您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
起因
最近給公司的一個系統寫了個啟動的腳本,但是領導說批處理這樣的腳本太low了,要使用EXE來啟動,未來還要使用加密工具對EXE進行加密。
好吧,我就在網上到處找bat轉exe的工具,找了很久,都沒有找到合適的,只有一個用winrar制作自解壓包的方法還算可以,但是這玩意兒有兩個坑爹的問題:
使用了自定義圖標后,安裝時會被360報告有木馬;
用winrar制作的exe,其本質還是解壓后執行,解壓后的文件其實可以在系統臨時目錄下找到,因此以后想要加密其實很容易就會被破解;
所以最好的辦法看來就是自己寫一個exe了,考慮到我以前用過C,因此下載了Dev-Cpp這個工具來編寫代碼。
思路
在C語言中執行DOS命令的方法很多,如:ShellExecute, WinExec, CreateProcess等,但是這些接口都是只能一次執行一條命令,在我的啟動腳本里有很多命令,有一些是設置環境變量的,這樣就沒法在代碼中一條條執行腳本中的命令,必須要找到一個辦法可以一次性執行多條命令。
在網上找了很久,最終確定使用CreateProcess,同時要使用管道技術。也就是使用CreateProcess創建一個cmd進程,然后通過輸入管道將待執行的命令傳遞給cmd進程,通過輸出管道獲取cmd進程的輸出信息,因為是通過管道進行,所以可以模擬在DOS窗口一行行輸入命令,從而實現執行多條DOS命令了。
實現
從MSDN上找到管道的示例代碼,簡單修改了一下。
首先,將CreateProcess的參數改為啟動cmd:
char cmdLine[] = "cmd";
// Create the child process.
bFuncRetn = CreateProcess(NULL,
cmdLine, // command line
NULL, // process security attributes
NULL, // primary thread security attributes
TRUE, // handles are inherited
0, // creation flags
NULL, // use parent's environment
NULL, // use parent's current directory
&siStartInfo, // STARTUPINFO pointer
&piProcInfo); // receives PROCESS_INFORMATION
然后,將原來批處理里面的腳本復制一下,放到一個變量里(這里我改了一下,沒有用我實際的腳本,因為那個不通用,不適合做例子),注意,每一行最后要加上回車符\n,這樣才能正確模擬DOS窗口中輸入命令的情況:
CHAR cmds[] = "@ECHO OFF\n"
"cd..\n"
"dir\n"
再然后,原來的示例代碼中是把批處理文件作為EXE的參數傳遞進來的,既然上面改為將批處理文件內容放到腳本里,代碼中從文件中讀取命令的那部分就要去掉了,這部分代碼就不多說了。
完整的示例代碼如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#define BUFSIZE 4096
HANDLE hChildStdinRd, hChildStdinWr, hChildStdinWrDup,
hChildStdoutRd, hChildStdoutWr, hChildStdoutRdDup,
hInputFile, hStdout;
BOOL CreateChildProcess(VOID);
VOID WriteToPipe(VOID);
VOID ReadFromPipe(VOID);
VOID ErrorExit(const char *);
VOID ErrMsg(LPTSTR, BOOL);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
// SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES結構包含一個對象的安全描述符,并指定檢索到指定這個結構的句柄是否是可繼承的。
// 這個結構為很多函數創建對象時提供安全性設置
SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES saAttr;
BOOL fSuccess;
// Set the bInheritHandle flag so pipe handles are inherited.
// 設置句柄為可繼承的,使得子線程可以使用父線程
saAttr.nLength = sizeof(SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES);
saAttr.bInheritHandle = TRUE;
saAttr.lpSecurityDescriptor = NULL;
// Get the handle to the current STDOUT.
// 取得當前應用的標準輸出句柄,對于Windows控制臺應用來說,一般是輸出到屏幕
hStdout = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
// Create a pipe for the child process's STDOUT.
// 創建一個用于輸出操作的匿名管道。
if (! CreatePipe(&hChildStdoutRd, &hChildStdoutWr, &saAttr, 0))
ErrorExit("Stdout pipe creation failed\n");
// Create noninheritable read handle and close the inheritable read handle.
// 將輸出管道的句柄綁定到當前進程
fSuccess = DuplicateHandle(GetCurrentProcess(), hChildStdoutRd,
GetCurrentProcess(), &hChildStdoutRdDup , 0,
FALSE,
DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS);
if( !fSuccess )
ErrorExit("DuplicateHandle failed");
CloseHandle(hChildStdoutRd);
// Create a pipe for the child process's STDIN.
// 創建一個用于輸入操作的匿名管道。
if (! CreatePipe(&hChildStdinRd, &hChildStdinWr, &saAttr, 0))
ErrorExit("Stdin pipe creation failed\n");
// Duplicate the write handle to the pipe so it is not inherited.
