溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了C++如何實現一個命令行進度條,內容清晰明了,對此有興趣的小伙伴可以學習一下,相信大家閱讀完之后會有幫助。
緣起
最近做遙感影像融合的GWPCA方法,在帶寬比較大的時候速度太慢了,需要有個進度條指示一下,然后我去找進度條的庫,發現github上面的C/C++的相應的庫似乎沒有能在VS下跑的,自己花了點時間寫了一個。
效果
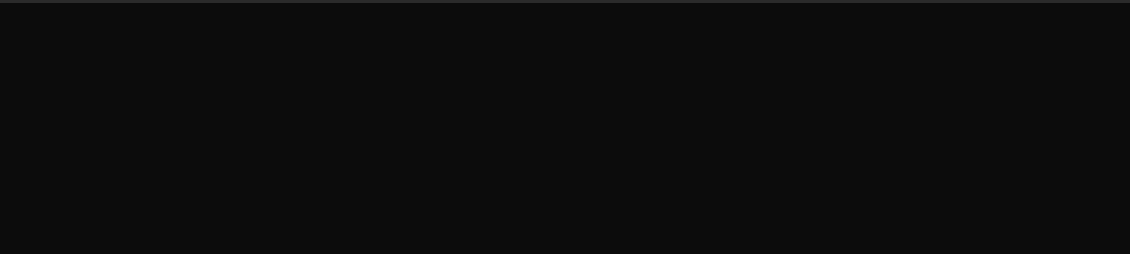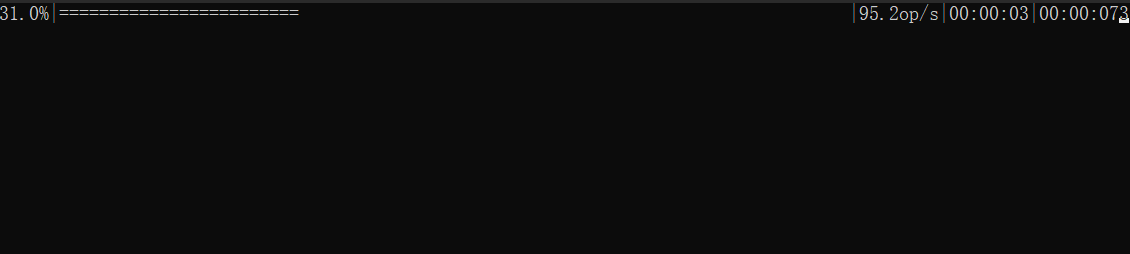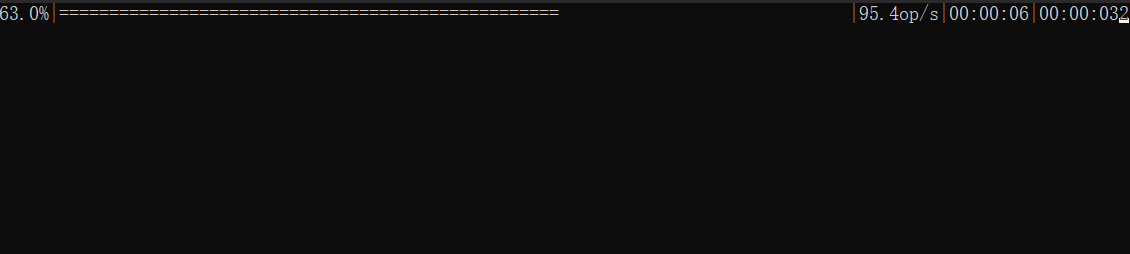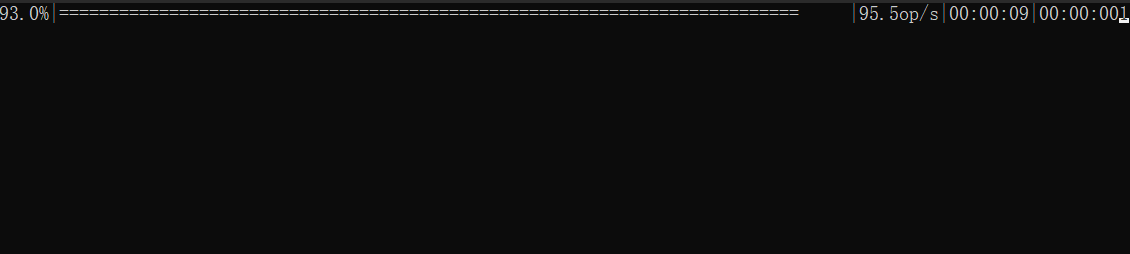
實現
大概需要考慮這樣幾個要素
另外進度條的引入不能破壞已有的執行結構,最好和Python的tqdm庫類似,通過 start , update 等函數來完成整個進度條,因此對于C語言來說,需要一個定時器,定期將進度條進行重繪(不可能更新一次就重繪一次),因此整個進度條就包含了兩個類,一個是進度條類,一個是定時器類。另外需要考慮線程安全的問題。
// Progress.hpp
#pragma once
#include <ctime>
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include "Timer.hpp"
using namespace std::chrono;
class ProgressBar
{
protected:
// 進度條的長度(不包含前后綴)
unsigned int ncols;
// 已完成的數量
std::atomic<unsigned int> finishedNum;
// 上次的已完成數量
unsigned int lastNum;
// 總數
unsigned int totalNum;
// 進度條長度與百分比之間的系數
double colsRatio;
// 開始時間
steady_clock::time_point beginTime;
// 上次重繪的時間
steady_clock::time_point lastTime;
// 重繪周期
milliseconds interval;
Timer timer;
public:
ProgressBar(unsigned int totalNum, milliseconds interval) : totalNum(totalNum), interval(interval), finishedNum(0), lastNum(0), ncols(80), colsRatio(0.8) {}
// 開始
void start();
// 完成
void finish();
// 更新
void update() { return this->update(1); }
// 一次更新多個數量
void update(unsigned int num) { this->finishedNum += num; }
// 獲取進度條長度
unsigned int getCols() { return this->ncols; }
// 設置進度條長度
void setCols(unsigned int ncols) { this->ncols = ncols; this->colsRatio = ncols / 100; }
// 重繪
void show();
};
void ProgressBar::start() {
// 記錄開始時間,并初始化定時器
this->beginTime = steady_clock::now();
this->lastTime = this->beginTime;
// 定時器用于定時調用重繪函數
this->timer.start(this->interval.count(), std::bind(&ProgressBar::show, this));
}
// 重繪函數
void ProgressBar::show() {
// 清除上次的繪制內容
std::cout << "\r";
// 記錄重繪的時間點
steady_clock::time_point now = steady_clock::now();
// 獲取已完成的數量
unsigned int tmpFinished = this->finishedNum.load();
// 獲取與開始時間和上次重繪時間的時間間隔
auto timeFromStart = now - this->beginTime;
auto timeFromLast = now - this->lastTime;
// 這次完成的數量
unsigned int gap = tmpFinished - this->lastNum;
// 計算速度
double rate = gap / duration<double>(timeFromLast).count();
// 應顯示的百分數
double present = (100.0 * tmpFinished) / this->totalNum;
// 打印百分數
std::cout << std::setprecision(1) << std::fixed << present << "%|";
// 計算應該繪制多少=符號
int barWidth = present * this->colsRatio;
// 打印已完成和未完成進度條
std::cout << std::setw(barWidth) << std::setfill('=') << "=";
std::cout << std::setw(this->ncols - barWidth) << std::setfill(' ') << "|";
