scroll origin. 上一次滑動的y軸距離
*/
@Override
protected void onScrollChanged(int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt) {
super.onScrollChanged(l, t, oldl, oldt);
if(mOnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged!=null){
mOnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged.onObservableScrollViewScrollChanged(l,t,oldl,oldt);
}
}
}這里就可以開始寫我們的調用類了
package com.lcw.view.FixedHeaderScrollView;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements ObservableScrollView.OnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged{
private ObservableScrollView sv_contentView;
private LinearLayout ll_topView;
private TextView tv_topView;
private LinearLayout ll_fixedView;
//用來記錄內層固定布局到屏幕頂部的距離
private int mHeight;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
sv_contentView= (ObservableScrollView) findViewById(R.id.sv_contentView);
ll_topView= (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll_topView);
tv_topView= (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_topView);
ll_fixedView= (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll_fixedView);
sv_contentView.setOnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged(this);
// ViewTreeObserver viewTreeObserver=ll_topView.getViewTreeObserver();
// viewTreeObserver.addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
// @Override
// public void onGlobalLayout() {
// ll_topView.getViewTreeObserver().removeOnGlobalLayoutListener(this);
// mHeight=ll_topView.getTop();
// }
// });
}
@Override
public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) {
super.onWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus);
if(hasFocus){
//獲取HeaderView的高度,當滑動大于等于這個高度的時候,需要把topView移除當前布局,放入到外層布局
mHeight=ll_topView.getTop();
}
}
/**
* @param l Current horizontal scroll origin. 當前滑動的x軸距離
* @param t Current vertical scroll origin. 當前滑動的y軸距離
* @param oldl Previous horizontal scroll origin. 上一次滑動的x軸距離
* @param oldt Previous vertical scroll origin. 上一次滑動的y軸距離
*/
@Override
public void onObservableScrollViewScrollChanged(int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt) {
if(t>=mHeight){
if(tv_topView.getParent()!=ll_fixedView){
ll_topView.removeView(tv_topView);
ll_fixedView.addView(tv_topView);
}
}else{
if(tv_topView.getParent()!=ll_topView){
ll_fixedView.removeView(tv_topView);
ll_topView.addView(tv_topView);
}
}
}
}這里我們實現了ObservableScrollView.OnObservableScrollViewScrollChanged接口,當我們對ScrollView注冊監聽的時候,就可以在回調接口里拿到對應的滑動數據,其中第二個參數t就是滑動y軸的距離,現在我們只需要拿到固定布局到頂部的距離就可以判斷什么時候需要移除和添加View了。
相關講解:
1、首先我們需要知道,在Activity生命周期里的onCreate方法里對一個View去執行getWidth,getHeight,getTop,getBottom等一系列的方法是拿不到數據的,得到的結果都為0,由于此時Activity還沒有得到焦點,依附在Activity的View自然也就得不到數據,所以我們需要在onResume后去進行對View的數據獲取。
這里我們可以通過onGlobalLayoutListener或者onWidnowFocusChanged等方法去獲取,這里的執行順序是:Activity.onCreate->Activity.onResume->View.onMeasure->View.onLayout->onGlobalLayoutListener->Activity.onWidnowFocusChanged..(具體用哪個,看當前環境情況,比如在Fragment里是沒有onWidnowFocusChanged,如果需要獲取一個View的相關數據,就可以根據onGlobalLayoutListener來做,上面代碼提供兩種示例)
2、關于獲取滑動的高度,首先我們來看一張圖:
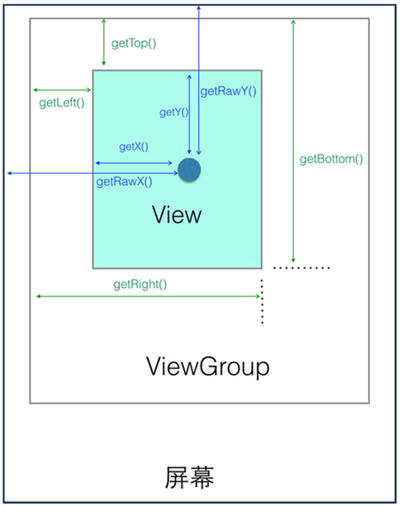
Andorid里關于View的坐標系
這里需要注意的是,除了getRawX和getRawY是相對屏幕的位置,其他的是相對應所在父布局的位置,所以在確定數據的時候,需要注意布局的嵌套。
3、當我們拿到所需要滑動的高度時,我們需要對固定布局進行臨界值做判斷(這里設當前滑動值為t,所需滑動值為y)
比如當我們界面一開始向上滑的時候t值是小于y值的,此時內部固定欄是不需要移除的,而當我們超過y值往回滑t值又小于y值的時候,此時內部固定欄是需要從外部移除添加到內部的,所以這里我們需要對固定欄所在的父布局(ViewGroup)做判斷。
最后補充:
微博詳情頁
1、不管你的頂部固定欄布局多簡單,建議在外套一層ViewGroup,這樣方便addView的操作,不然需要去控制外層ViewGroup的addView的index位置。
2、確定View的寬高度數據可以借助onGlobalLayoutListener或者onWidnowFocusChanged來做,注意相對父布局的嵌套。
3、這種頁面的設計最早來源于iOS的設計,在iOS里ScrollView嵌套TableView(相當于ListView)是沒有問題的,但是在Android里,這樣子的嵌套會導致ListView的復用機制作廢,也就是會不斷是去進行onMeasure的計算,執行多次Adapter里的getView,也就意味著多次的findViewById,使得ViewHolder失效。
4、這是個小技巧,在快速滑動的時候有些人會出現固定布局的閃爍,其實這個和removeView和addView有關系,如果你的ViewGroup設置成了warp_content,這是一個測量的耗時操作,這里只需要配合上面提到的第1點,給固定欄外層布局一個固定的高度值即可(與固定欄高度保持一致)。
感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“Android如何模仿實現微博詳情頁滑動固定頂部欄的效果”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持億速云,關注億速云行業資訊頻道,更多相關知識等著你來學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。