// 將輸入管道的句柄綁定到當前進程
fSuccess = DuplicateHandle(GetCurrentProcess(), hChildStdinWr,
GetCurrentProcess(), &hChildStdinWrDup, 0,
FALSE, // not inherited
DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS);
if (! fSuccess)
ErrorExit("DuplicateHandle failed");
CloseHandle(hChildStdinWr);
// Now create the child process.
// 創建DOS子進程
fSuccess = CreateChildProcess();
if (! fSuccess)
ErrorExit("Create process failed");
// Write to pipe that is the standard input for a child process.
WriteToPipe();
// Read from pipe that is the standard output for child process.
ReadFromPipe();
return 0;
}
BOOL CreateChildProcess() {
PROCESS_INFORMATION piProcInfo;
STARTUPINFO siStartInfo;
BOOL bFuncRetn = FALSE;
// Set up members of the PROCESS_INFORMATION structure.
ZeroMemory( &piProcInfo, sizeof(PROCESS_INFORMATION) );
// Set up members of the STARTUPINFO structure.
// 設定DOS進程的標準輸入、輸出和錯誤信息的管道
// 使用前面創建的值,DOS窗口的輸入輸出都會被定向到本應用中
ZeroMemory( &siStartInfo, sizeof(STARTUPINFO) );
siStartInfo.cb = sizeof(STARTUPINFO);
siStartInfo.hStdError = hChildStdoutWr;
siStartInfo.hStdOutput = hChildStdoutWr;
siStartInfo.hStdInput = hChildStdinRd;
siStartInfo.dwFlags |= STARTF_USESTDHANDLES;
char cmdLine[] = "cmd";
// Create the child process.
bFuncRetn = CreateProcess(NULL,
cmdLine, // command line
NULL, // process security attributes
NULL, // primary thread security attributes
TRUE, // handles are inherited
0, // creation flags
NULL, // use parent's environment
NULL, // use parent's current directory
&siStartInfo, // STARTUPINFO pointer
&piProcInfo); // receives PROCESS_INFORMATION
if (bFuncRetn == 0)
ErrorExit("CreateProcess failed");
else {
CloseHandle(piProcInfo.hProcess);
CloseHandle(piProcInfo.hThread);
return bFuncRetn;
}
}
VOID WriteToPipe(VOID) {
DWORD dwRead, dwWritten;
CHAR chBuf[BUFSIZE];
CHAR cmds[] = "@ECHO ON\n"
"cd..\n"
"dir\n";
WriteFile(hChildStdinWrDup, cmds, sizeof(cmds), &dwWritten, NULL);
// Close the pipe handle so the child process stops reading.
if (! CloseHandle(hChildStdinWrDup))
ErrorExit("Close pipe failed");
}
VOID ReadFromPipe(VOID) {
DWORD dwRead, dwWritten;
CHAR chBuf[BUFSIZE];
// Close the write end of the pipe before reading from the
// read end of the pipe.
if (!CloseHandle(hChildStdoutWr))
ErrorExit("CloseHandle failed");
// Read output from the child process, and write to parent's STDOUT.
// 獲取子線程,即DOS窗口的輸出,顯示到標準輸出設備上
for (;;) {
if( !ReadFile( hChildStdoutRdDup, chBuf, BUFSIZE, &dwRead,
NULL) || dwRead == 0) break;
if (! WriteFile(hStdout, chBuf, dwRead, &dwWritten, NULL))
break;
}
}
VOID ErrorExit (const char *lpszMessage) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", lpszMessage);
ExitProcess(0);
}
執行效果如下圖:
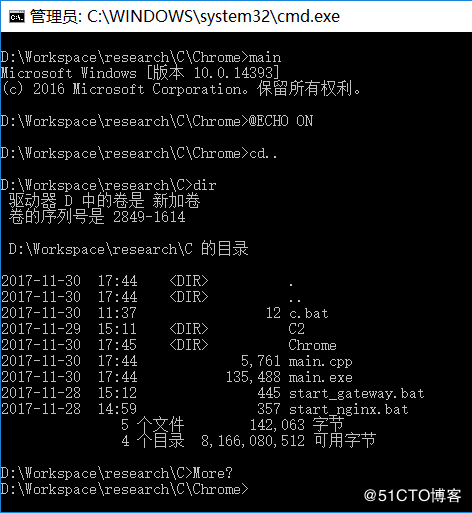
main.exe的原始目錄是D:\Workspace\research\C\Chrome\,執行時,首先執行了cd..,退到上一層目錄,然后執行dir,顯示上一層目錄的內容,證明上面的代碼確實可以一次執行多條DOS命令。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。