您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
C++ 鏈表
之前一直沒怎么在意C++中的鏈表,但是突然一下子讓自己寫,就老是出錯。沒辦法,決定好好惡補一下該方面的知識,也為今后的數據結構大下個良好的基礎,于是我總結出以下幾點,有些地方可能不正確,還望大家不吝賜教,旨在共同進步。
總結:
1、鏈表List的基本單元是節點Node,因此想要操作方便,就必須為每一步打好基礎,Node的基本結構如下:
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node(int da=0,Node *p=NULL){
this->data=da;
this->next=p;
}
};
我們可以看出,Node的成員變量一共有兩個,都是public,因為我們要對這兩個變量進行操作,所以不能是private類型的。然后是一個構造函數,第二個參數默認值為NULL,也就是說如果我們創建新節點時只指定第一個參數,而不寫第二個參數,那么它默認的就是NULL,以這種方式可以更靈活的使用Node,個人建議這么使用哦。
2、第二步就是創建我們的鏈表了,同樣我們這里先給出鏈表的代碼,在進行一一的解釋。
class List{
private:
Node *head,*tail;
int position;
public:
List(){head=tail=NULL;};
~List(){delete head;delete tail;};
void print();
void Insert(int da=0);
void Delete(int da=0);
void Search(int da=0);
};
我們這里面有兩個數據類型,一個是Node。另一個是指代節點位置的成員變量(起不到什么作用,且不去管它吧)。使用head和tail來命名便是為了見名知意,使操作更加準確。然后是重要的六個函數,各自的功能不言而喻咯,其實最重要的是在每一個函數中我們都默認能操作head和tail兩個成員變量,這樣能簡化我們的參數列表,使得函數更加優雅。
下面是我的一個單鏈表的實現,包含創建鏈表,插入值,刪除特定的值,查找特定值得在鏈表中的位置。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node(int da=0,Node *p=NULL){
this->data=da;
this->next=p;
}
};
class List{
private:
Node *head,*tail;
int position;
public:
List(){head=tail=NULL;};
~List(){delete head;delete tail;};
void print();
void Insert(int da=0);
void Delete(int da=0);
void Search(int da=0);
int getValueAt(int position);
void setValueAt(int position,int da);
};
int List::getValueAt(int position){
Node *p=head;
if(p==NULL){
cout<<"The List is Empty!"<<endl;
}else{
int posi=0;
while(p!=NULL&&posi!=position){
posi++;
p=p->next;
}
if(p==NULL){
cout<<"There is no value of this position in this List!"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"In this Position,the value is"<<p->data<<endl;
}
}
return p->data;
}
void List::setValueAt(int position,int da){
Node *p=head;
if(p==NULL){
cout<<"The List is Empty!"<<endl;
}else{
int posi=0;
while(p!=NULL&&posi!=position){
posi++;
p=p->next;
}
if(p==NULL){
cout<<"There is No Position in this List!"<<endl;
}else{
p->data=da;
cout<<"The Value in this position has been Updated!"<<endl;
}
}
}
void List::Search(int da){
Node *p=head;
if(p==NULL){
cout<<"Sorry, The List is Empty!"<<endl;
return;
}
int count=0;
while(p!=NULL&&p->data!=da){
p=p->next;
count++;
}
cout<<"the value you want to search is at position %d"<<count<<endl;
}
void List::Delete(int da){
Node *p=head,*q=head;
if(p==NULL){
cout<<"Sorry, The List is Empty!"<<endl;
return;
}
while(p!=NULL&&p->data!=da){
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
q->next=p->next;
cout<<"The Deletion Operation had been finished!"<<endl;
}
void List::Insert(int da){
if(head==NULL){
head=tail=new Node(da);
head->next=NULL;
tail->next=NULL;
}else{
Node *p=new Node(da);
tail->next=p;
tail=p;
tail->next=NULL;
}
}
void List::print(){
Node *p=head;
while(p!=NULL){
cout<<p->data<<" \a";
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
cout<<"Hello World!"<<endl;
List l1;
l1.Insert(1);
l1.Insert(2);
l1.Insert(3);
l1.Insert(4);
l1.Insert(5);
l1.Insert(6);
l1.Insert(7);
l1.print();
l1.Search(4);
l1.Delete(6);
l1.print();
l1.getValueAt(3);
l1.setValueAt(3,9);
l1.print();
cout<<"The End!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
//在此我想解釋的是,之所以數字4在鏈表中的位置為3,是因為其是從零開始計數的
下面是代碼運行后的結果:
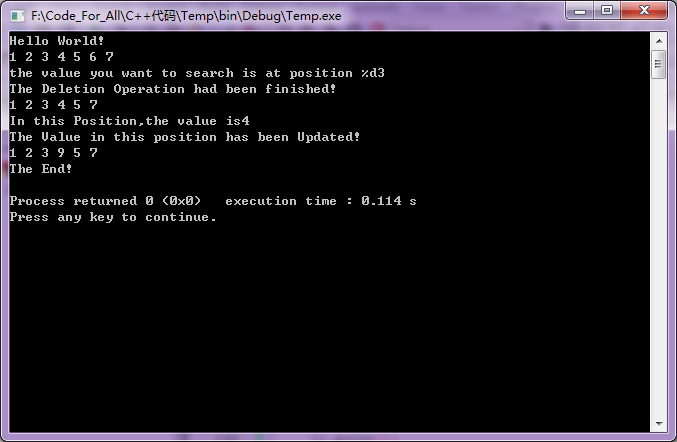
好了,單鏈表的基本操作大致就是這樣了,希望我們都能從中有所收獲。如果您發現代碼中有什么錯誤,還望不吝賜教,讓我們共同進步吧。
感謝閱讀,希望能幫助到大家,謝謝大家對本站的支持!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。