// 打印速度
std::cout << std::setprecision(1) << std::fixed << rate << "op/s|";
// 之后的兩部分內容分別為打印已過的時間和剩余時間
int timeFromStartCount = duration<double>(timeFromStart).count();
std::time_t tfs = timeFromStartCount;
tm tmfs;
gmtime_s(&tmfs, &tfs);
std::cout << std::put_time(&tmfs, "%X") << "|";
int timeLast;
if (rate != 0) {
// 剩余時間的估計是用這次的速度和未完成的數量進行估計
timeLast = (this->totalNum - tmpFinished) / rate;
}
else {
timeLast = INT_MAX;
}
if ((this->totalNum - tmpFinished) == 0) {
timeLast = 0;
}
std::time_t tl = timeLast;
tm tml;
gmtime_s(&tml, &tl);
std::cout << std::put_time(&tml, "%X");
this->lastNum = tmpFinished;
this->lastTime = now;
}
void ProgressBar::finish() {
// 停止定時器
this->timer.stop();
std::cout << std::endl;
}// Timer.hpp
#pragma once
#include <functional>
#include <chrono>
#include <thread>
#include <atomic>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
using namespace std::chrono;
class Timer
{
public:
Timer() : _expired(true), _try_to_expire(false)
{}
Timer(const Timer& timer)
{
_expired = timer._expired.load();
_try_to_expire = timer._try_to_expire.load();
}
~Timer()
{
stop();
}
void start(int interval, std::function<void()> task)
{
// is started, do not start again
if (_expired == false)
return;
// start async timer, launch thread and wait in that thread
_expired = false;
std::thread([this, interval, task]() {
while (!_try_to_expire)
{
// sleep every interval and do the task again and again until times up
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(interval));
task();
}
{
// timer be stopped, update the condition variable expired and wake main thread
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(_mutex);
_expired = true;
_expired_cond.notify_one();
}
}).detach();
}
void startOnce(int delay, std::function<void()> task)
{
std::thread([delay, task]() {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(delay));
task();
}).detach();
}
void stop()
{
// do not stop again
if (_expired)
return;
if (_try_to_expire)
return;
// wait until timer
_try_to_expire = true; // change this bool value to make timer while loop stop
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(_mutex);
_expired_cond.wait(locker, [this] {return _expired == true; });
// reset the timer
if (_expired == true)
_try_to_expire = false;
}
}
private:
std::atomic<bool> _expired; // timer stopped status
std::atomic<bool> _try_to_expire; // timer is in stop process
std::mutex _mutex;
std::condition_variable _expired_cond;
};看完上述內容,是不是對C++如何實現一個命令行進度條有進一步的了解,如果還想學習更多內容,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。